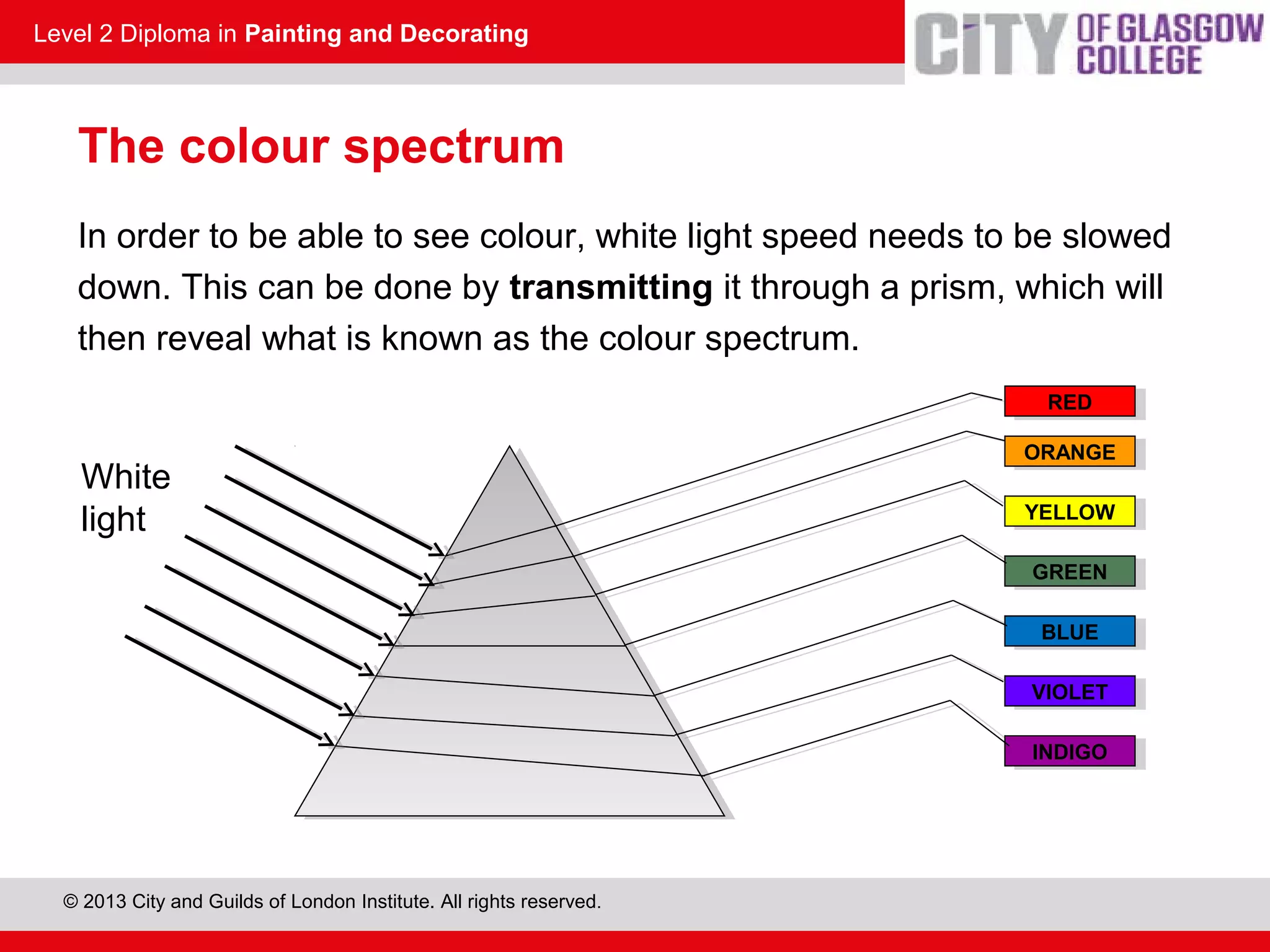
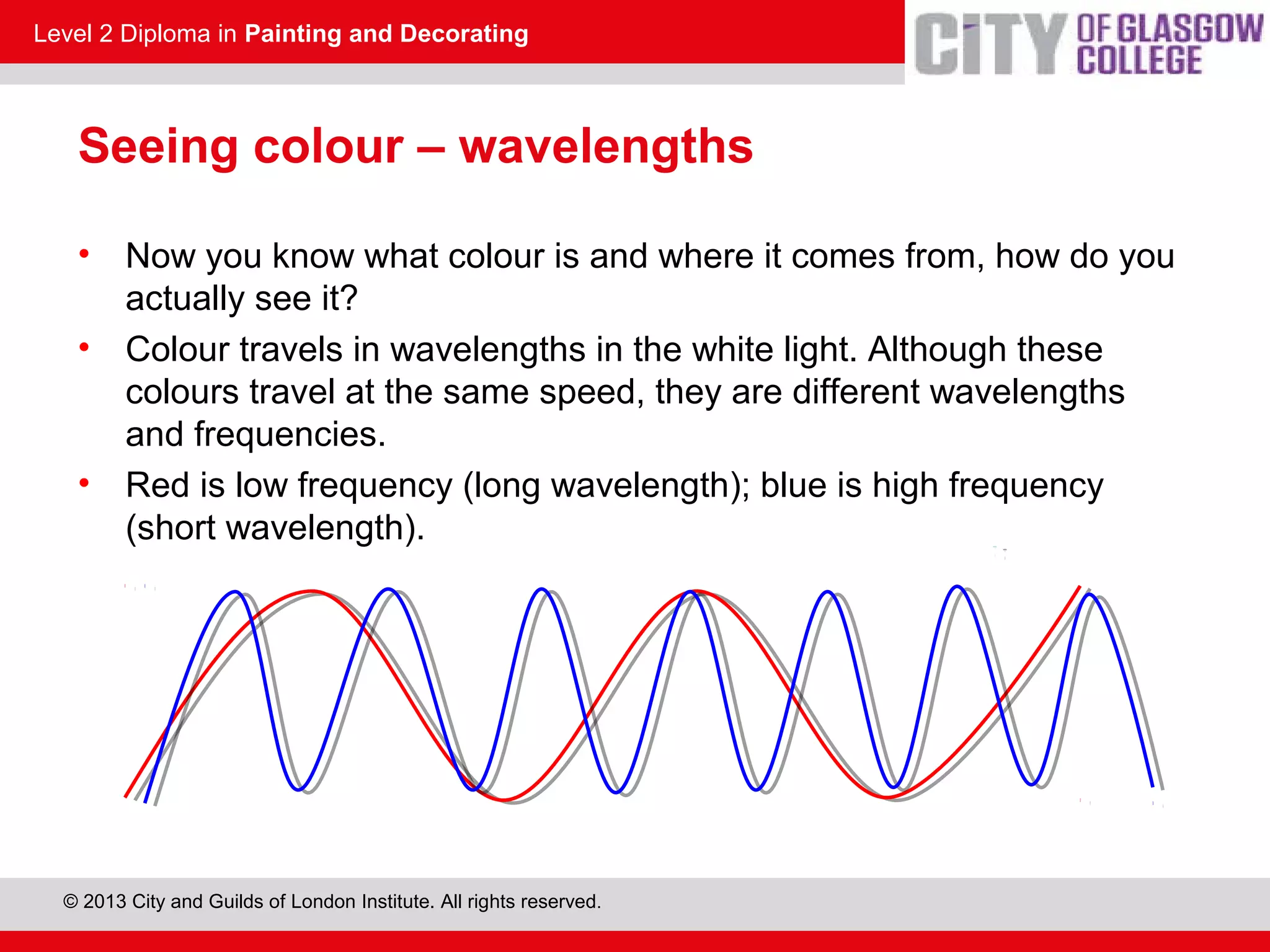
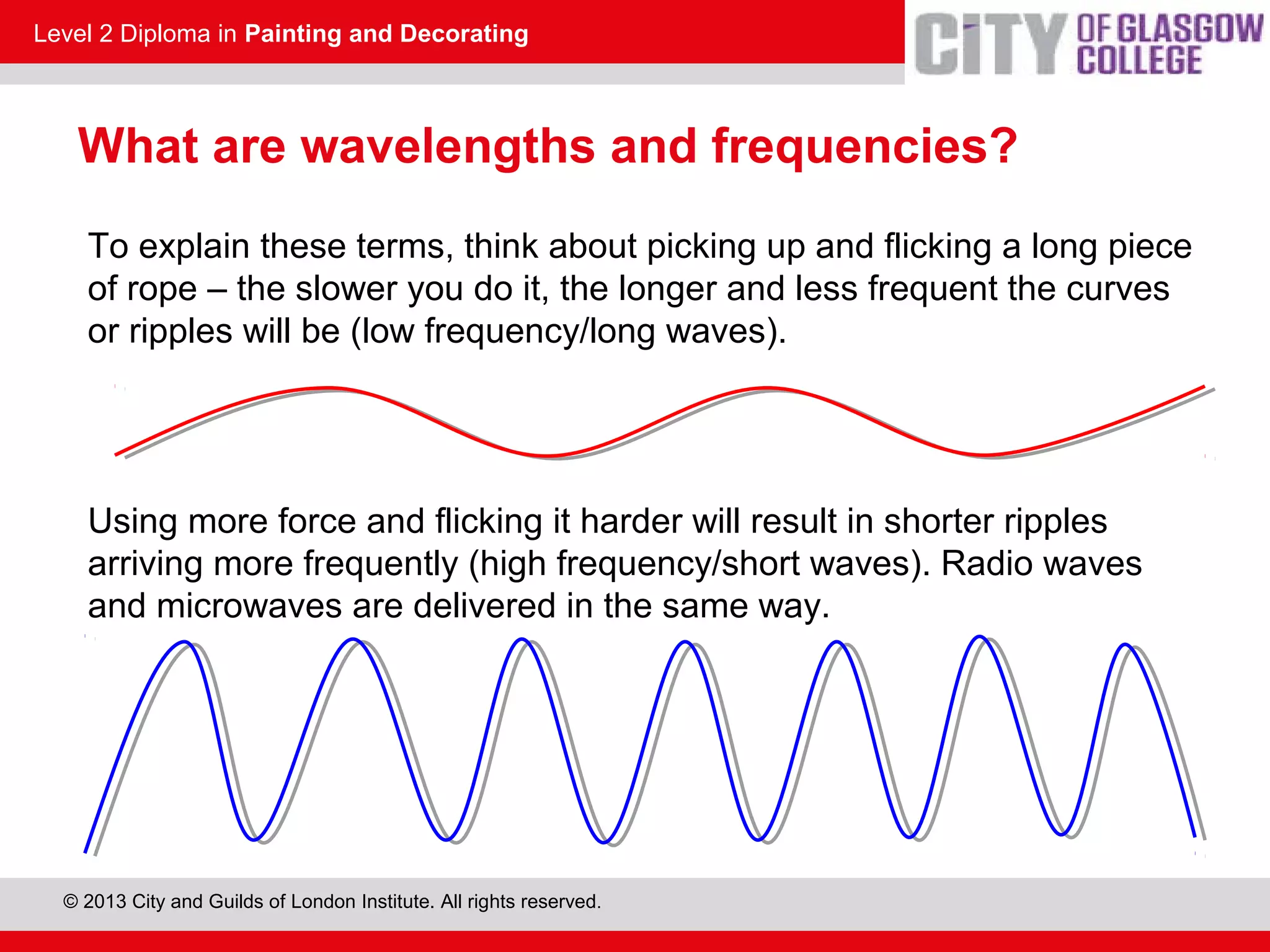
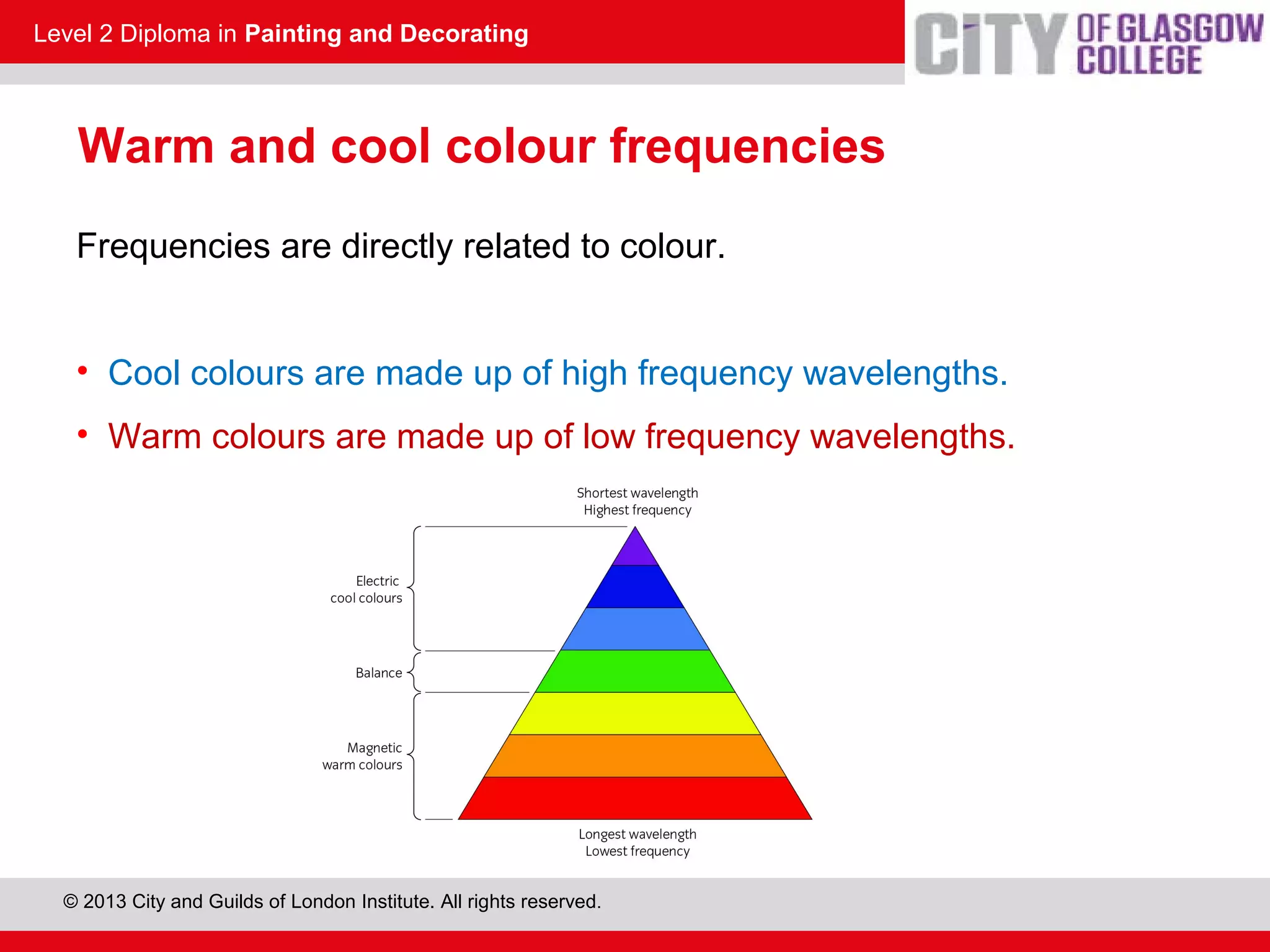
