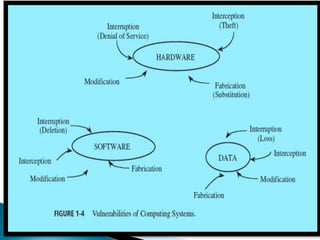
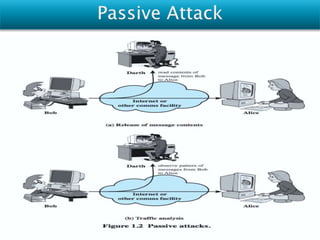
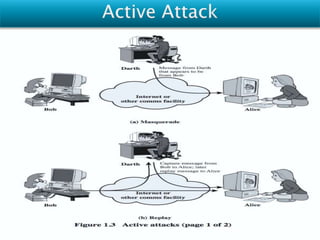
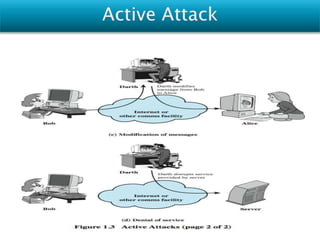
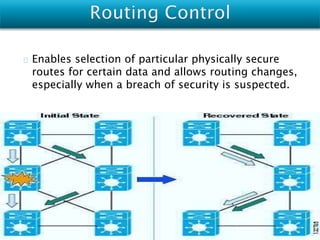
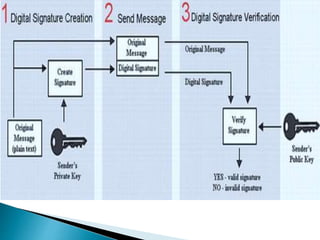
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses that attackers can exploit to gain unauthorized access to a network or its resources. Attacks are attempts to damage, access, or misuse assets without permission. Network security mechanisms detect, prevent, and recover from attacks using methods like routing control, traffic padding, encryption, access control, digital signatures, and ensuring data integrity.