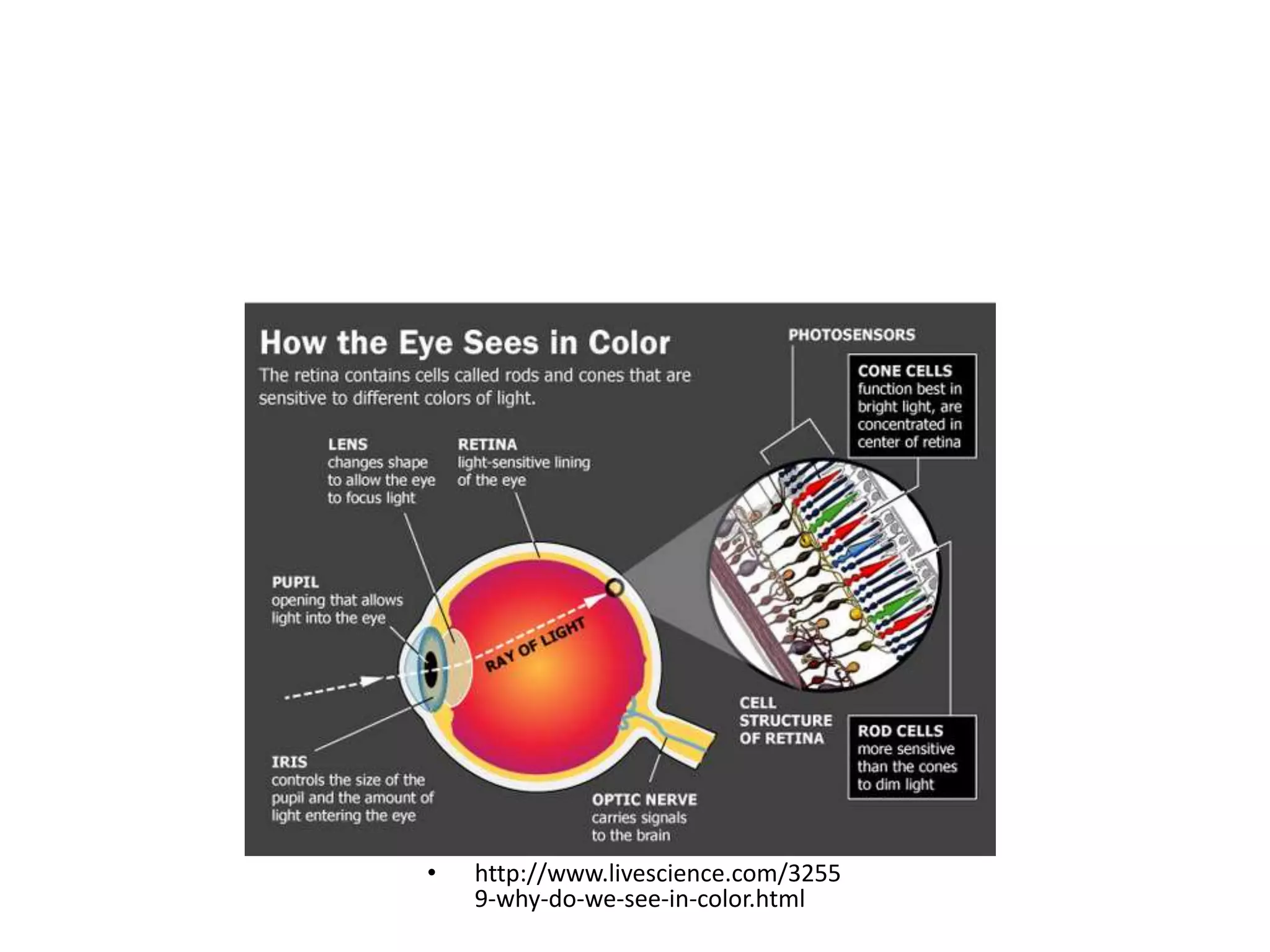
