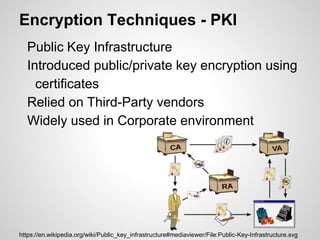
The document discusses email security flaws and various techniques for encrypting email communications. It describes how email is currently sent in plain text over outdated protocols, revealing metadata in headers. Encryption methods like Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) aim to address these issues using public/private key encryption and decentralized authentication. Applications like GNU Privacy Guard have implemented these techniques, while future development focuses on end-to-end encryption and usability in projects like the Dark Mail Project.