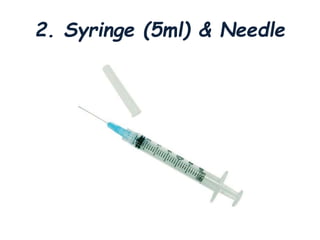
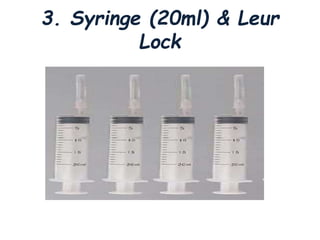
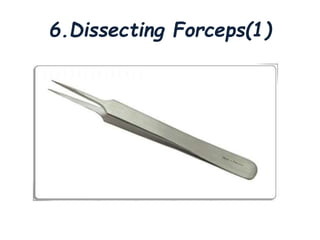
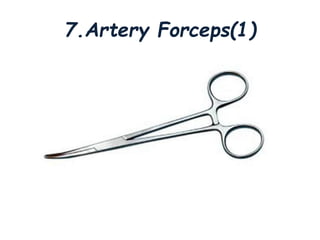
Thoracentesis is a medical procedure that involves inserting a needle into the pleural space to remove fluid or air, decrease lung pressure, conduct diagnostic studies, or deliver medication. The procedure requires informed consent, patient preparation, and careful monitoring of vital signs, aiming to remove 1000-2000ml for therapeutic purposes or 30-60ml for diagnostic purposes. Post-procedure care includes monitoring for complications and instructing the patient on breathing exercises.