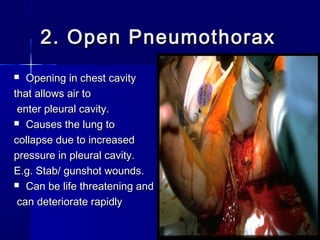
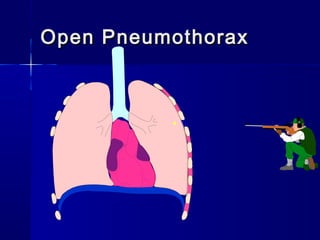
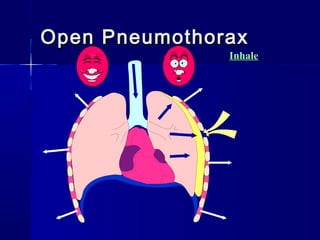
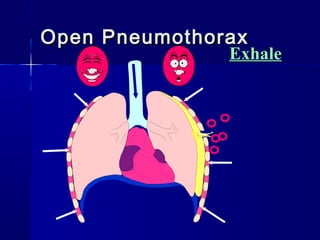
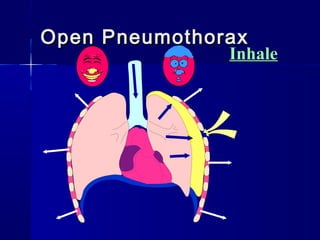
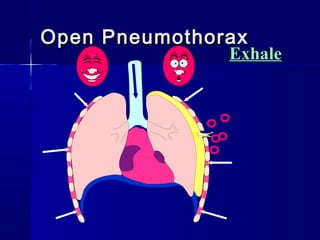
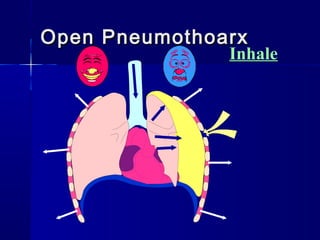
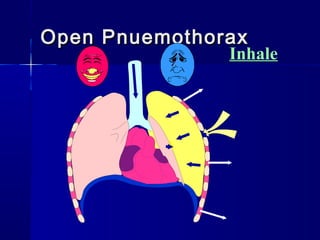
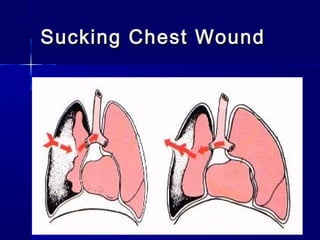
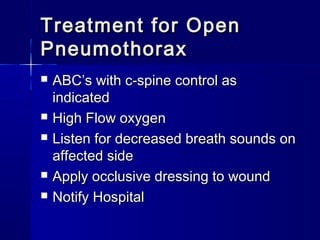
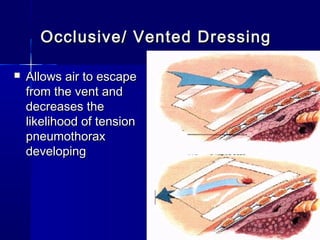
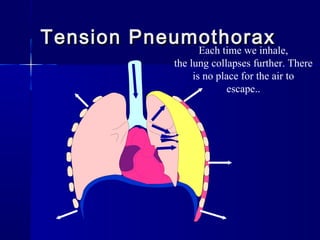
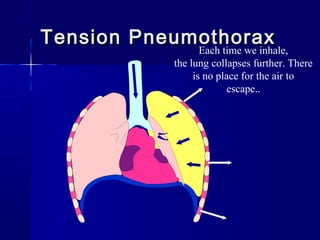
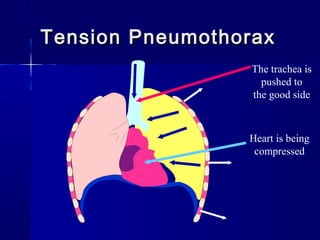
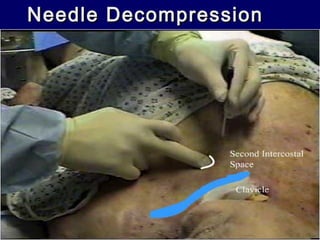
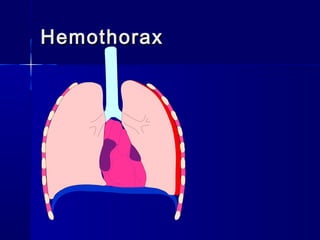
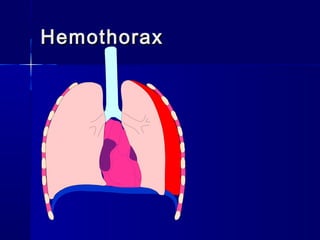
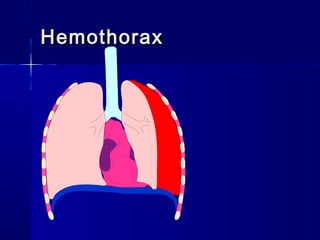
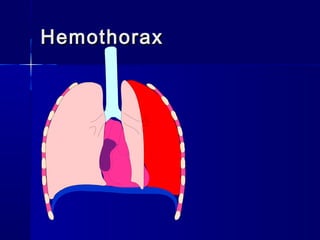
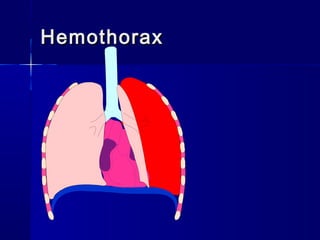
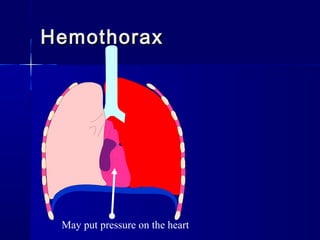
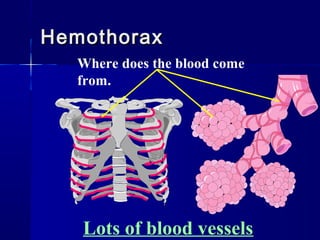
