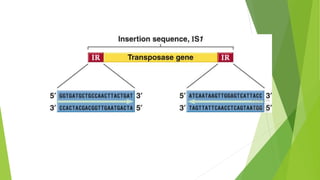
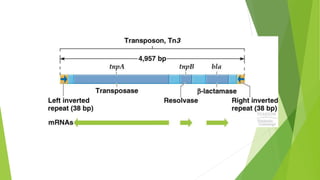
Transposable elements are DNA sequences that can change their position within a genome. They move via a "cut-and-paste" or "copy-and-paste" mechanism. There are two main classes - Class I transposons copy their RNA before inserting elsewhere, while Class II transposons move DNA directly. Transposons can contain genes unrelated to transposition, while insertion sequences only encode functions for insertion. Most transposable elements in genomes are no longer active, but were once mobile genetic elements that contributed to genetic diversity.