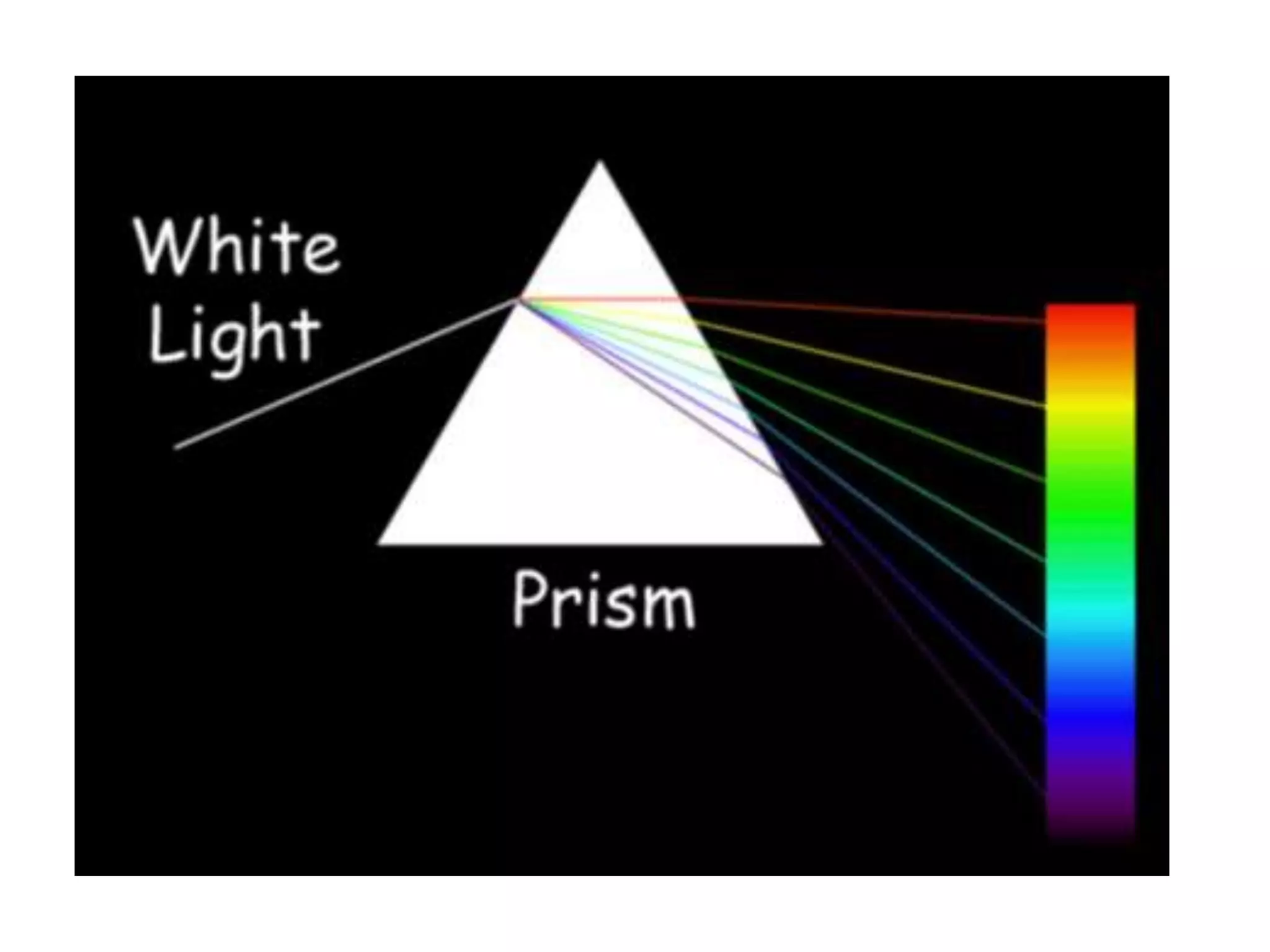
