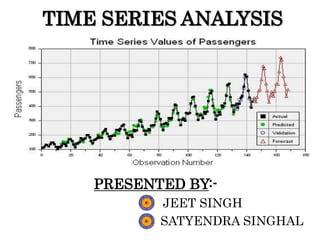
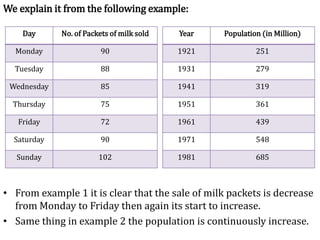
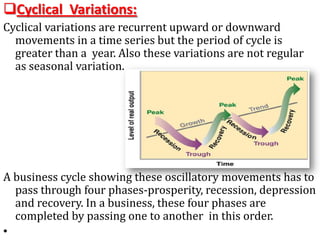
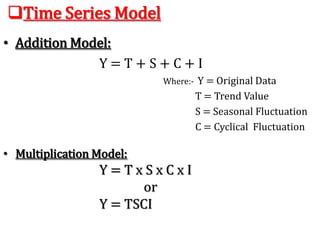
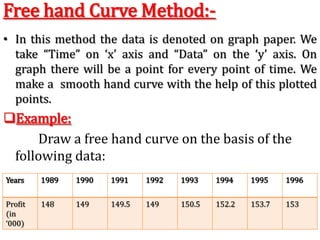
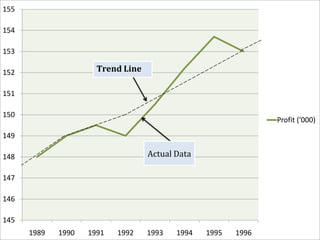
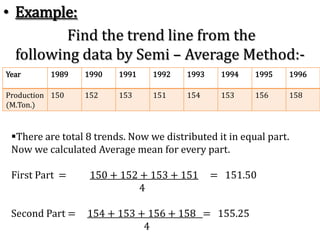
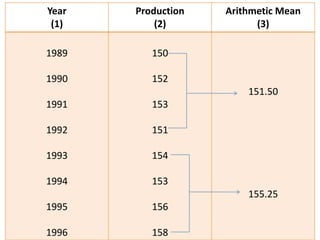
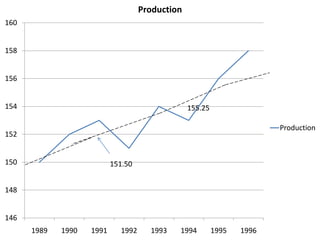
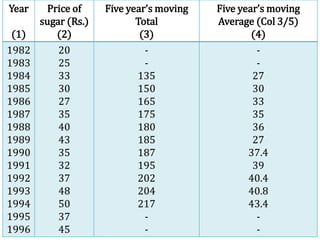
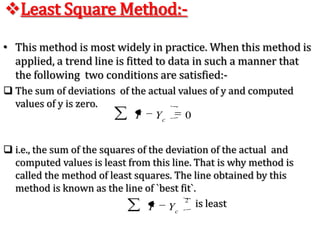
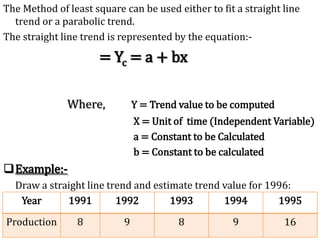
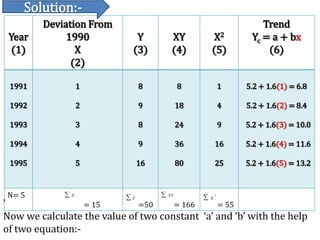
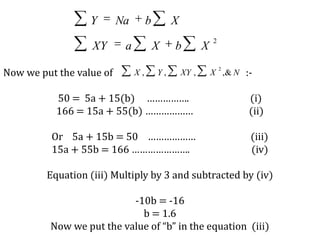
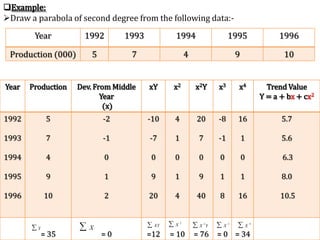
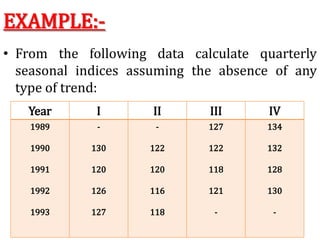
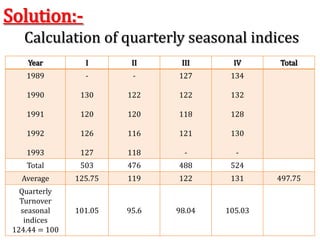
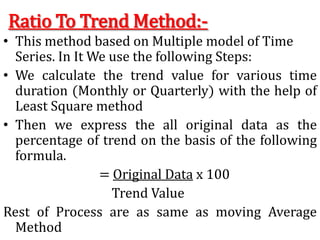
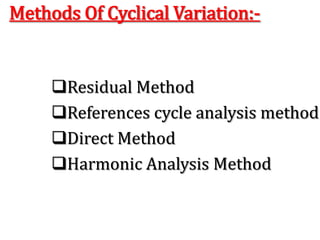
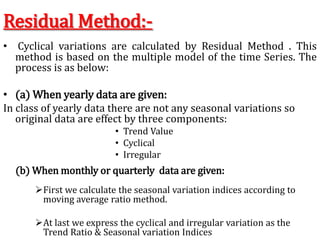
Time series analysis involves analyzing data collected over time. A time series is a set of data points indexed in time order. The key components of a time series are trends, seasonality, cycles, and irregular variations. Trend refers to the long-term movement of a time series over time. Seasonality refers to periodic fluctuations that occur each year, such as higher sales in winter. Cyclical variations are longer term fluctuations in business cycles. Irregular variations are random, unpredictable fluctuations. Time series analysis is important for forecasting, economic analysis, and business planning. Common methods for analyzing time series components include moving averages, least squares regression, decomposition models, and harmonic analysis.