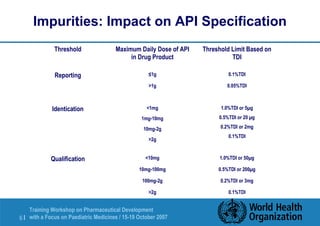
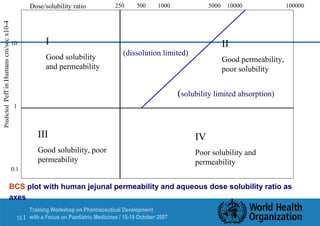
This document outlines an agenda for a training workshop on pharmaceutical development with a focus on paediatric formulations being held from October 15-19, 2007 in Tallinn, Estonia. The workshop will cover various topics including pre-formulation analytical studies, stress testing APIs, the impact of impurities on API specifications, excipient compatibility studies, degradation pathways like hydrolysis and oxidation, and the role of preformulation in selecting appropriate drug products and manufacturing processes. One of the presentations will focus on pre-formulation analytical studies and their impact on API and formulation development.