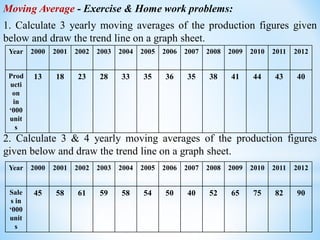
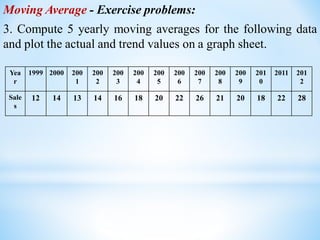
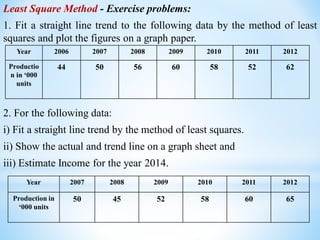
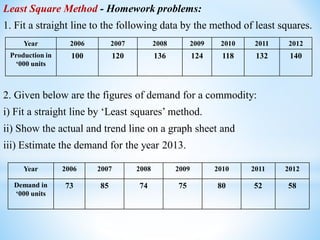
This document discusses time series analysis and its key components. It begins by defining a time series as a sequence of data points measured over successive time periods. The four main components of a time series are identified as: 1) Trend - the long-term pattern of increase or decrease, 2) Seasonal variations - repeating patterns over 12 months, 3) Cyclical variations - fluctuations lasting more than a year, and 4) Irregular variations - unpredictable fluctuations. Two common methods for measuring trends are introduced as the moving average method and least squares method. Formulas and examples are provided for calculating trend values using these techniques.