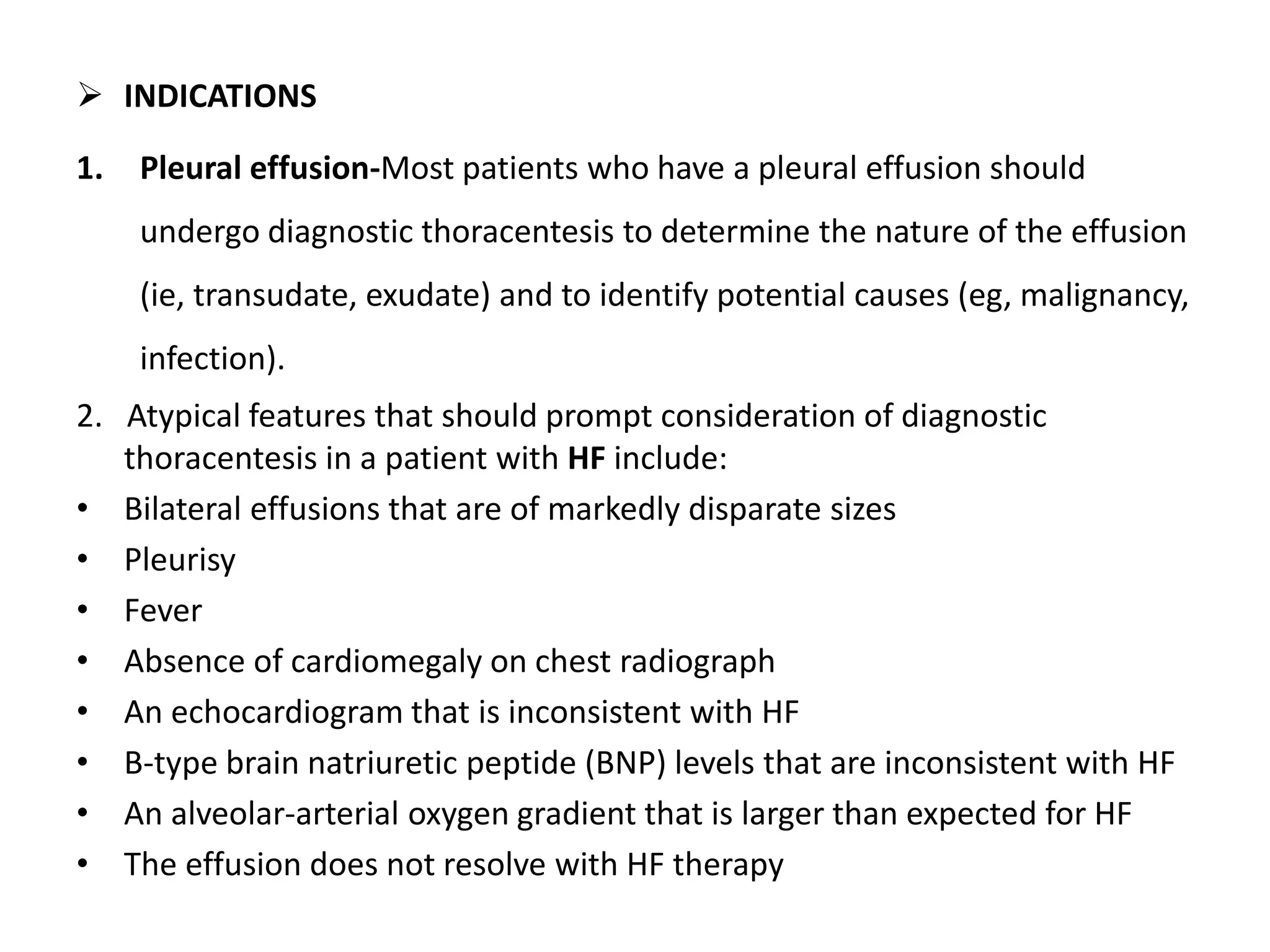
Thoracentesis is a procedure where a needle is inserted into the pleural space to remove pleural fluid for analysis or relief of symptoms. It can be done for diagnostic purposes to analyze the fluid or therapeutically to drain a large volume of fluid. Indications include evaluating an undiagnosed pleural effusion or atypical features in heart failure patients. Contraindications include bleeding risks or small effusions. The procedure involves localizing the site, administering anesthesia, inserting a needle while aspirating to drain fluid, and analyzing the fluid removed. Potential complications include pain, bleeding, pneumothorax, and infection, with pneumothorax being the most common clinically significant complication.