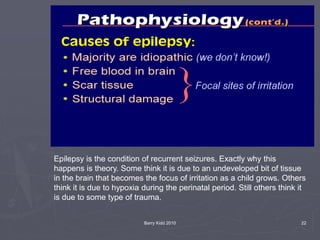
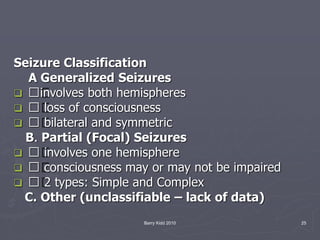
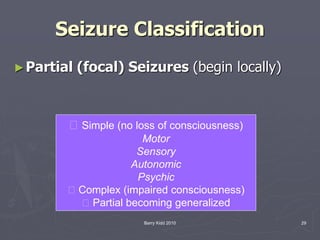
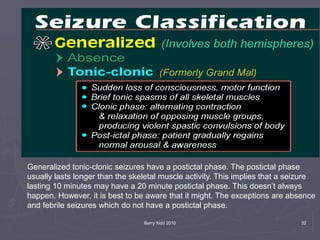
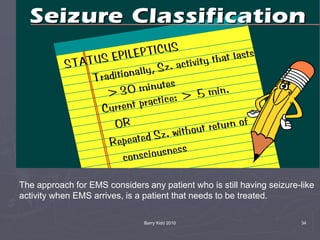
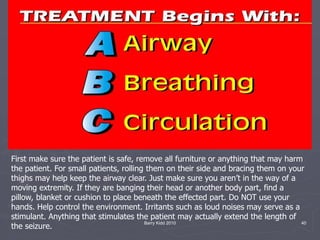
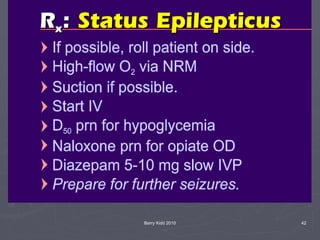
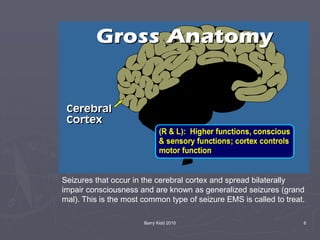
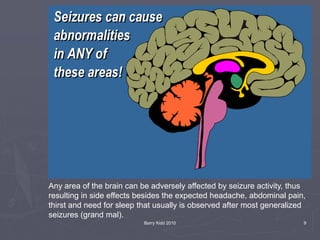
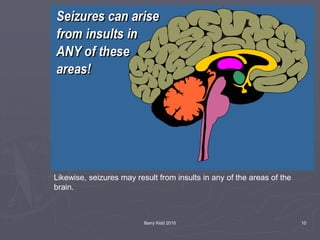
The document discusses seizures, their classification, and treatment considerations for EMS. It describes how seizures are classified based on mental status (simple vs complex) and laterality (partial vs generalized). Generalized seizures involve both hemispheres and can cause loss of consciousness, while partial seizures originate in one hemisphere and may or may not affect consciousness. Status epilepticus is a medical emergency defined as continuous seizure activity. The document provides guidance for EMS on safely managing patients during and after seizure activity without forcing interventions.














![Barry Kidd 2010 20
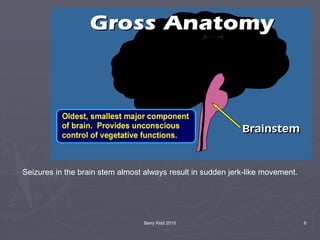
Posturing and grinding teeth are brain stem reflexes that will occur as a
response to stimulation (such as noise, touch, pain, etc.). During a
seizure, irritating stimuli (such as loud noises) may be interpreted as a
threat [remember the reptilian system?] and a response may occur.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seizureemergenciesppt-201205050715/85/Seizure-emergencies-20-320.jpg)