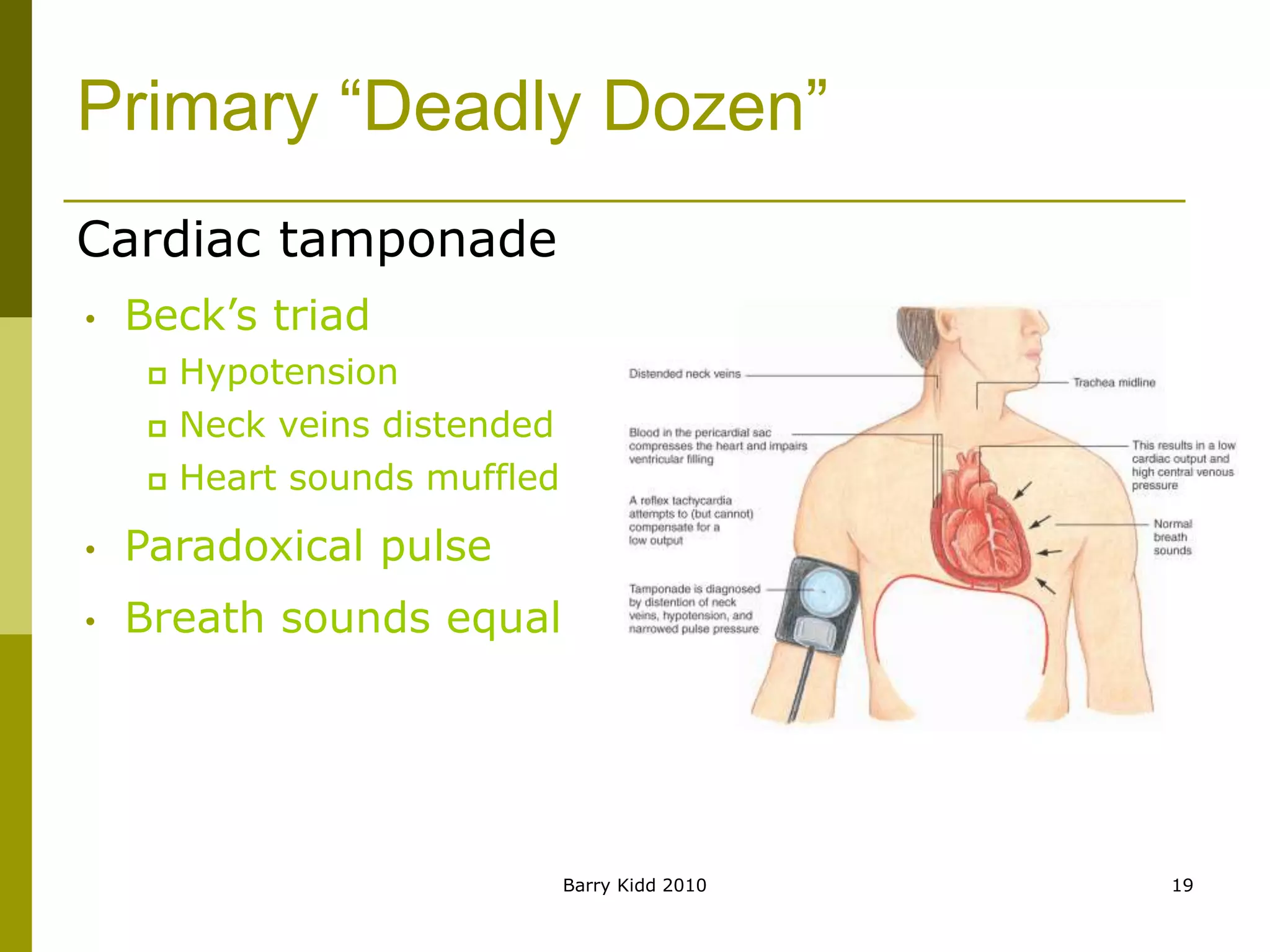
Thoracic trauma is common, accounting for 50% of multiple trauma cases and 25% of trauma deaths. Potentially fatal thoracic injuries like tension pneumothorax, massive hemothorax, and cardiac tamponade require rapid recognition and intervention to save lives. The primary survey focuses on the "Deadly Dozen" immediate threats like airway obstruction, open pneumothorax, and flail chest, while the secondary survey evaluates less immediately life-threatening injuries like pulmonary contusion and myocardial contusion. Chest injuries frequently necessitate prompt treatment and often require urgent transport or "load-and-go" to definitive care.