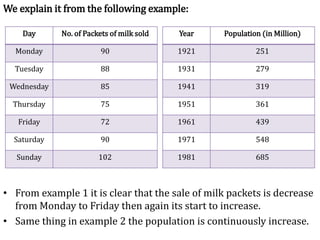
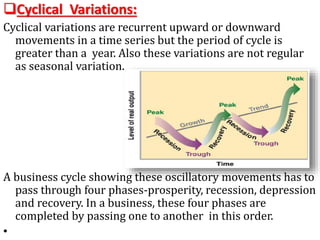
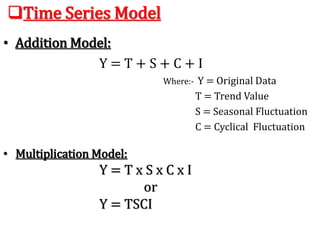
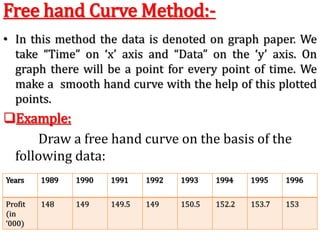
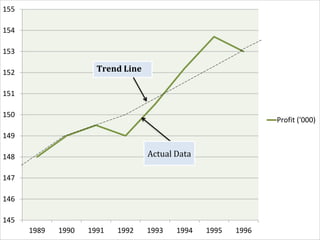
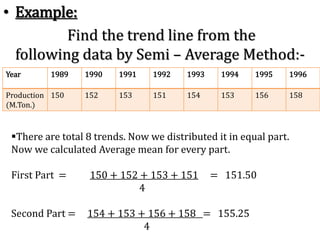
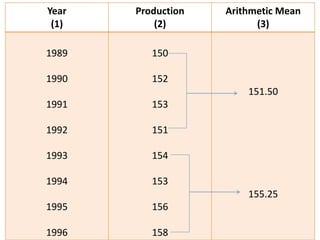
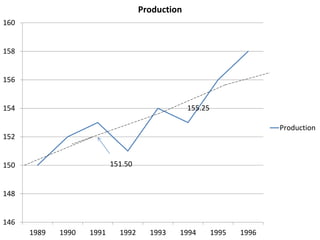
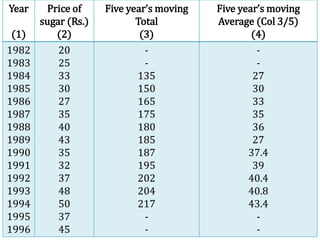
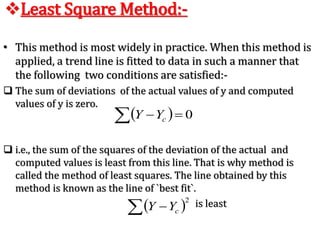
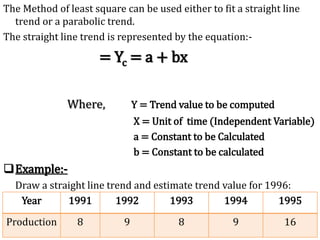
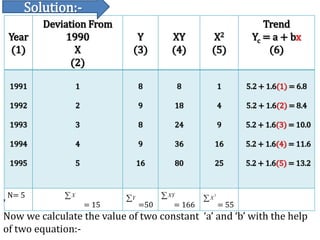
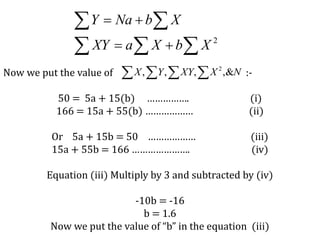
This document discusses time series analysis and forecasting. It defines forecasting as making predictions about the future based on past data and trends. Business forecasting estimates future sales, expenses, and profits. Time series analysis establishes relationships between variables over time. Key components of time series that influence trends include seasonal, cyclical, secular, and irregular variations. Common forecasting methods mentioned are regression analysis, exponential smoothing, and time series analysis. Measurement of trends can be done using techniques like least squares, moving averages, and semi-averages.