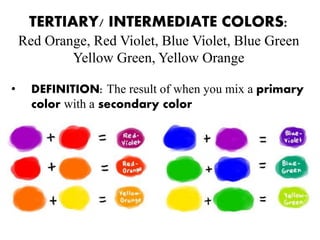
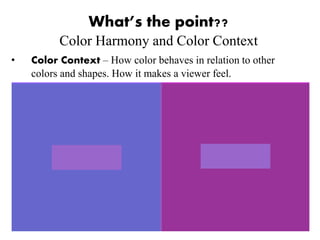
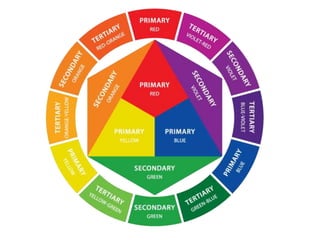
Color is what our eyes see that is reflected or absorbed by light. There are three primary colors - red, yellow, and blue - that can be combined to create all other colors. Secondary colors like orange, green, and purple are created by mixing two primary colors. Color schemes use different types of colors arranged together, such as complementary, analogous, warm, cool, and monochromatic colors. Effective use of color considers both harmony, which creates a pleasing balance, and context, or how color relates to other elements and makes people feel.