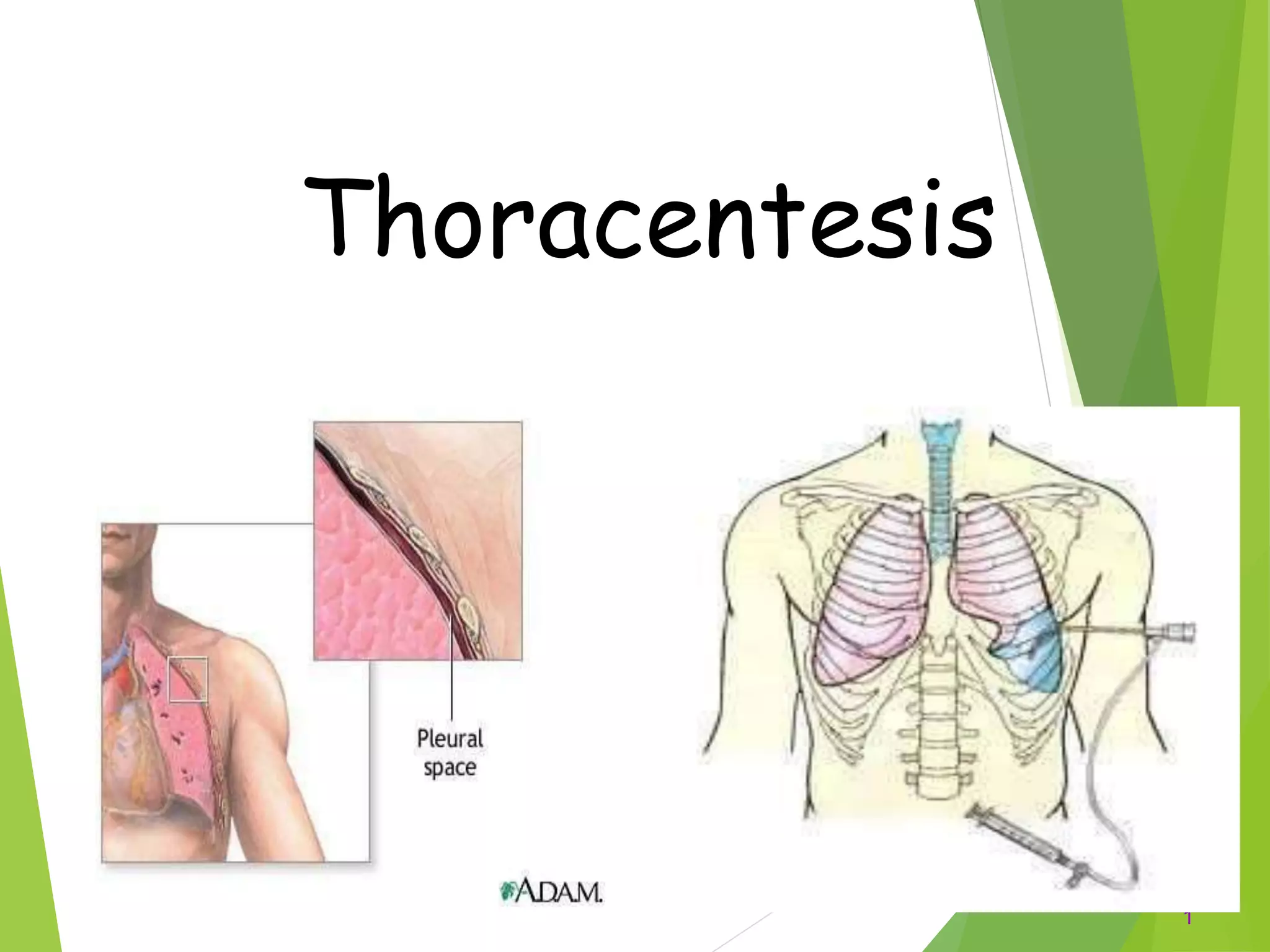
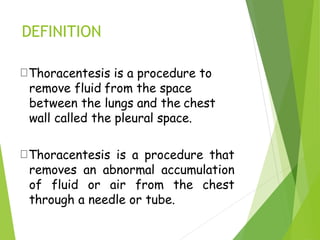
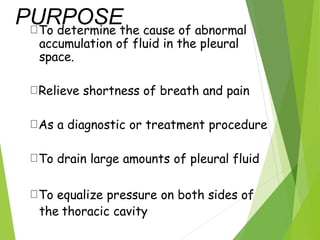
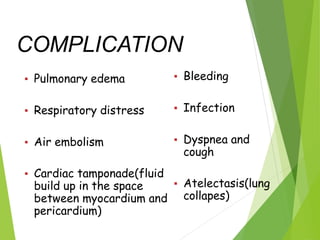
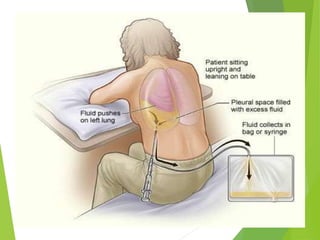
Thoracentesis is a procedure to drain fluid from the pleural space between the lungs and chest wall. It is done to determine the cause of fluid accumulation, relieve symptoms like shortness of breath, and as a diagnostic or treatment procedure. The doctor will take a medical history, prepare equipment, position the patient upright, clean the skin, and administer local anesthetic. During the procedure, vital signs and breathing are monitored. Afterward, a chest x-ray is taken, fluid samples are labeled and sent for testing, and the patient rests in bed while being monitored for complications before resuming regular activities.