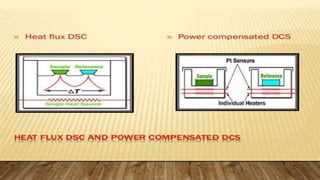
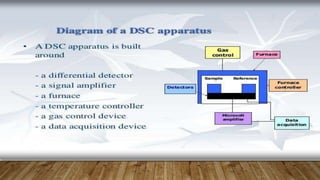
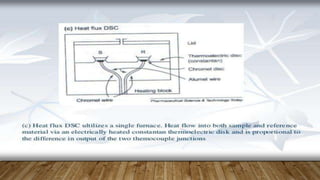
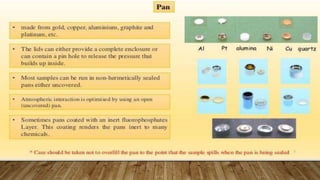
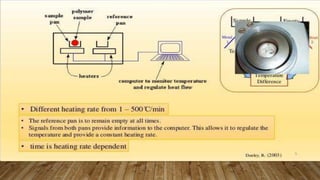
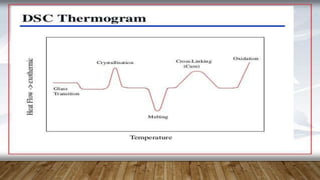
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) is a technique used to analyze thermal transitions in materials. There are two main types of DSC instruments: heat-flux DSC and power-compensated DSC. Heat-flux DSC measures the difference in heat flow into the sample and reference, while power-compensated DSC maintains the sample and reference at equal temperatures while measuring the power difference required. DSC can be used to analyze properties such as glass transitions, melting points, crystallization kinetics, and heat of reactions. It has applications in fields such as materials science, polymers, and pharmaceuticals.