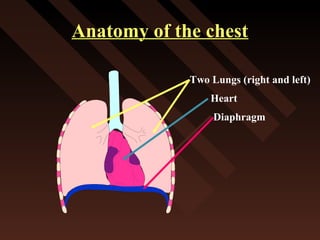
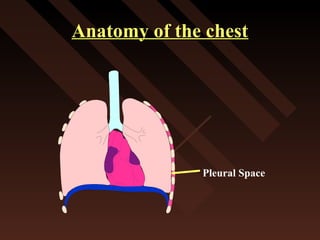
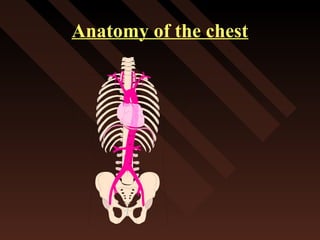
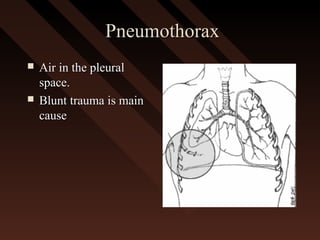
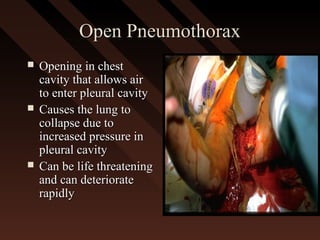
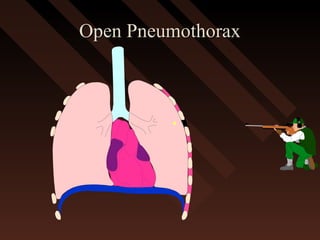
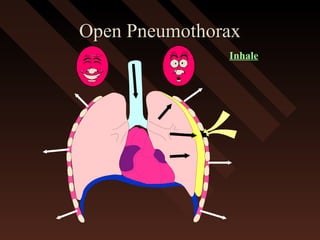
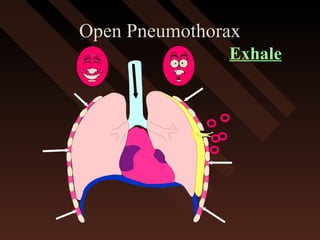
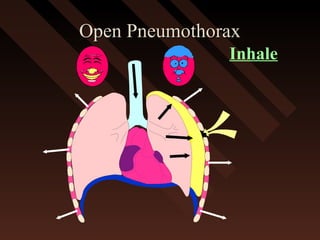
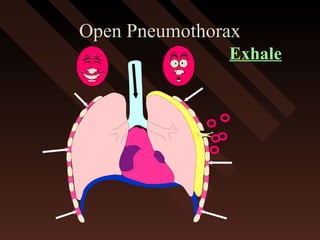
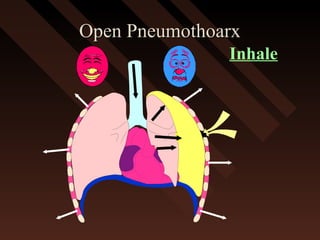
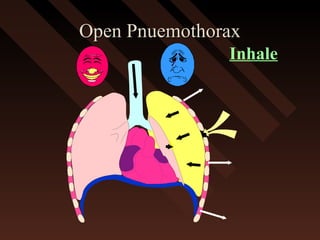
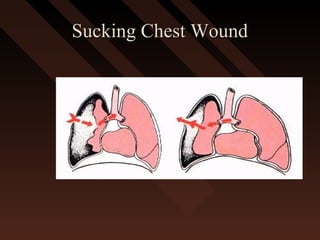
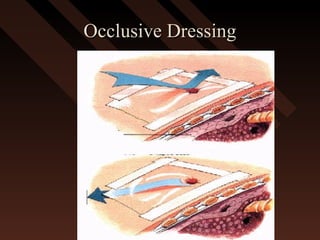
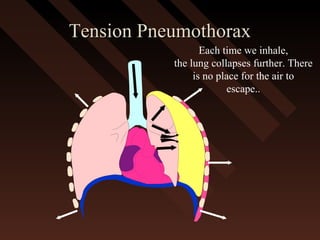
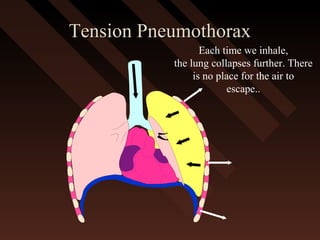
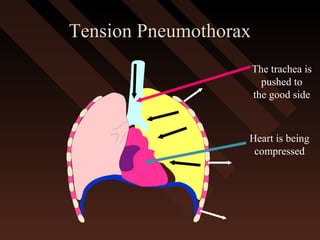
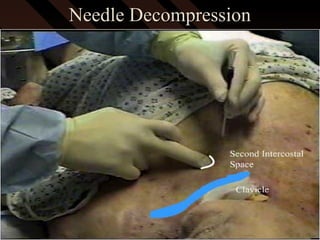
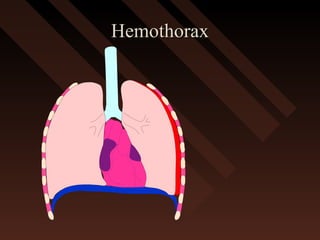
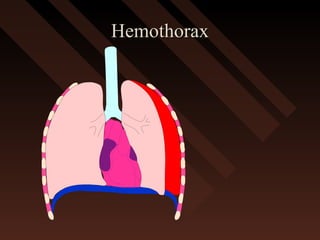
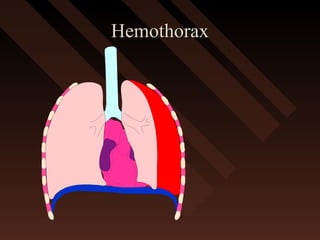
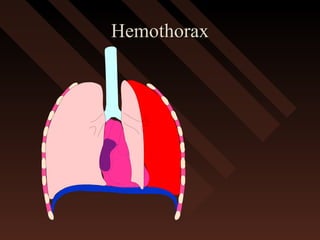
