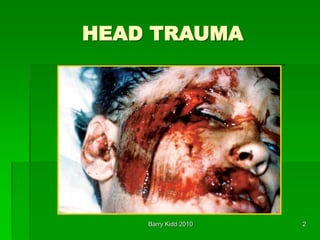
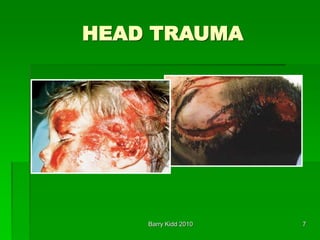
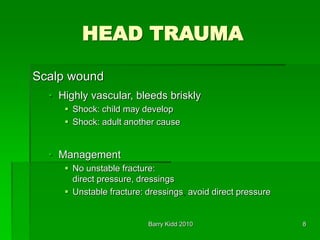
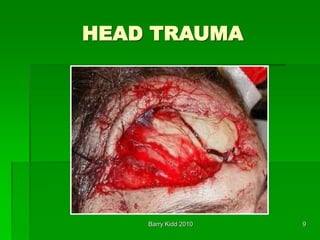
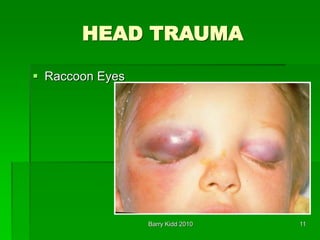
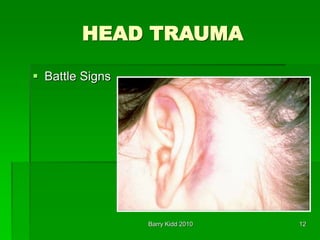
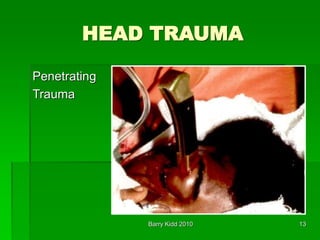
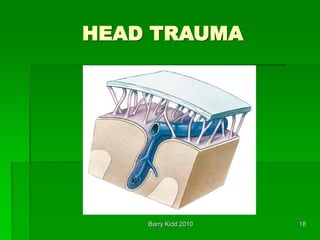
This document discusses head trauma, including:
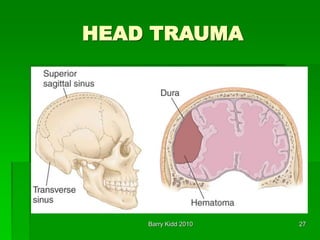
- The anatomy of the head and brain and types of injuries like concussions, contusions, hematomas.
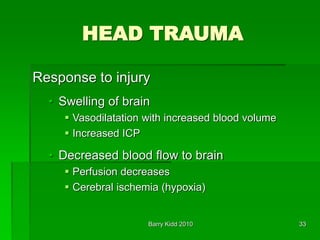
- Primary and secondary brain injuries, with primary occurring immediately from force and secondary developing over hours from hypoxia or decreased blood flow.
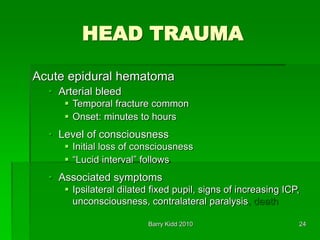
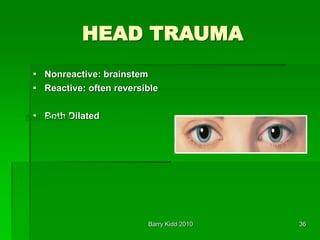
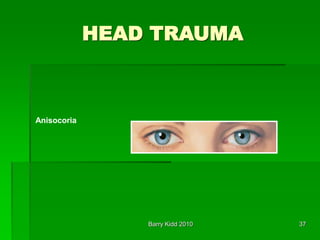
- Assessment of head injury patients including neurological exam signs like anisocoria and posturing that indicate increased intracranial pressure.
- Management focuses on airway control, preventing hypotension, limiting agitation to reduce intracranial pressure, and treating cerebral herniation syndrome aggressively.