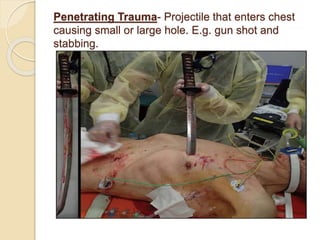
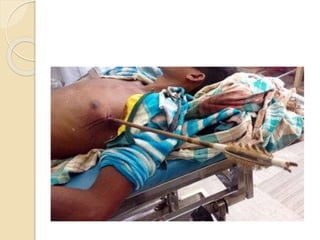
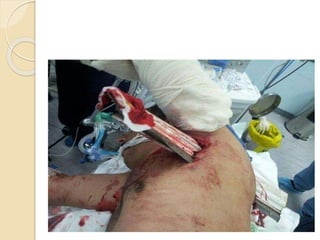
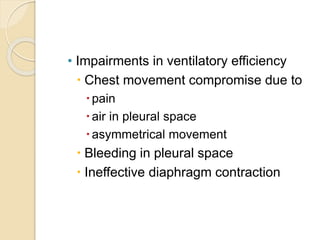
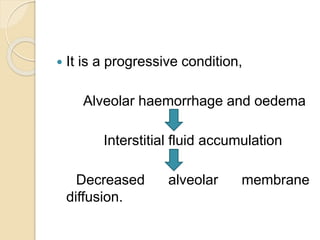
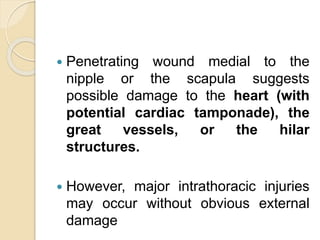
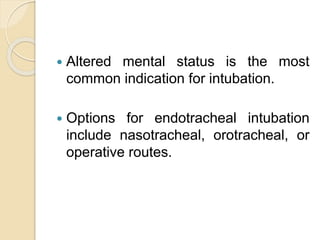
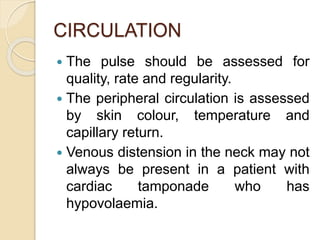
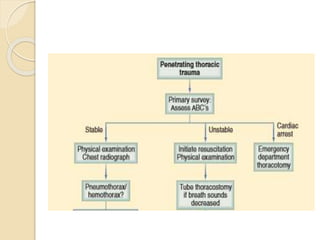
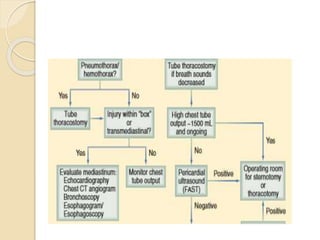
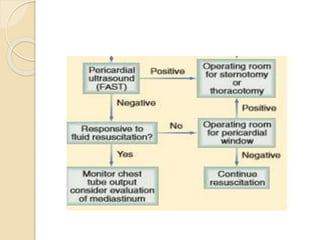
Chest trauma can cause significant morbidity and mortality if not managed promptly and effectively. The document discusses the pathophysiology of chest trauma from both blunt and penetrating mechanisms. It emphasizes the importance of the primary survey approach, including assessing the airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs). For patients who are unstable, interventions like intubation, chest tube insertion, and fluid resuscitation may be required during the initial assessment to stabilize their condition.