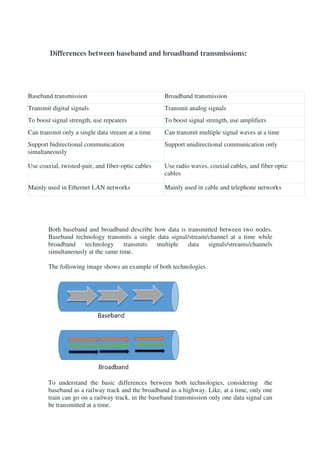
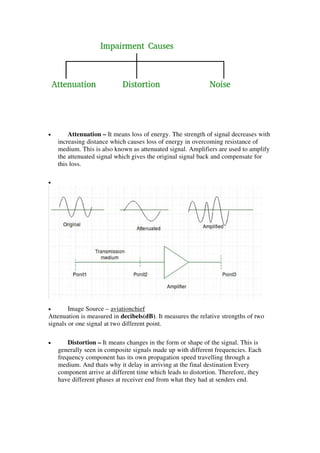
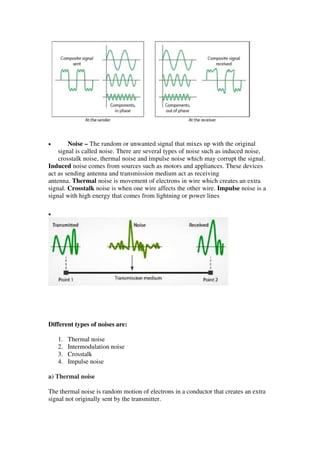
The document discusses the differences between baseband and broadband transmissions. It explains that baseband transmits a single data stream at a time using digital signals, while broadband transmits multiple data streams simultaneously using analog signals. It also discusses sources of transmission impairment including attenuation, distortion, and noise such as thermal noise and crosstalk.