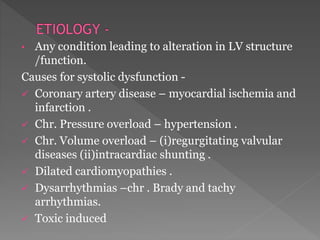
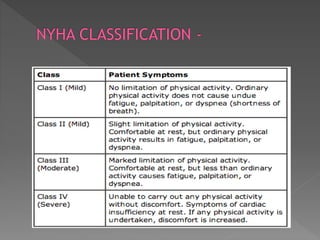
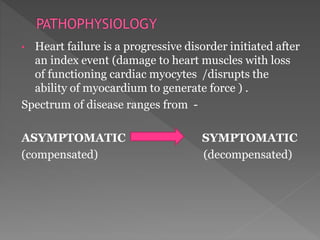
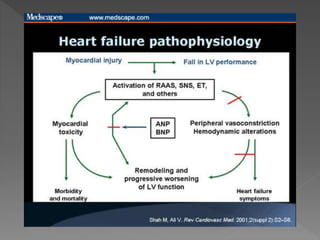
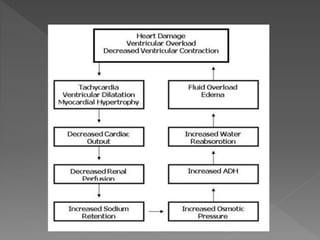
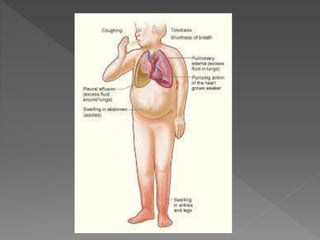
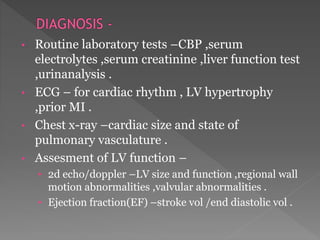
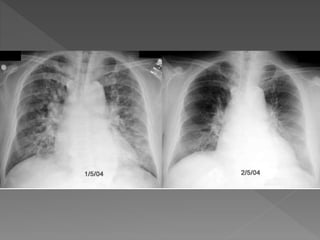
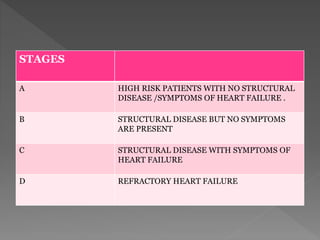
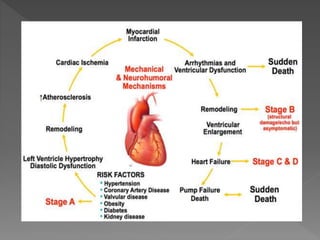
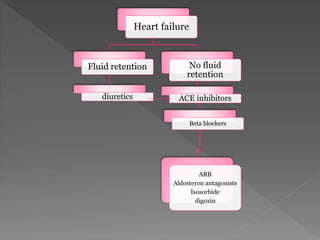
Heart failure is a common condition where the heart muscle is unable to pump sufficiently. It affects around 2% of developed countries' adult populations and risk increases with age. Heart failure can be systolic, with reduced ejection fraction below 40%, or diastolic, with preserved ejection fraction above 40-50%. Common causes include coronary artery disease, hypertension, valvular diseases, cardiomyopathies, and arrhythmias. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and reducing mortality risk through lifestyle changes, medications like diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists, and devices or procedures for advanced cases.