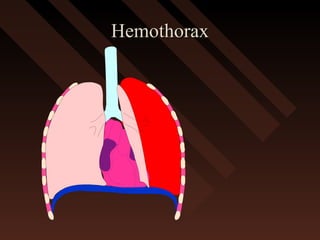
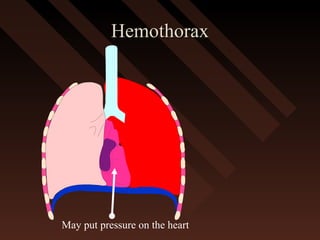
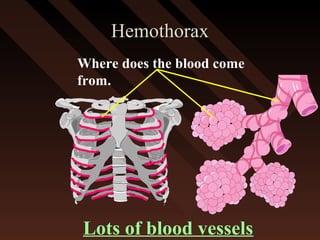
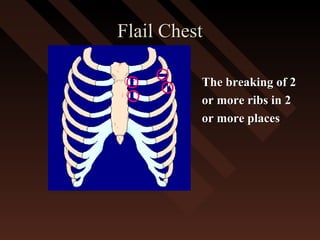
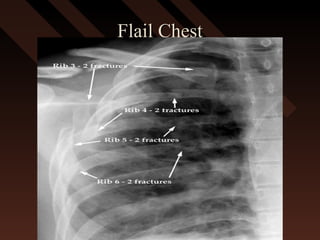
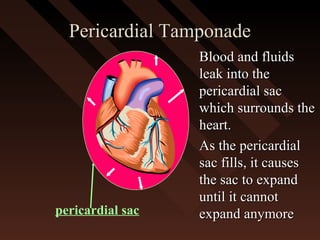
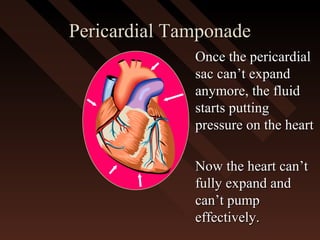
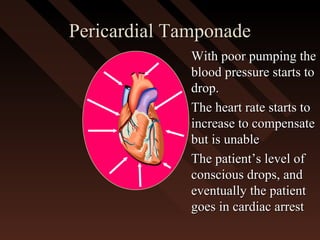
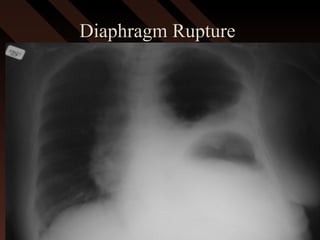
This document provides an overview of chest trauma, including the anatomy of the chest, common causes of injury, signs and symptoms of different types of chest injuries, and treatment approaches. It describes various chest injuries such as pneumothorax, hemothorax, open pneumothorax, tension pneumothorax, flail chest, cardiac tamponade, and diaphragmatic rupture. For each injury, it outlines the mechanism of injury, associated signs and symptoms, and recommended interventions. The goal is to educate on evaluating and managing different chest trauma presentations.