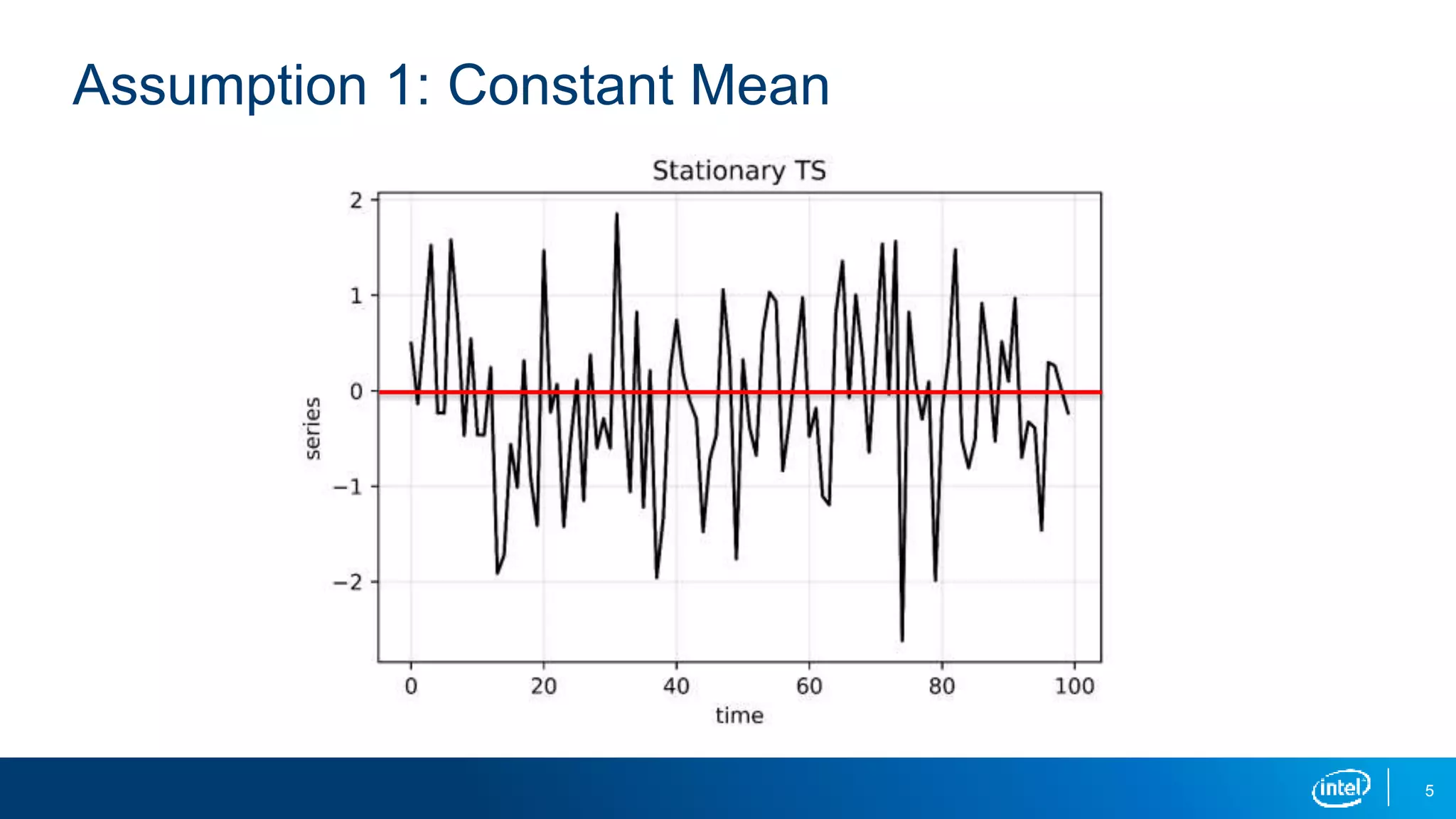
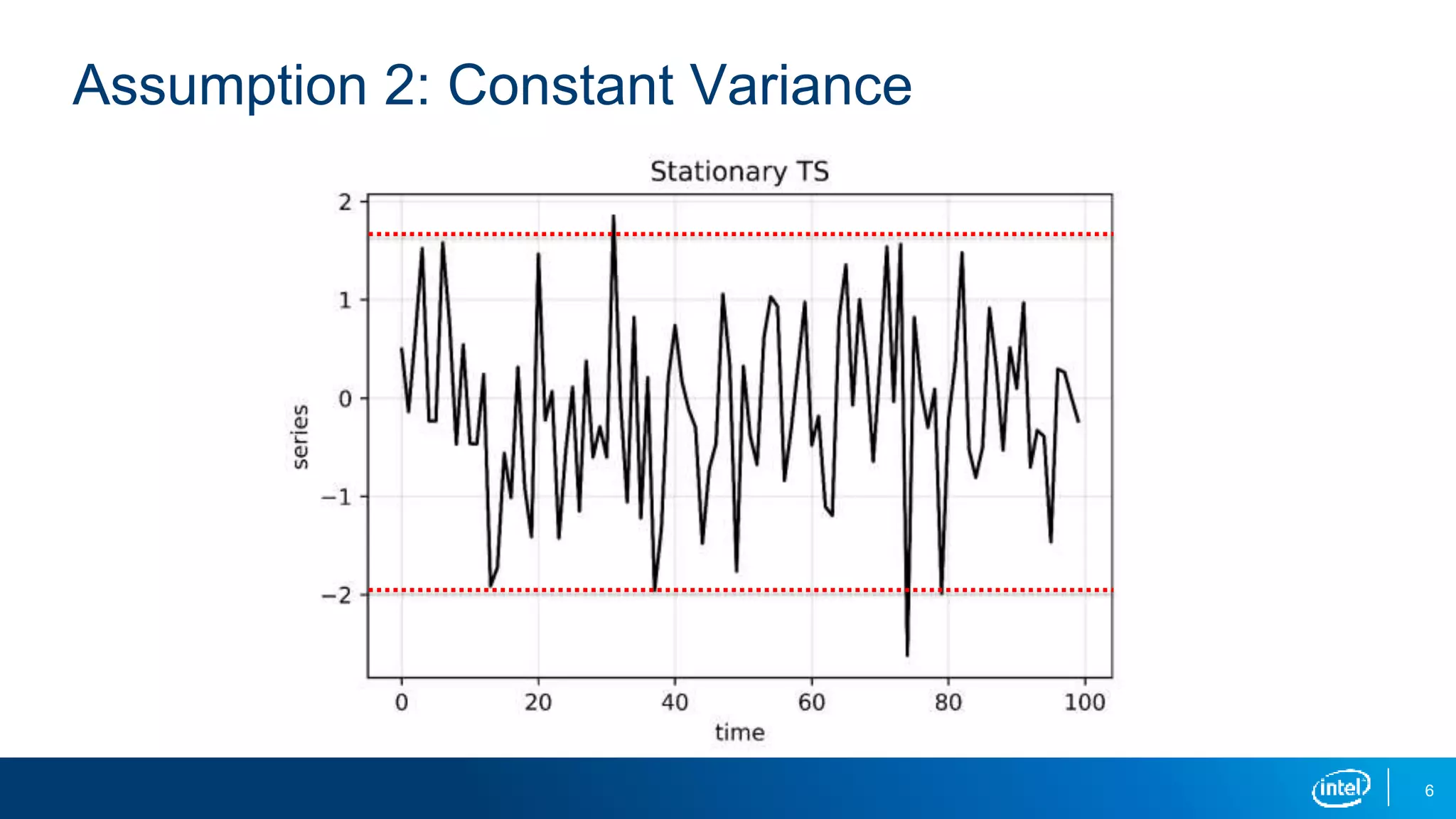
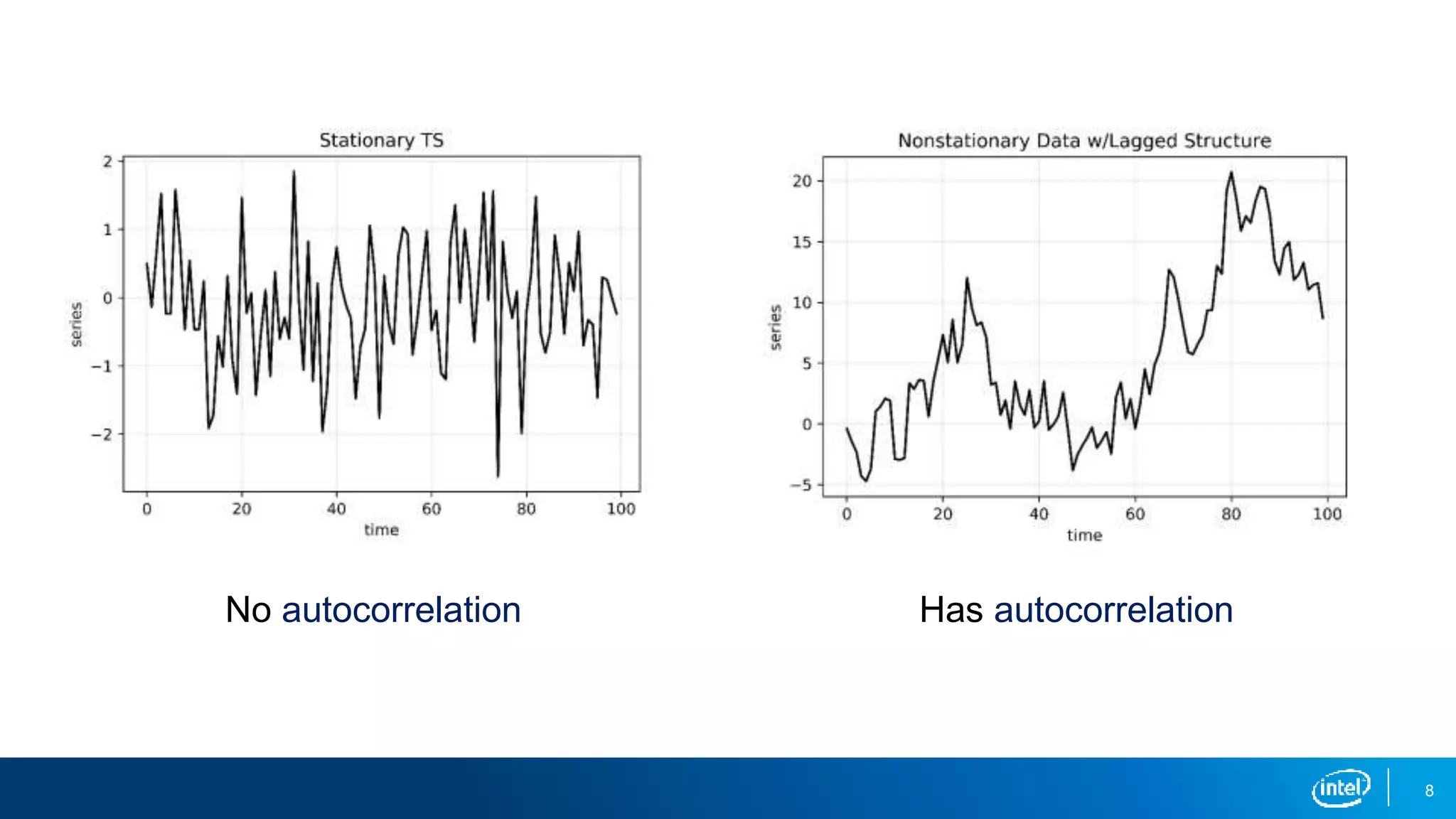
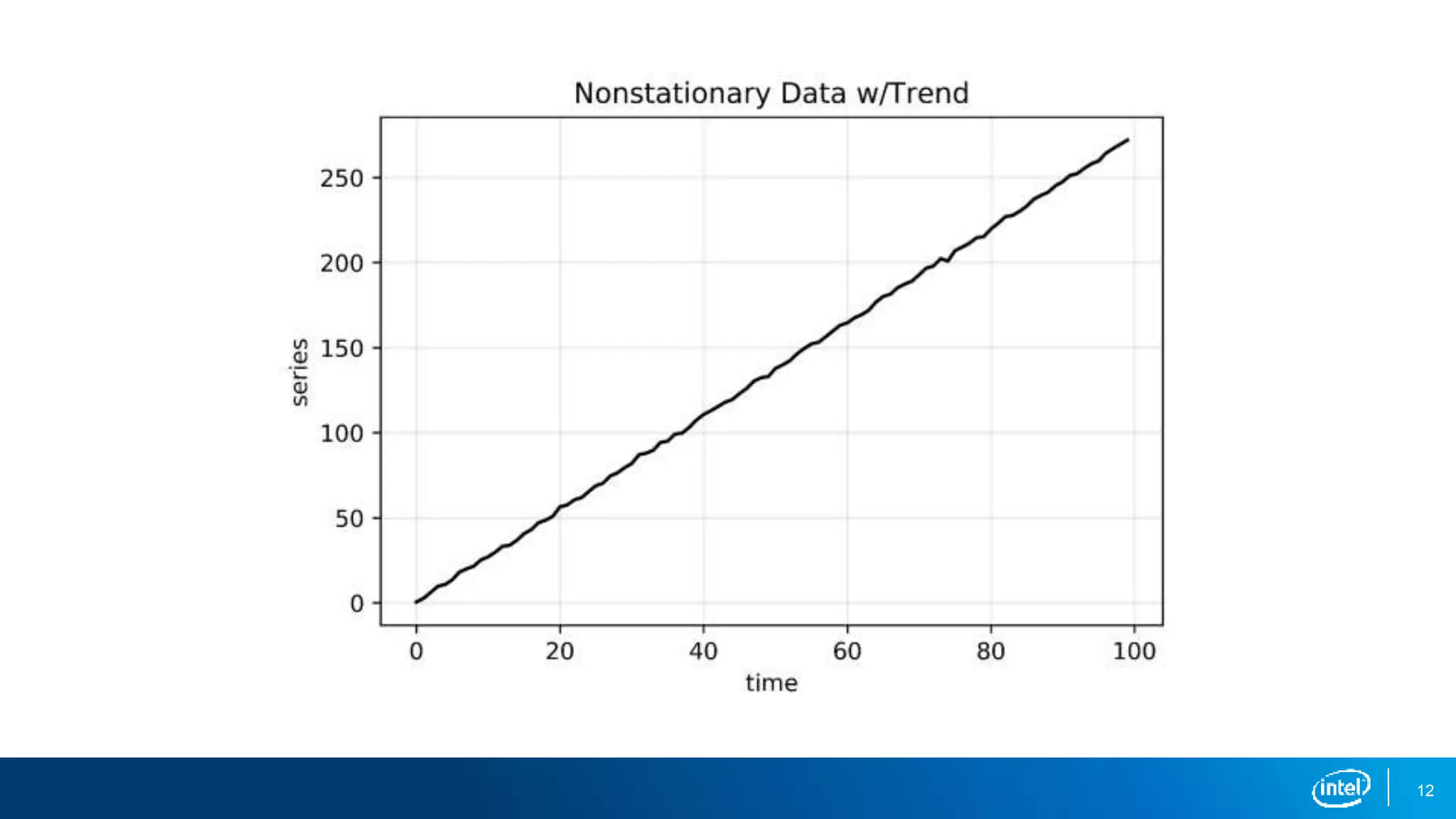
