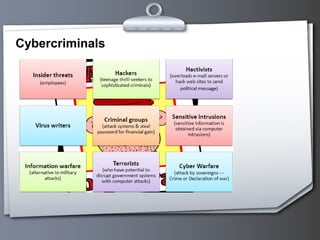
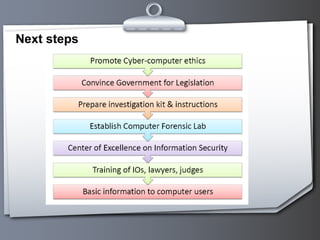
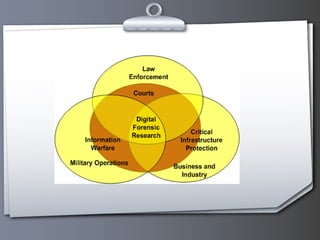
This document provides an overview of cyber crime and forensics. It discusses the types of cyber crimes like hacking, phishing, software piracy and cyber stalking. It also outlines the steps of computer forensics which include acquisition, identification, evaluation and presentation of digital evidence. Common tools used in computer forensics are also mentioned.