Embed presentation


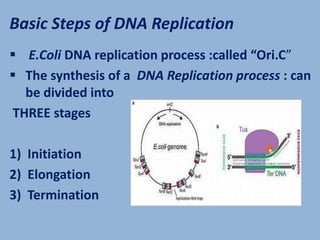


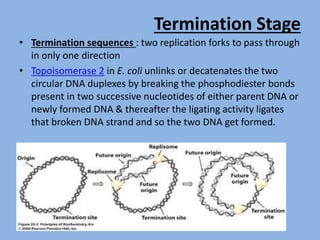

DNA replication in E. coli involves producing two identical DNA replicas from a single molecule, crucial for biological inheritance. The process includes initiation, elongation, and termination stages, with DNA polymerase III as the primary enzyme for creating the new strand. E. coli's genome is efficiently replicated in about 42 minutes from a single origin, with specific mechanisms for error correction and the formation of Okazaki fragments during discontinuous replication.








