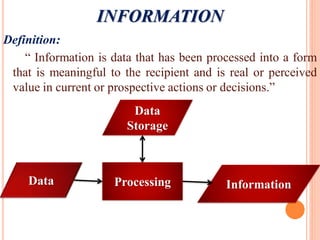
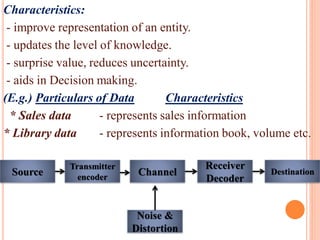
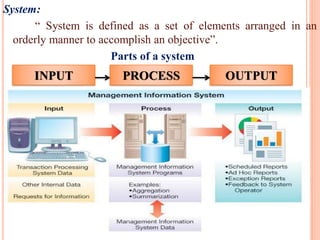
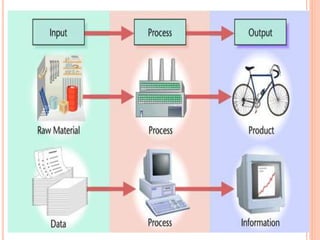
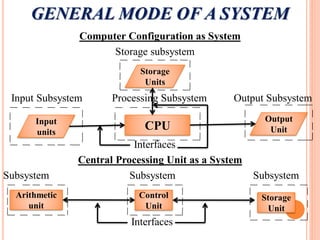
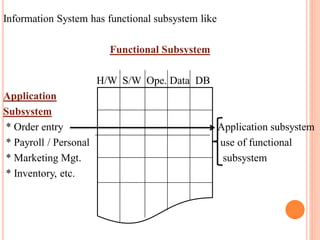
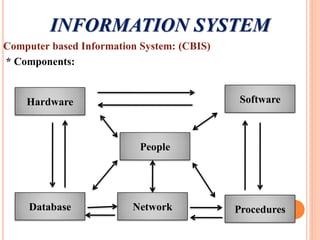
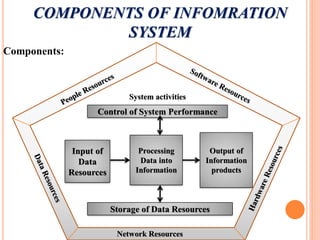
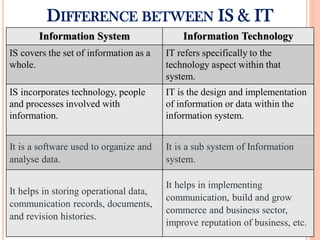
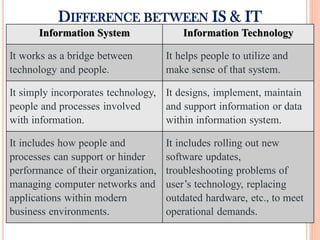
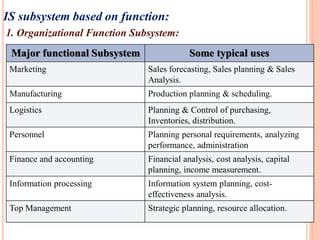
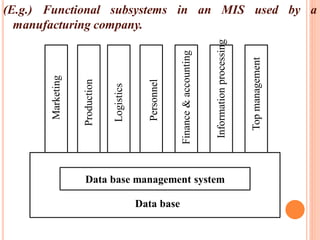
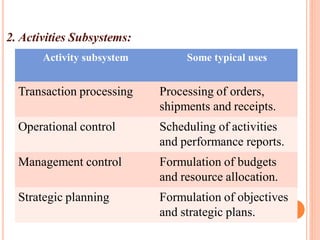
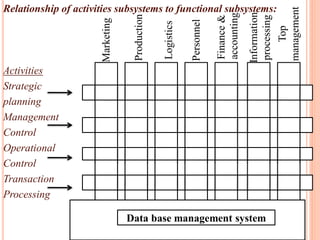
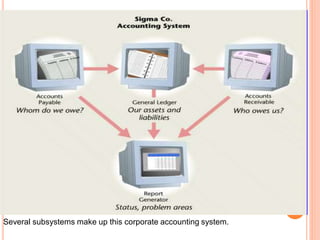
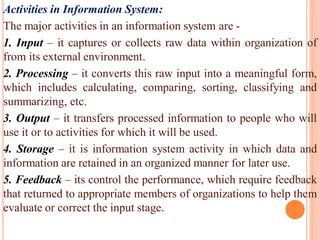
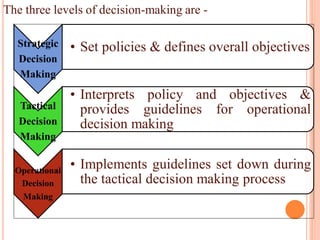
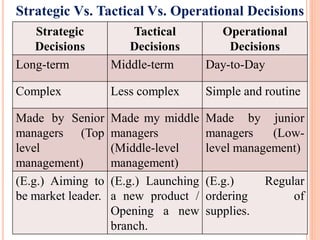
The document discusses the importance of information systems in decision making and strategy building for organizations. It defines information and information technology, and describes the difference between information systems and information technology. An information system is comprised of various components including hardware, software, data, people, and processes. Information systems help management make informed decisions, improve communication and business processes, and develop effective strategies. Managers play an important role in overseeing information systems and ensuring they meet the needs of the organization.