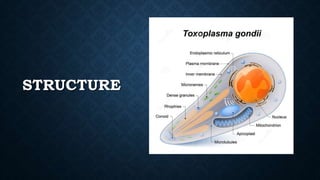
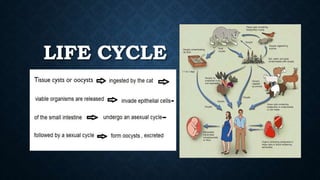
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite that causes toxoplasmosis, with transmission routes including consumption of undercooked meat and congenital transmission during pregnancy. The life cycle involves three stages: tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites, with various diagnostic techniques such as microscopy and serology used for detection. Treatment options for congenital cases include spiramycin for mothers and pyrimethamine with sulfadiazine for affected fetuses, alongside prevention strategies like proper food handling and hygiene.