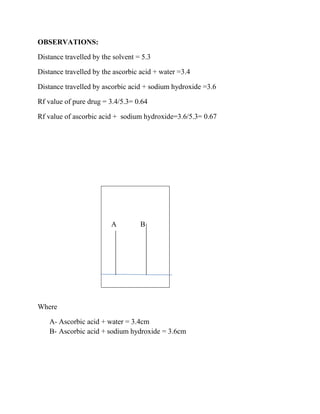
This document describes testing the degradation of ascorbic acid using thin layer chromatography (TLC). It discusses the principles of chromatography and TLC. The procedure involves spotting ascorbic acid solutions with and without sodium hydroxide on a TLC plate coated with silica gel as the stationary phase. The mobile phase moves up the plate by capillary action. The Rf values are calculated and show the degraded sample moves slightly farther, indicating degradation.

![developing reagents, such as strong acids can be used to detect the compounds
without destroying the substrate.
MOBILE PHASE: Mobile phase used in solvents of different polarity. Stationary
phase i.e. silica contains some free S-OH groups. These groups from H-bonds or
vanderwaal interactions with the analytic components thus adsorption takes place.
The Retention factor[Rf] is determined, which is specific for a compound and it is
calculated by a formula
Distance travelled by the solute
Rf =
Distance travelled by the solvent front
Drug degradation occurs during storage because of chemical alteration of active
ingredients or additives.
Solubility studies are necessary for following reasons:
1) Product instability or chemical degradation of active drug may lead to under
medication due to the lowering of the concentration of the drug in dosage form.
Example: Digoxin and theophylline
2) Drug decomposition of active drug toxic products may be necessary.
Example: P-amino salicylic acid is converted into P-amino phenol which is
toxic.
3) Instability due to change in physical appearance.
Example: Mottling of tablets, creaming of emulsions.
TYPES OF DEGRADATION OF PHARMACEUTICAL PRODUCTS:
1) Physical degradation or decomposition of drugs
2) Chemical degradation or decomposition of drugs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testingthedegradationofascorbicacidbytlc-140929001134-phpapp02/85/Testing-the-degradation-of-ascorbic-acid-by-tlc-2-320.jpg)