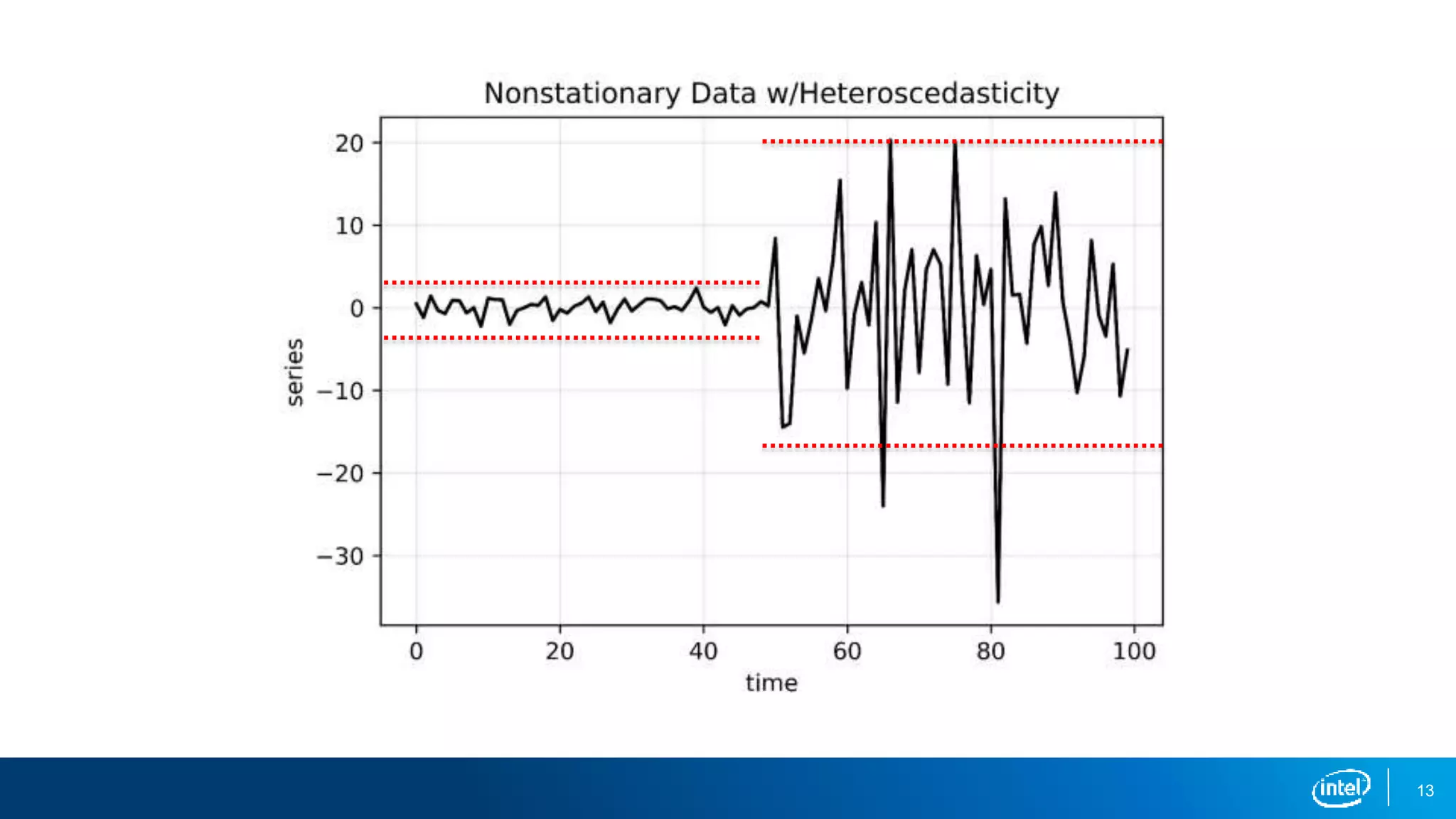
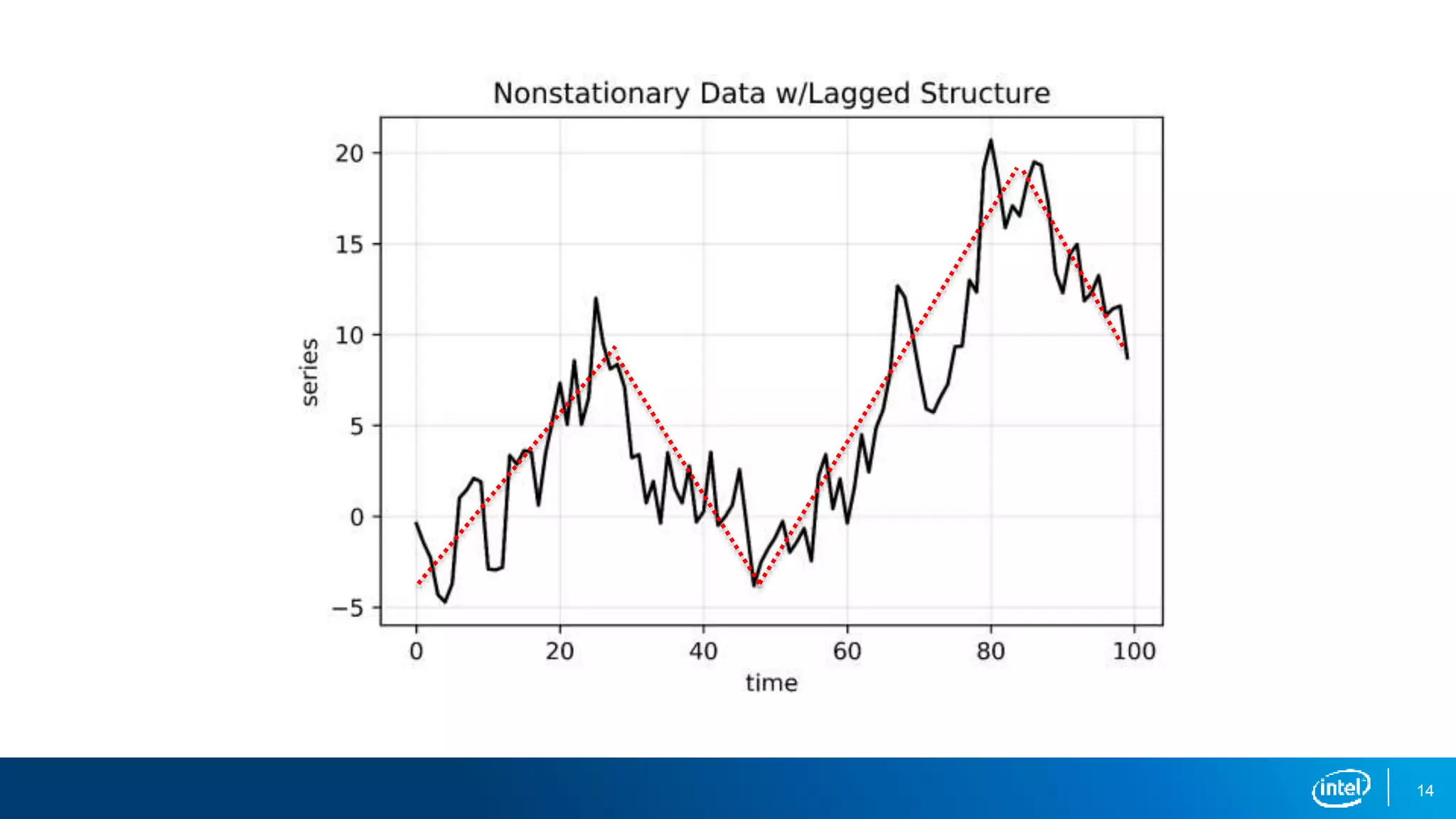
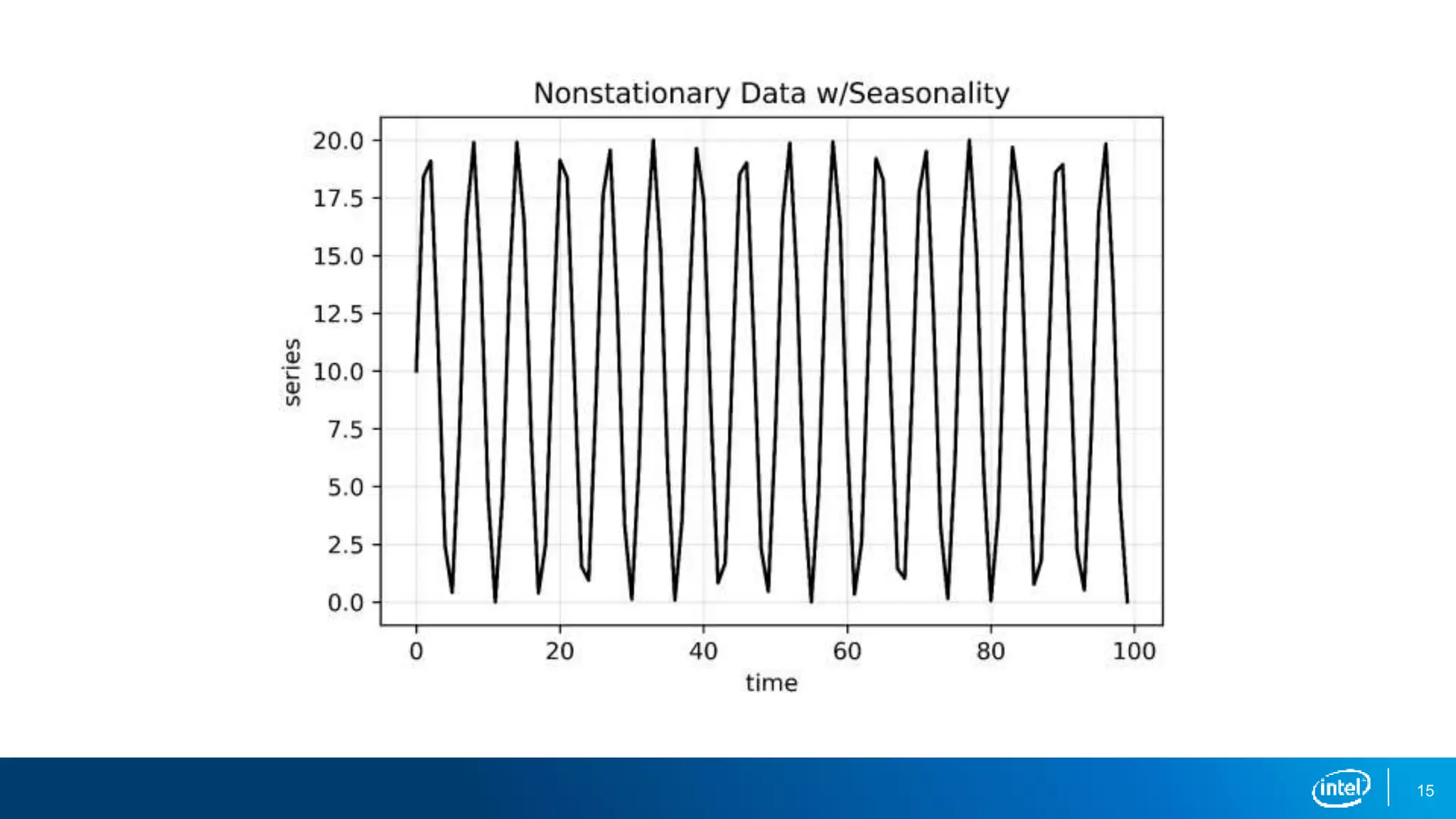
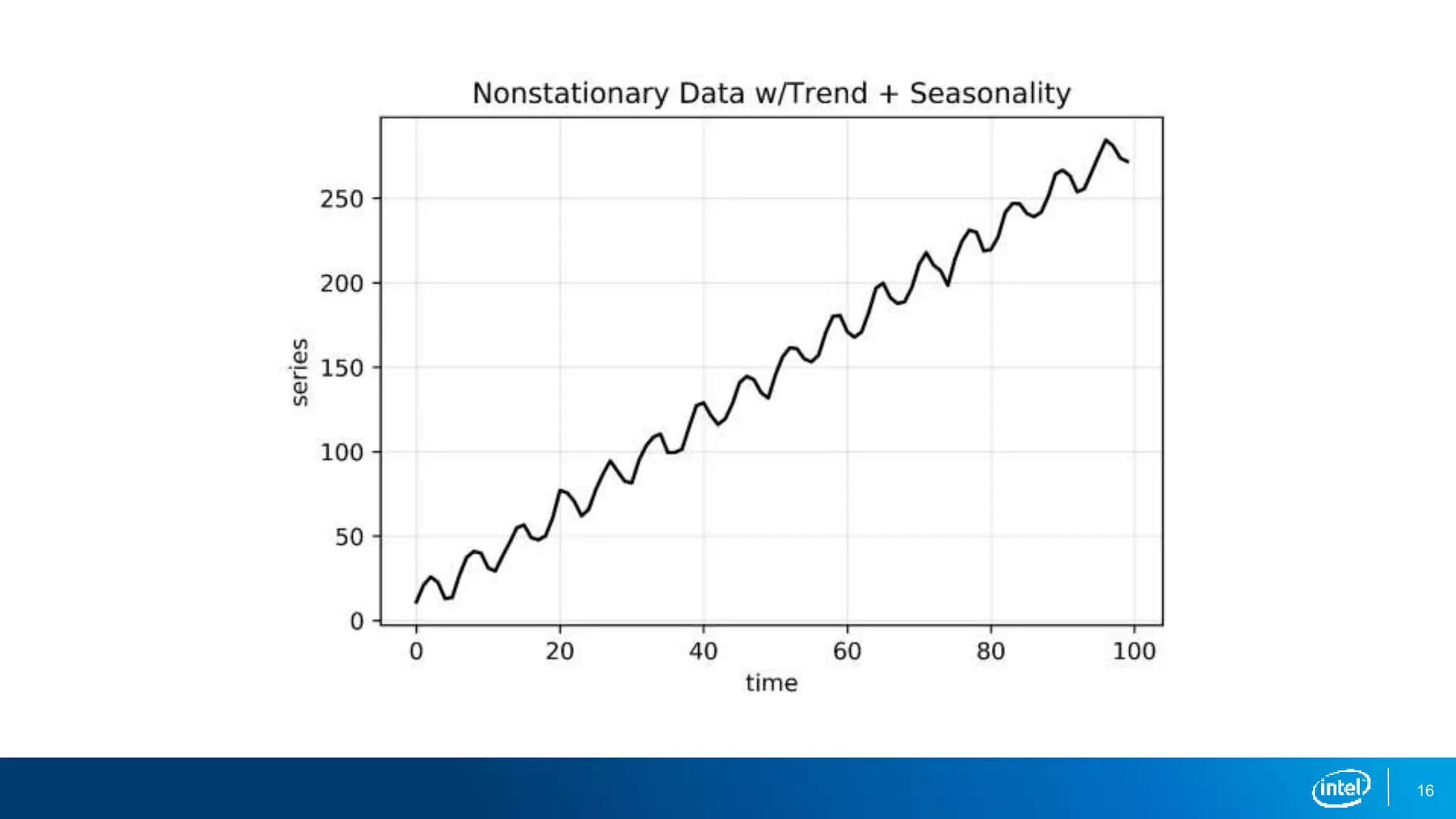
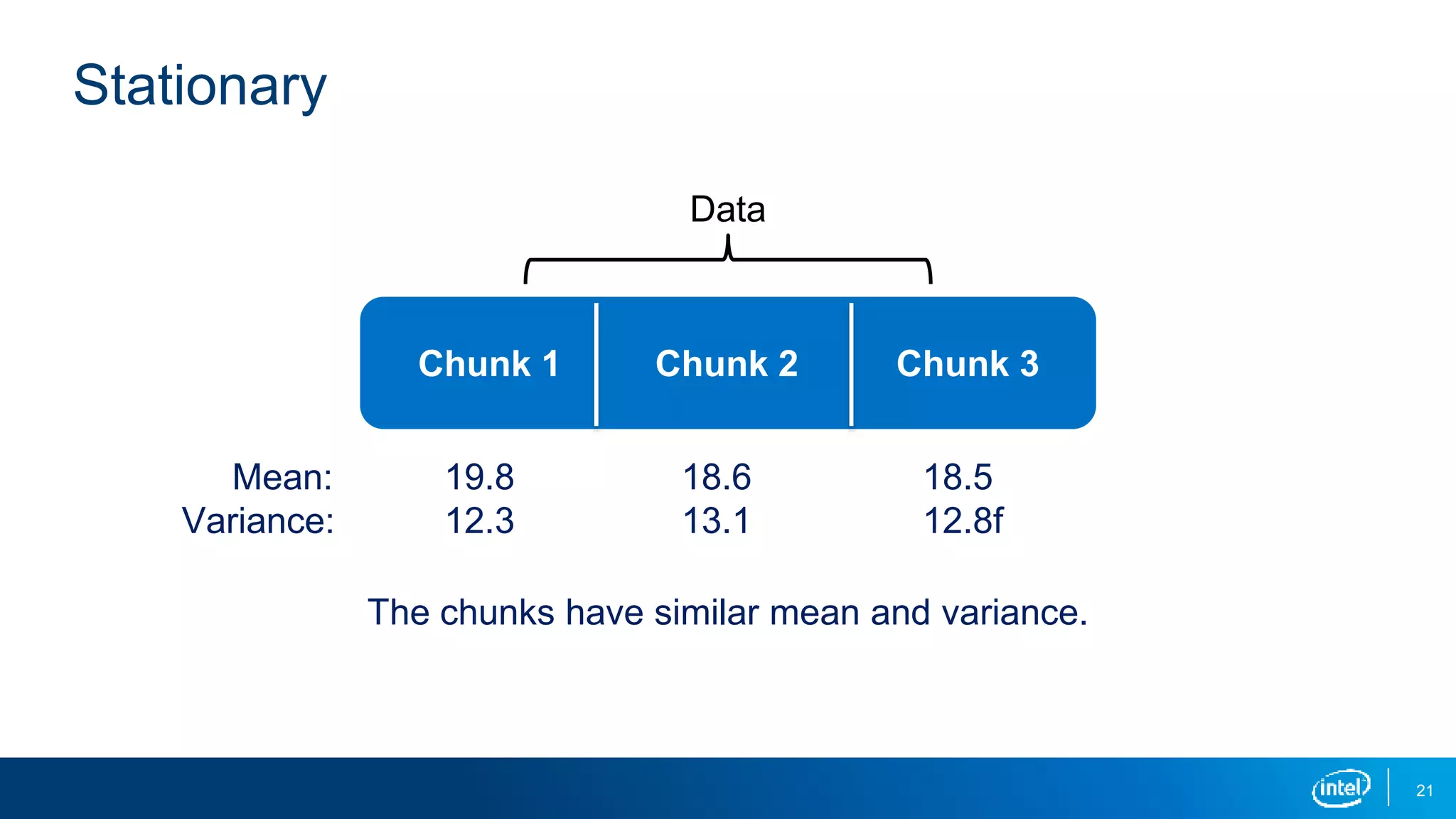