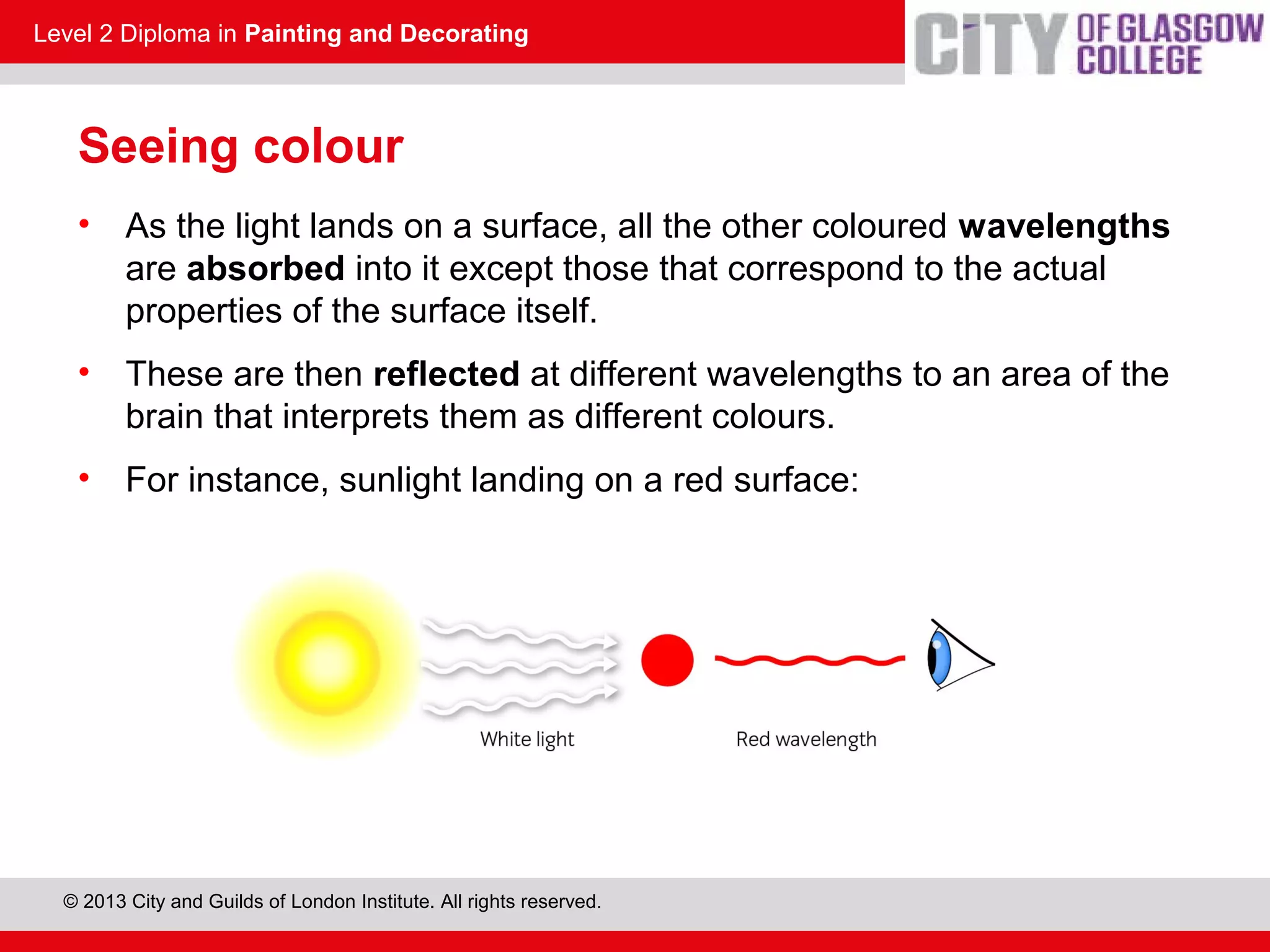
This document discusses the source and perception of color. It begins by explaining that color comes from light, specifically white light which contains all visible wavelengths. When white light passes through a prism, it separates into the colors of the visible spectrum from red to violet due to differences in wavelength. The human eye perceives color when these light wavelengths are reflected from surfaces and detected by the brain. In addition, there are invisible colors like infrared and ultraviolet that have wavelengths beyond the visible spectrum.