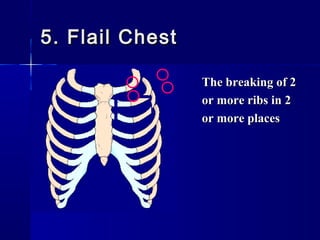
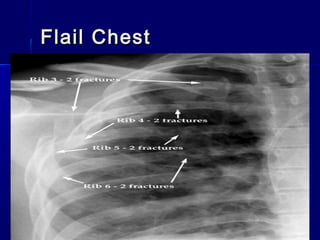
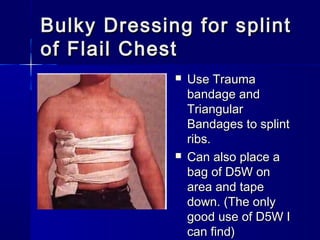
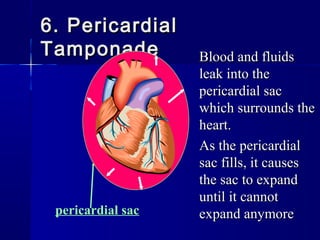
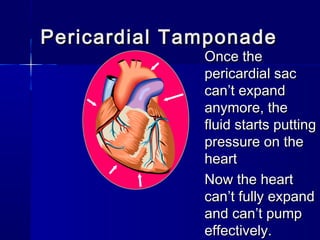
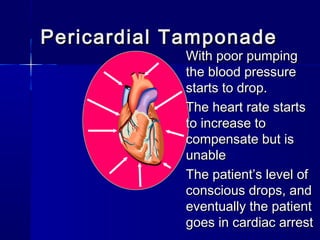
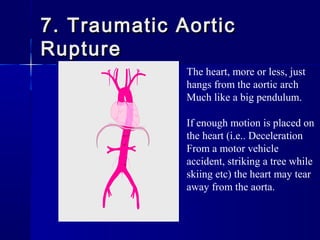
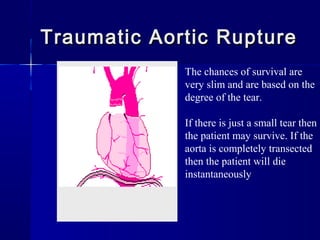
This document provides an overview of chest trauma. It begins by defining chest trauma as any injury to the chest, including the ribs, heart and lungs. Chest injuries are categorized as open or closed. Common causes are discussed, including blunt trauma from accidents or penetrating trauma from objects. Signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests, and specific injuries like pneumothorax are described. Treatment focuses on ABCs - airway, breathing and circulation while performing tests to evaluate cardiac and pulmonary function.