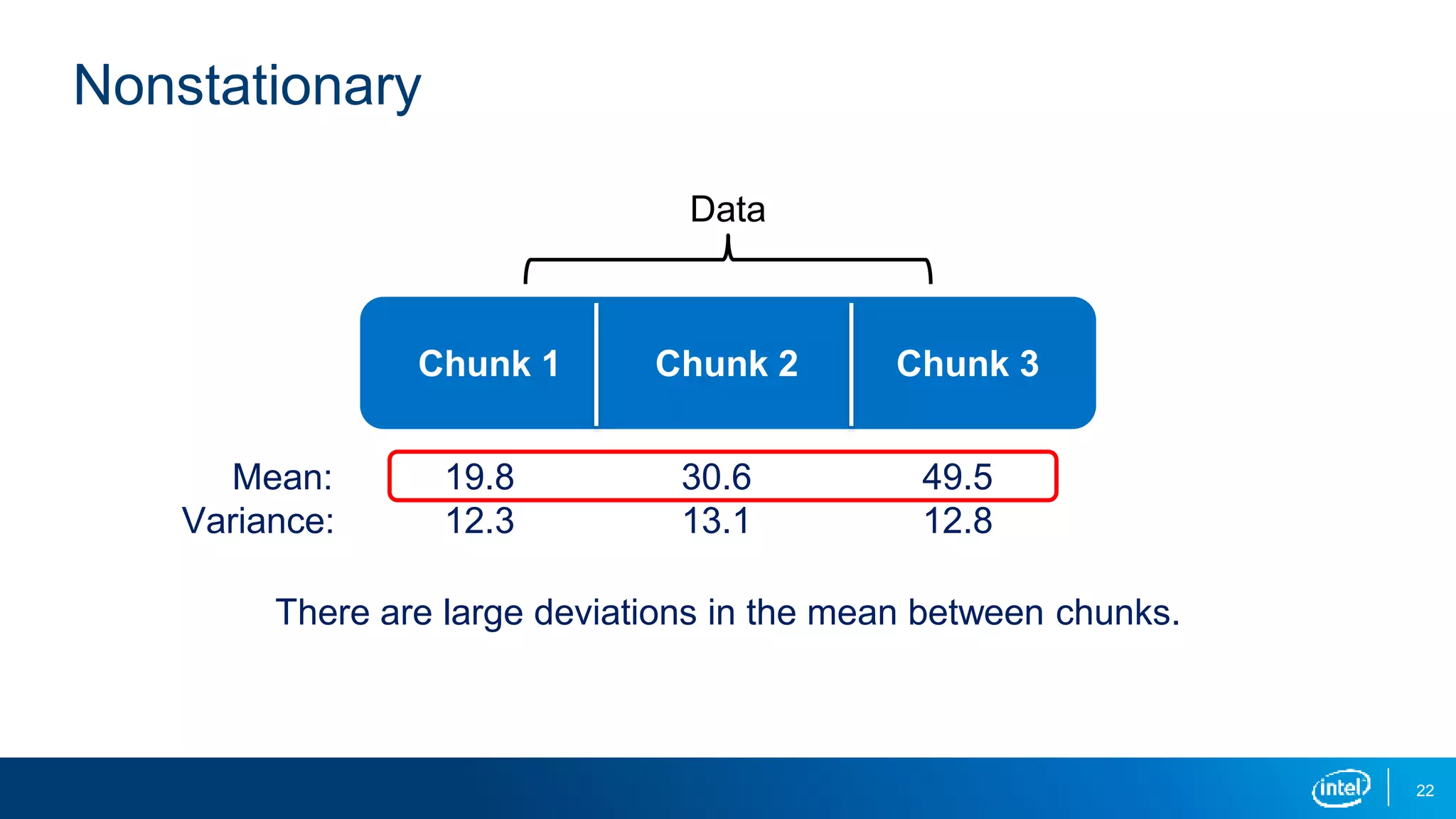
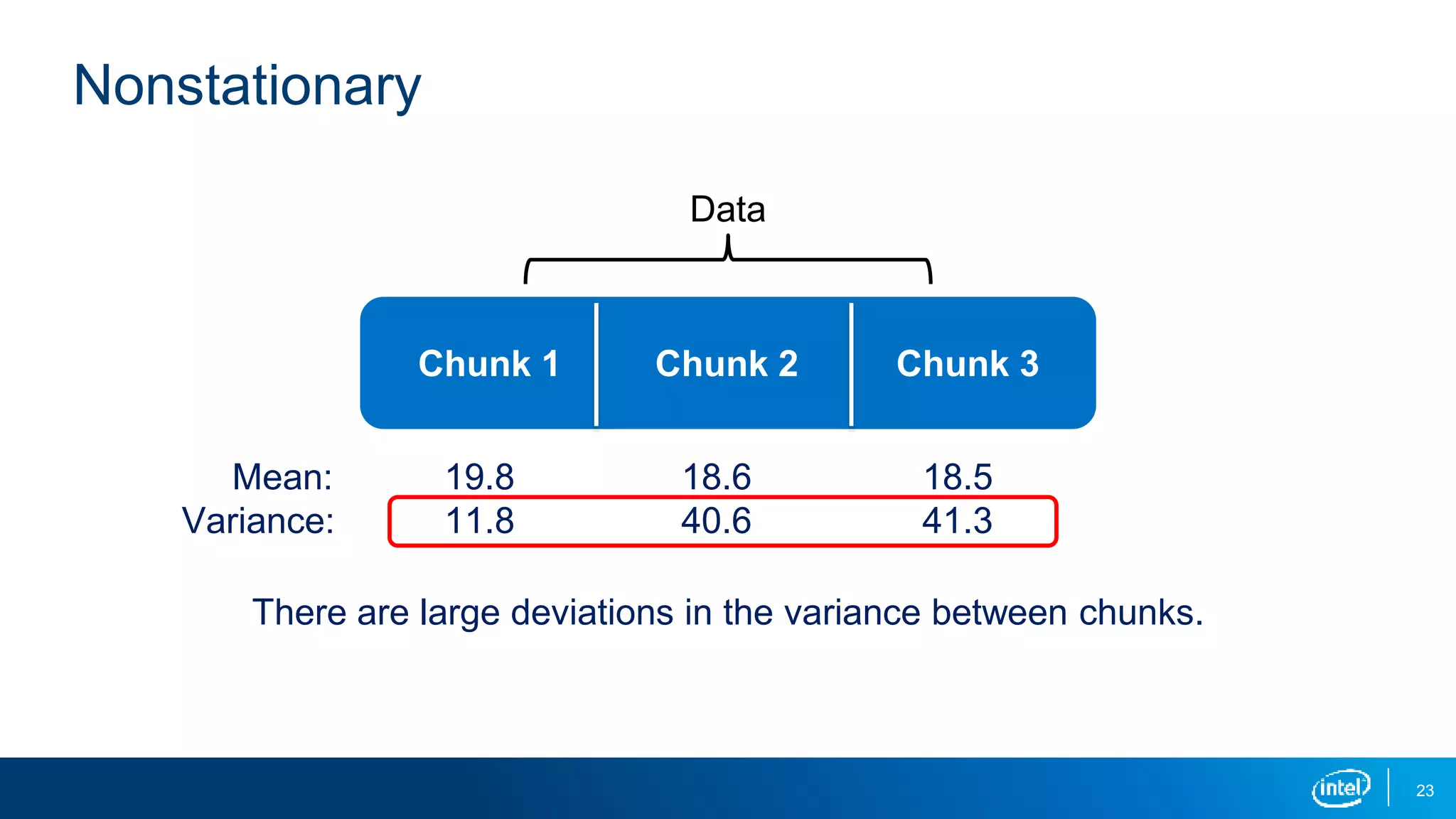
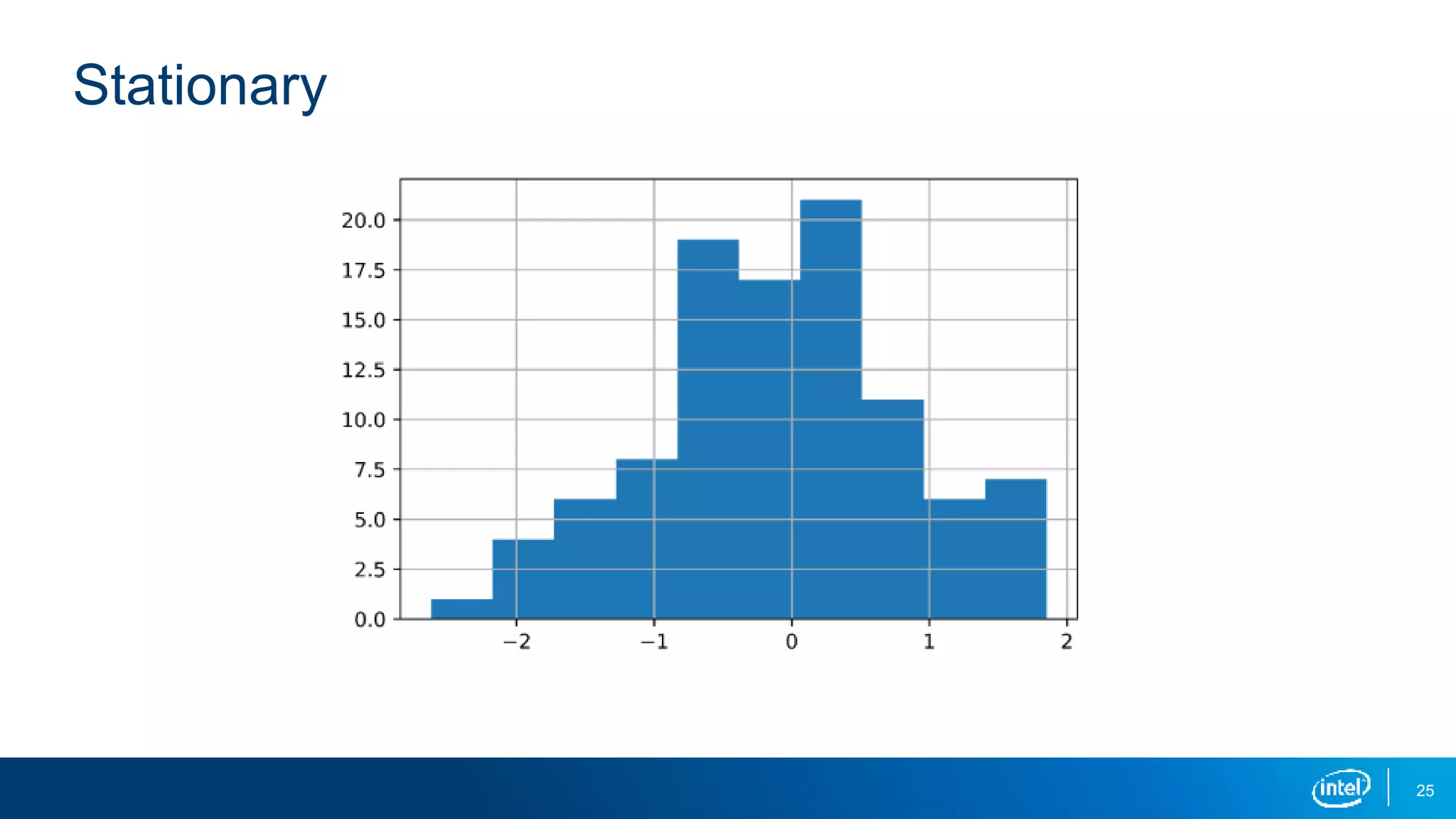
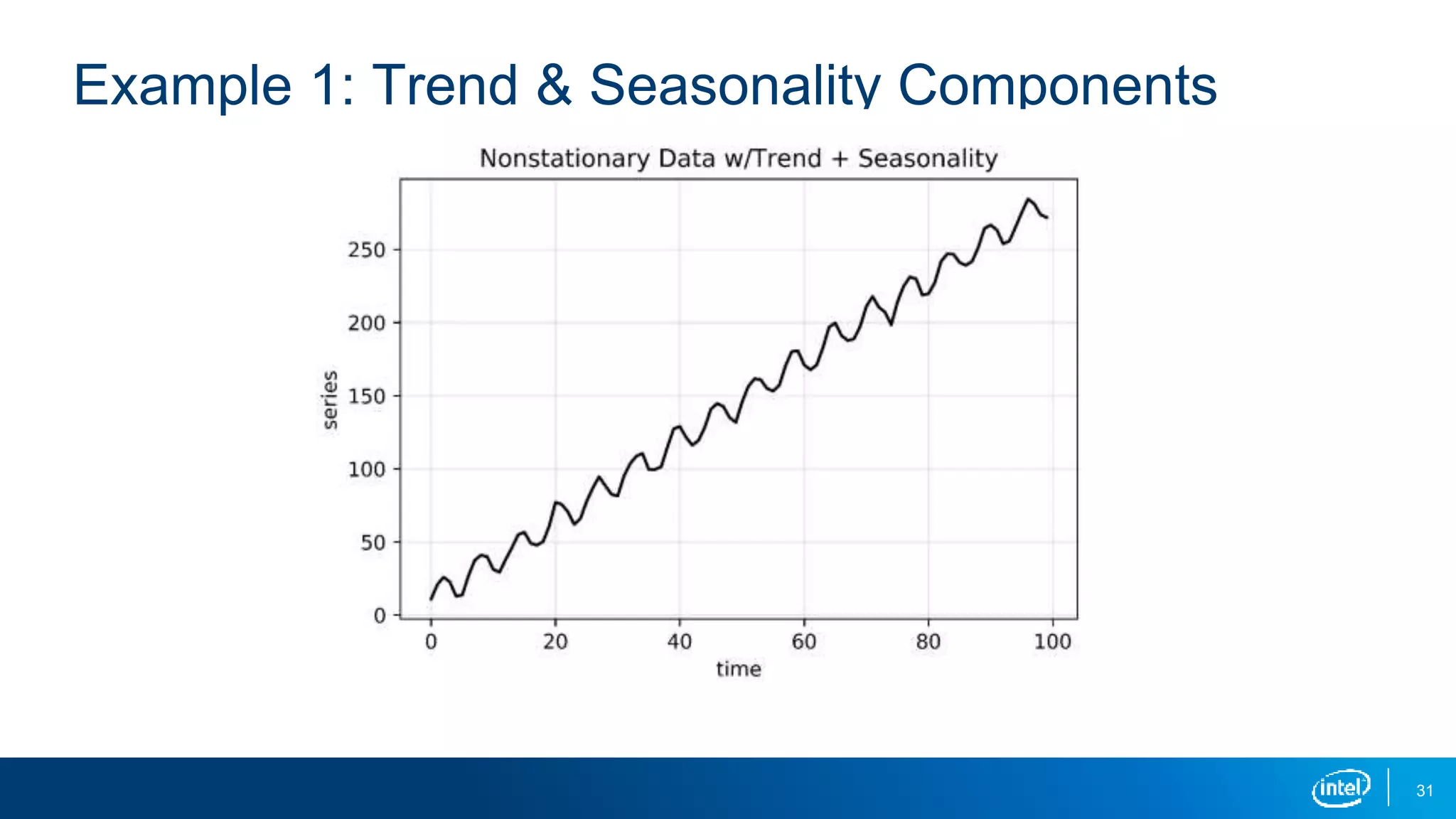
