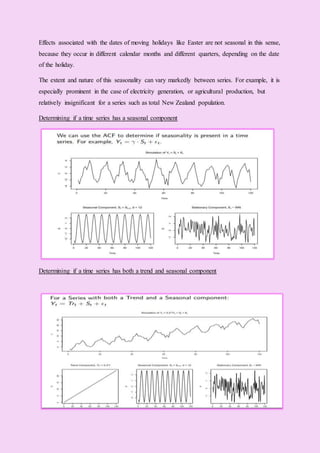
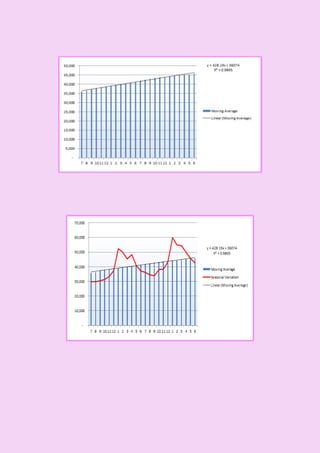
This document discusses trend and seasonal components in time series analysis. It defines trend as the long-term movement in a time series due to underlying economic or socioeconomic factors. Methods for estimating trends include moving averages and least squares. Seasonal components refer to regular fluctuations that occur within the same period each year, such as monthly or quarterly patterns driven by weather, holidays, or other seasonal factors. The document provides examples of trend and seasonal patterns and methods for determining if components are present in a time series, including fitting trend lines using least squares.