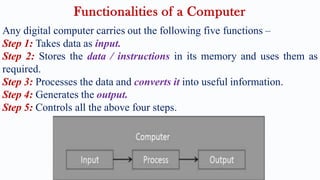
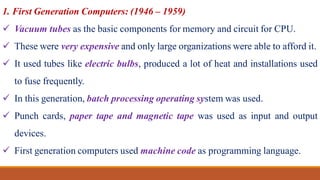
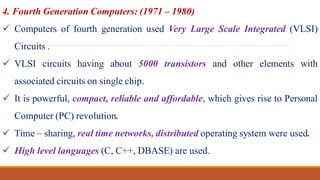
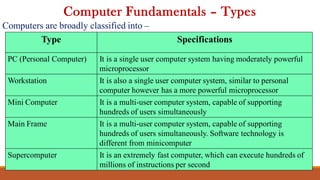
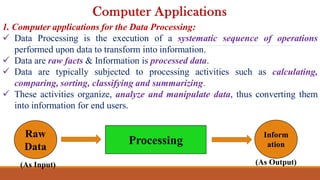
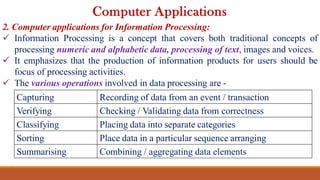
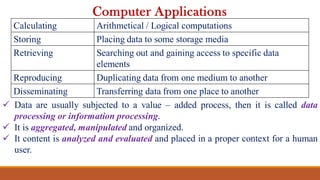
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computers, covering their evolution through five generations, main functionalities, characteristics, and applications in various fields such as business, healthcare, and education. It highlights both advantages, like speed and accuracy, and disadvantages, such as dependency and lack of intelligence. Additionally, it discusses disruptive technologies and the impact of computers on modern society.