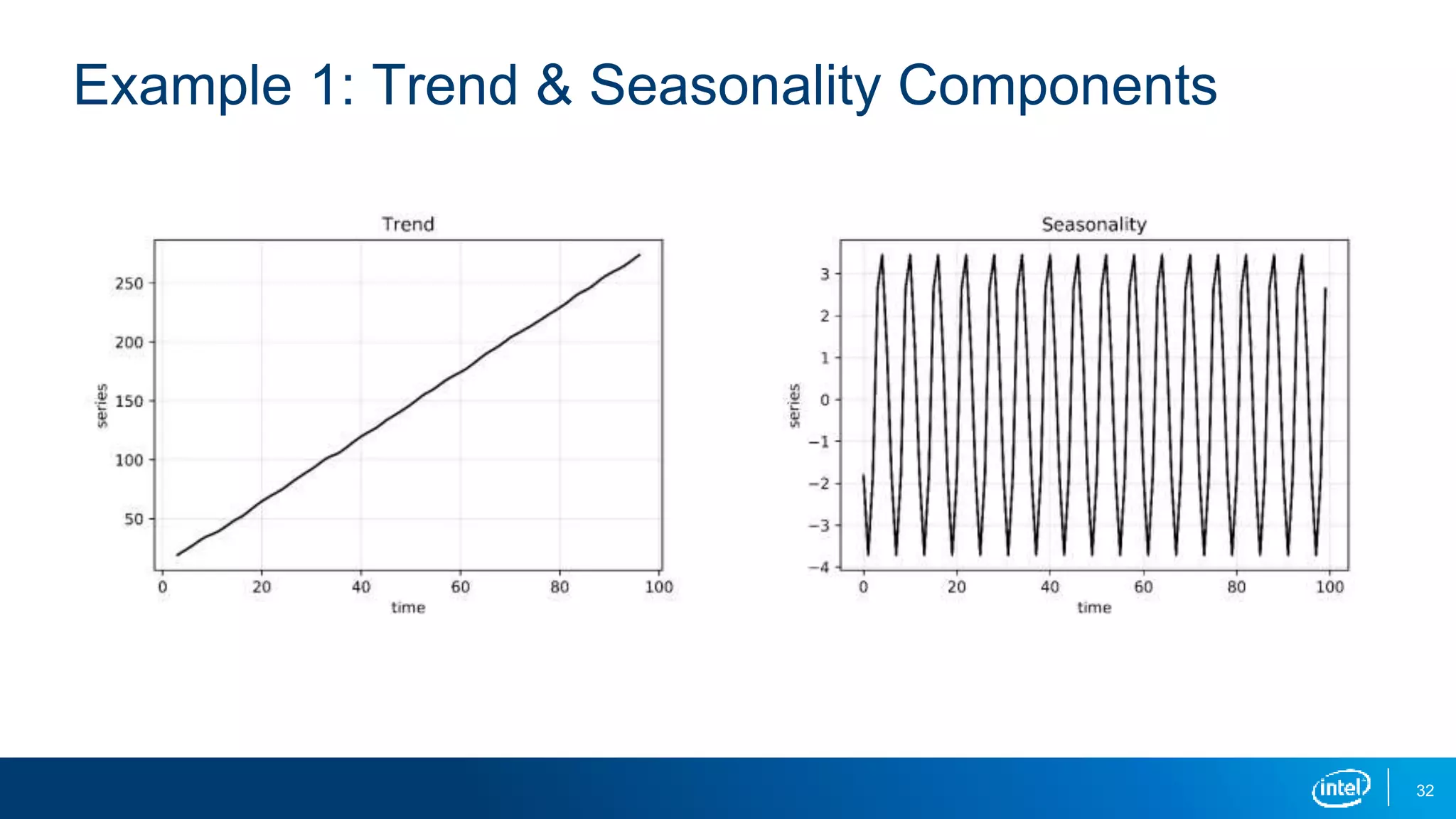
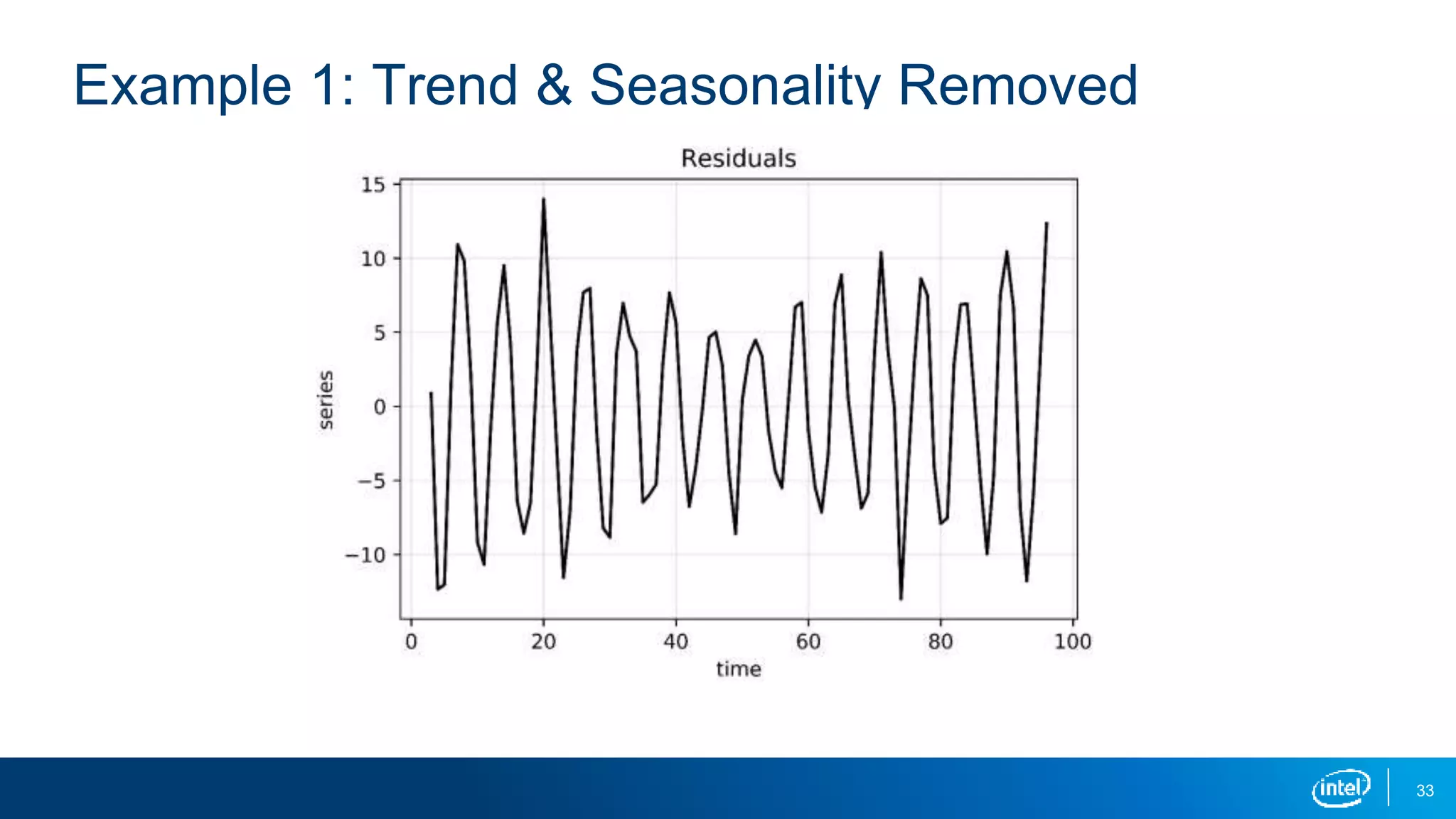
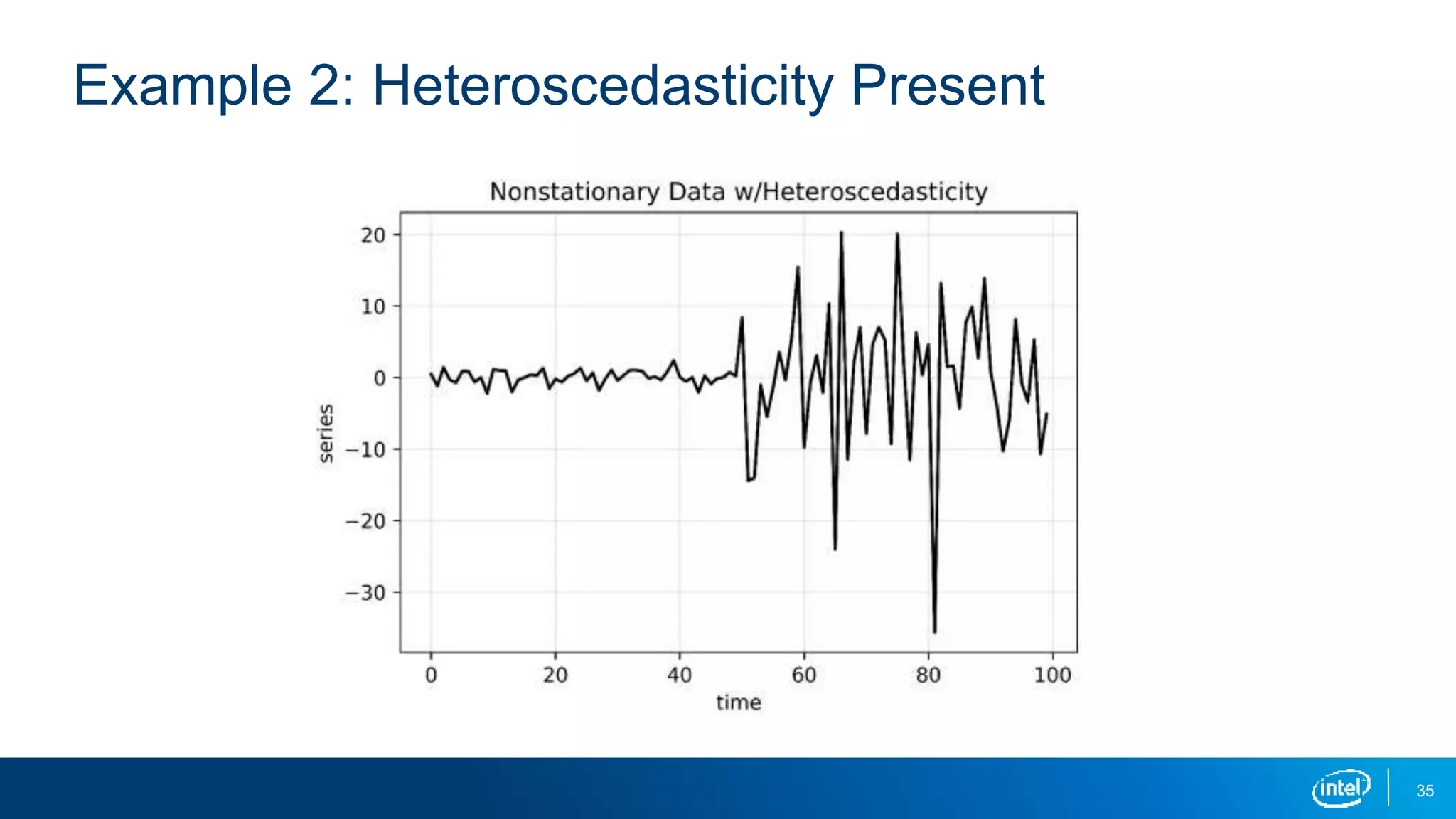
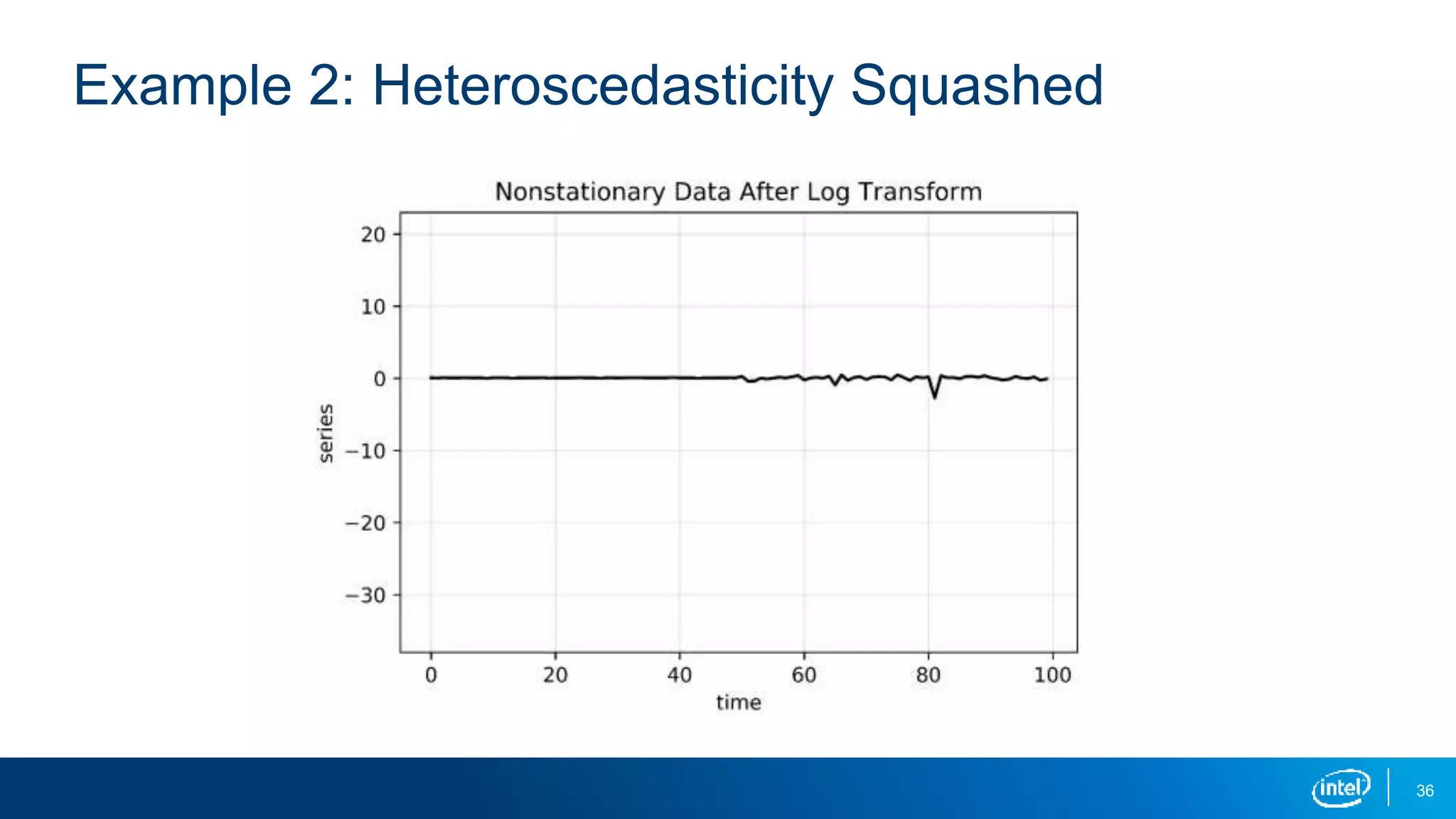
