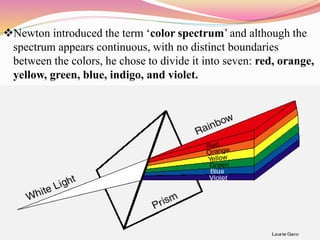
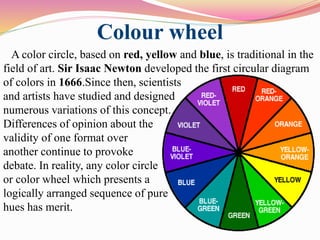
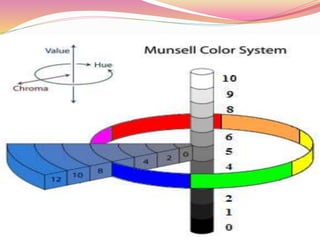
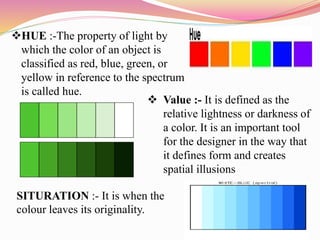
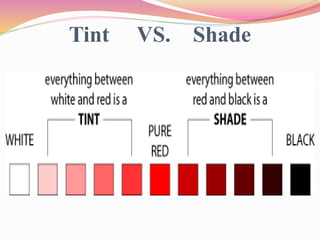
This document discusses color theory and how color and lighting affect interior design. It defines color as the visual perceptual property arising from the spectrum of light reflected or emitted by an object. The document outlines color schemes including monochromatic, complementary, analogous, and split complementary. It discusses how hue, value, and saturation impact color perception and how tints, tones and shades are created. The document also addresses how lighting impacts color appearance and can be used to manipulate mood. Color and lighting are presented as important artistic elements that designers consider for their psychological and physical effects.