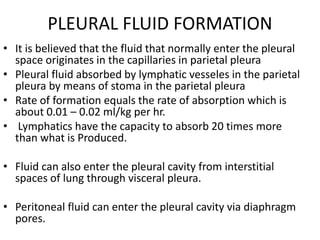
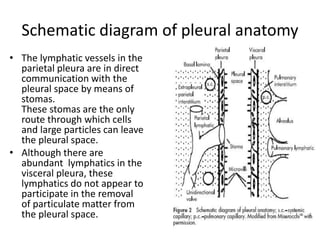
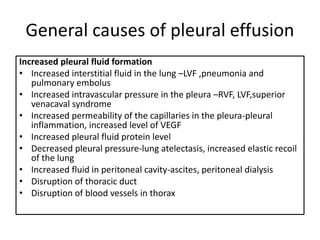
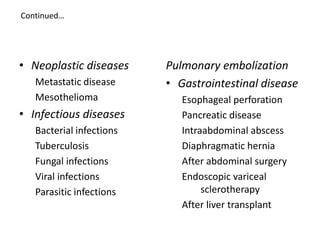
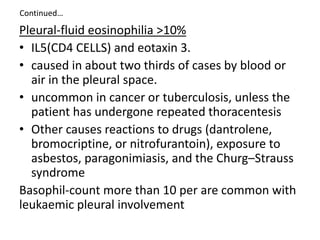
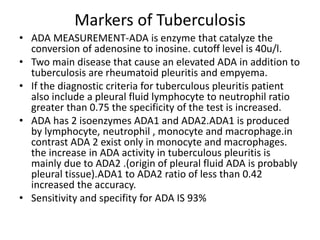
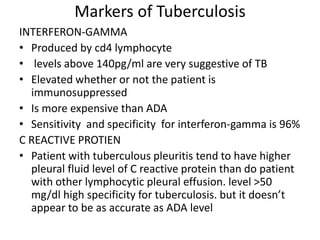
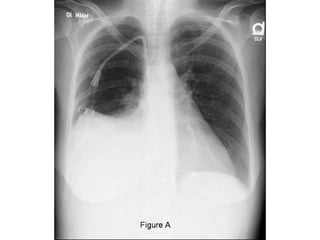
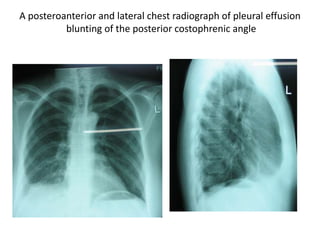
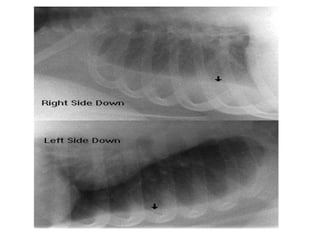
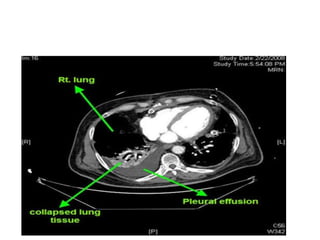
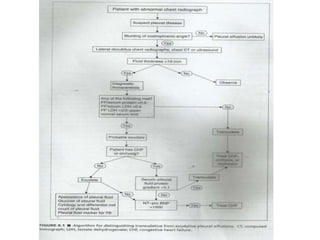
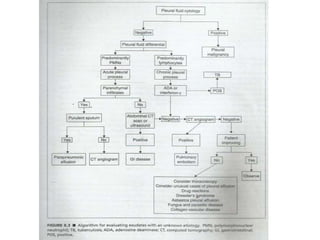
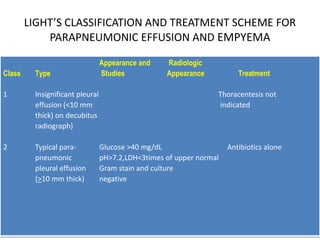
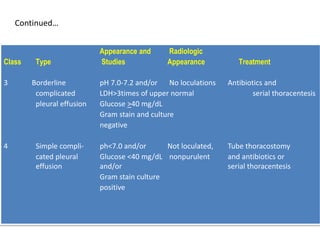
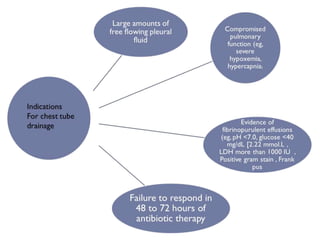
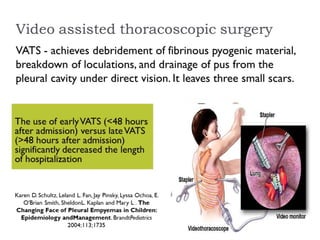
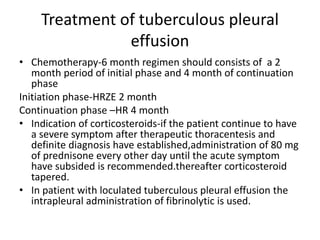
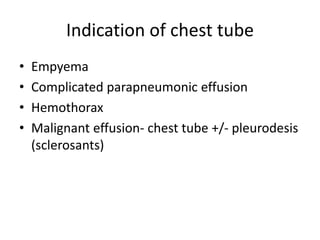
Pleural effusion results from an imbalance between pleural fluid formation and absorption, causing fluid to accumulate in the pleural space. Fluid formation occurs through capillaries in the parietal pleura, and absorption occurs via lymphatic vessels. When the rate of formation exceeds absorption, effusion occurs. Effusions are classified as transudative or exudative based on fluid characteristics. Diagnostic testing of pleural fluid aims to determine the cause of effusion. Radiography and ultrasound are used to identify and characterize pleural fluid.