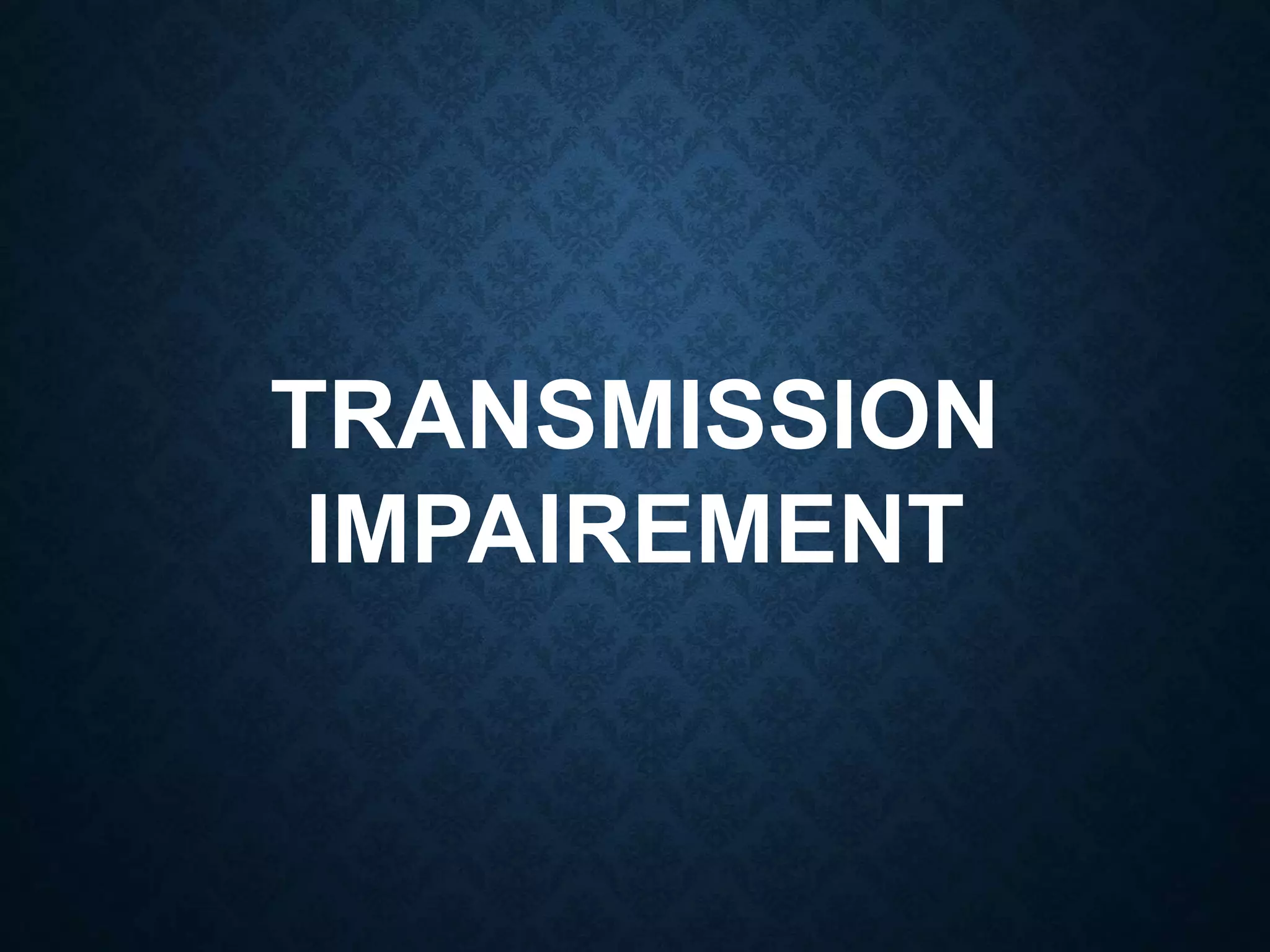
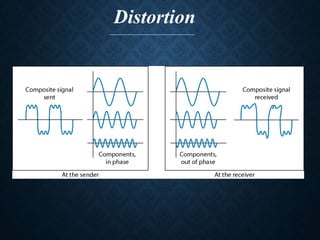
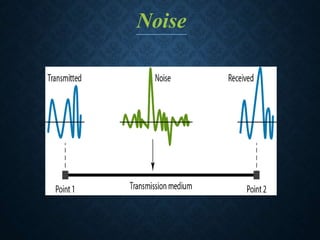
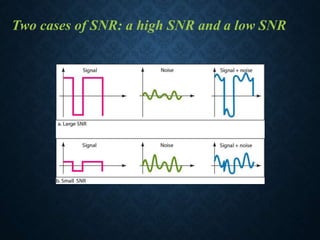
This document discusses transmission impairment, which refers to degradation of signals as they travel through transmission media. There are three main causes of transmission impairment: 1) attenuation, which is the loss of signal energy as it passes through a medium, 2) distortion, which is a change in the signal's form or shape, such as different frequency components arriving at different times, and 3) noise, which adds unwanted signals from sources like thermal effects, interference, or crosstalk between wires. Attenuation is measured in decibels and can be compensated for using amplifiers, while signal to noise ratio (SNR) measures the quality of a transmission system by comparing the signal strength to the noise power.