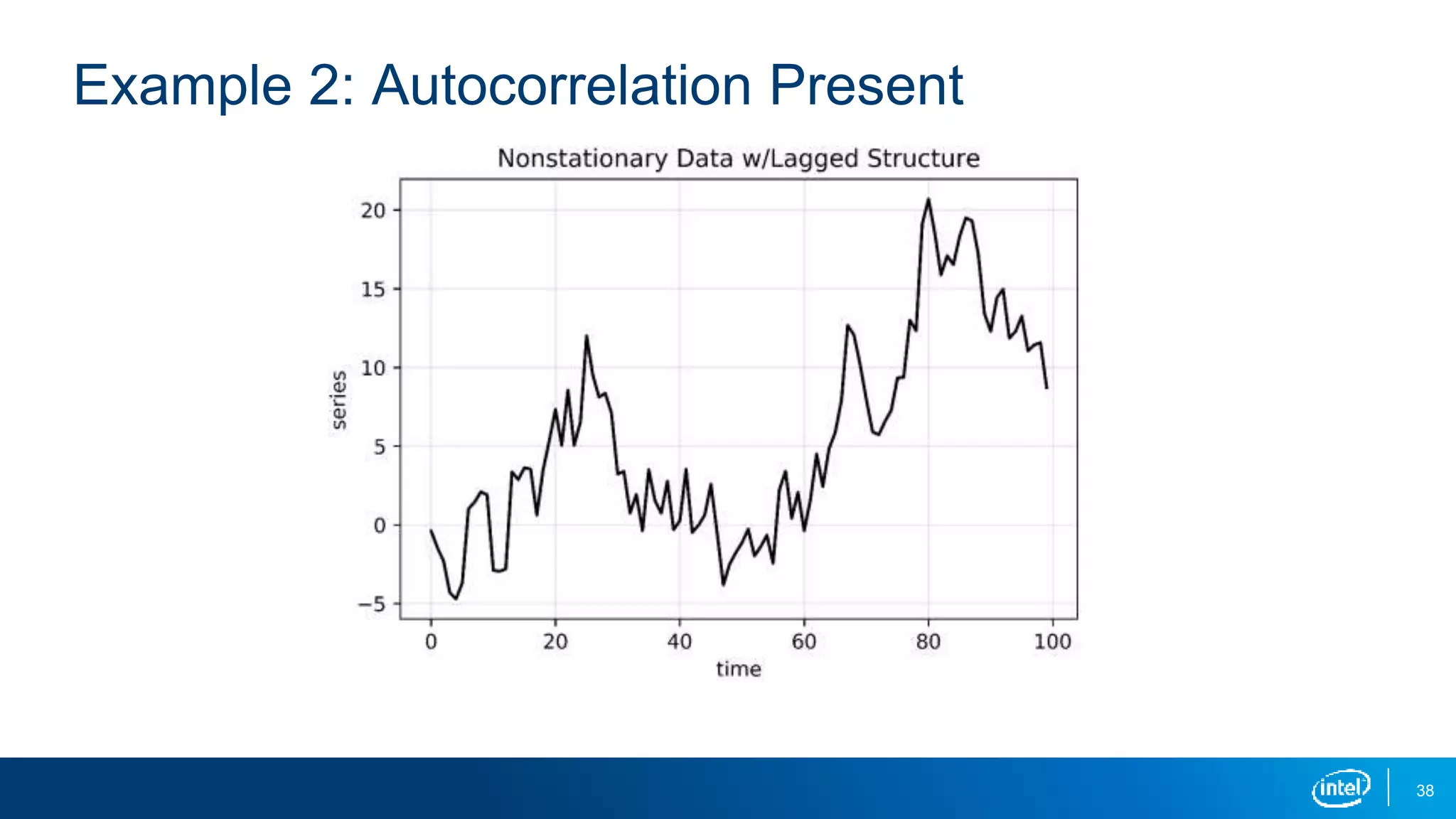
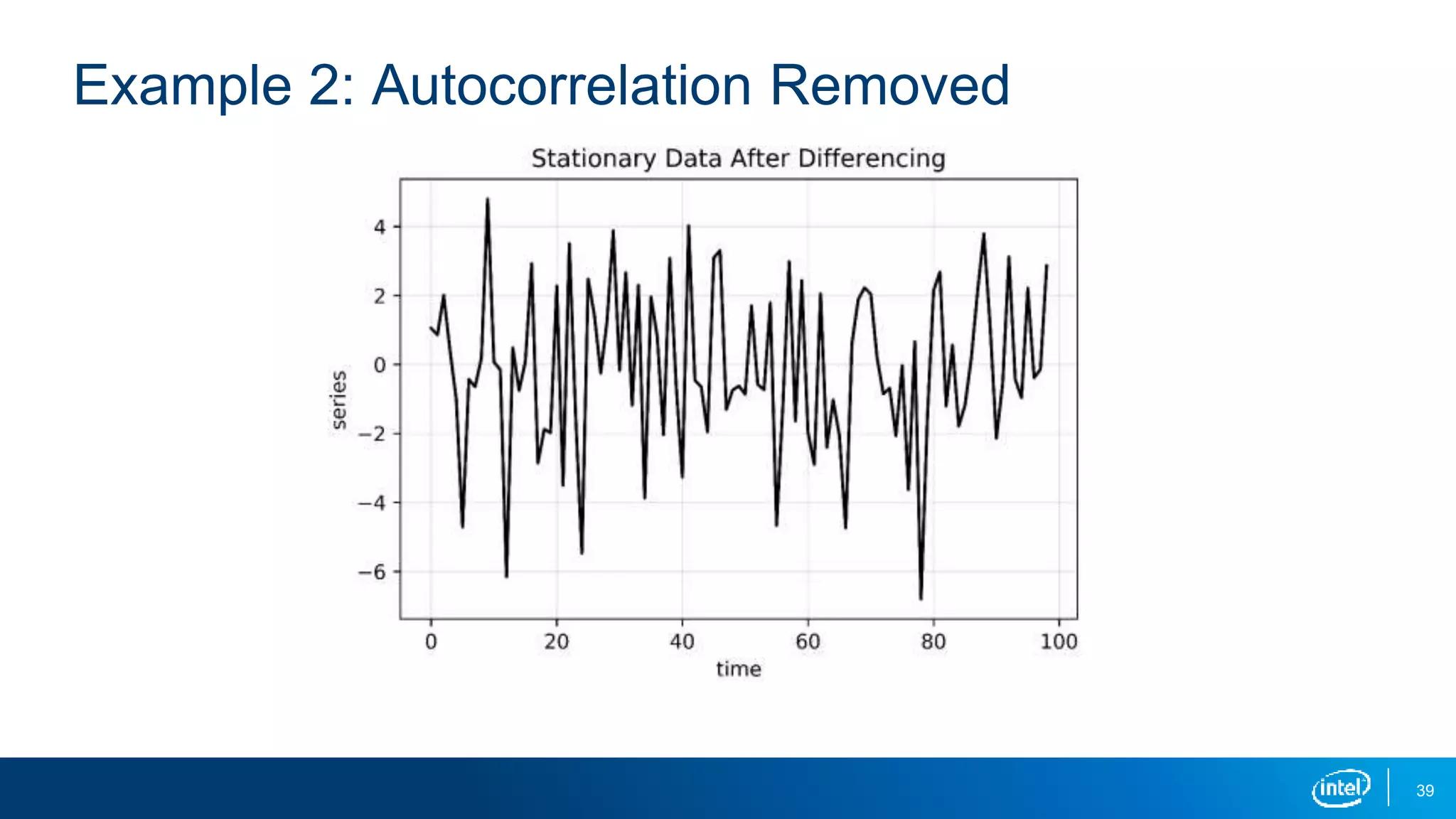
This document discusses stationarity in time series analysis. It defines stationarity as a time series having a constant mean, constant variance, and constant autocorrelation structure over time. Non-stationary time series can be identified through run sequence plots, summary statistics, histograms, and augmented Dickey-Fuller tests. Common transformations like removing trends, heteroscedasticity through logging, differencing to remove autocorrelation, and removing seasonality can be used to make non-stationary time series data stationary. Python is used to demonstrate identifying and transforming non-stationary time series data.