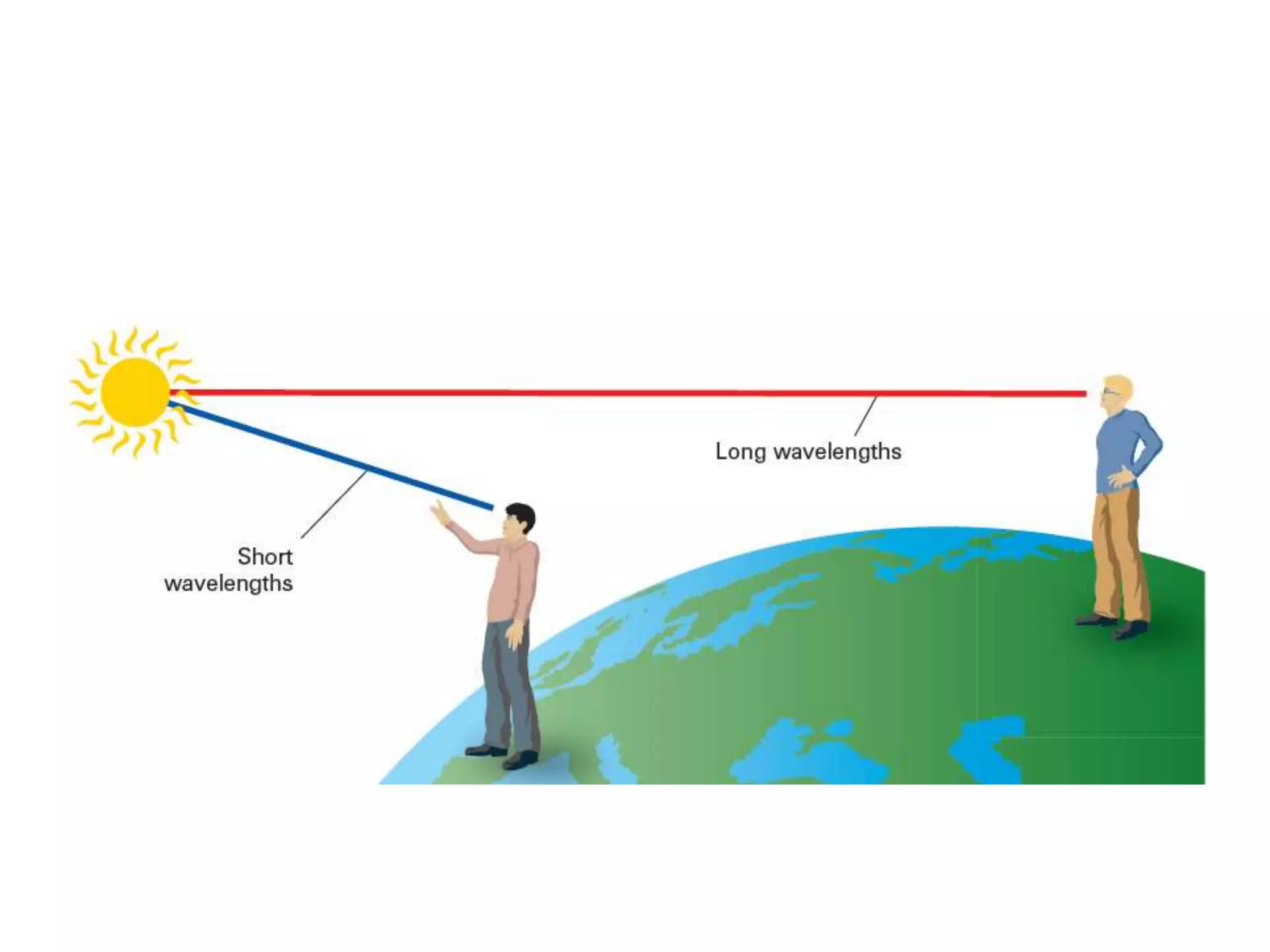
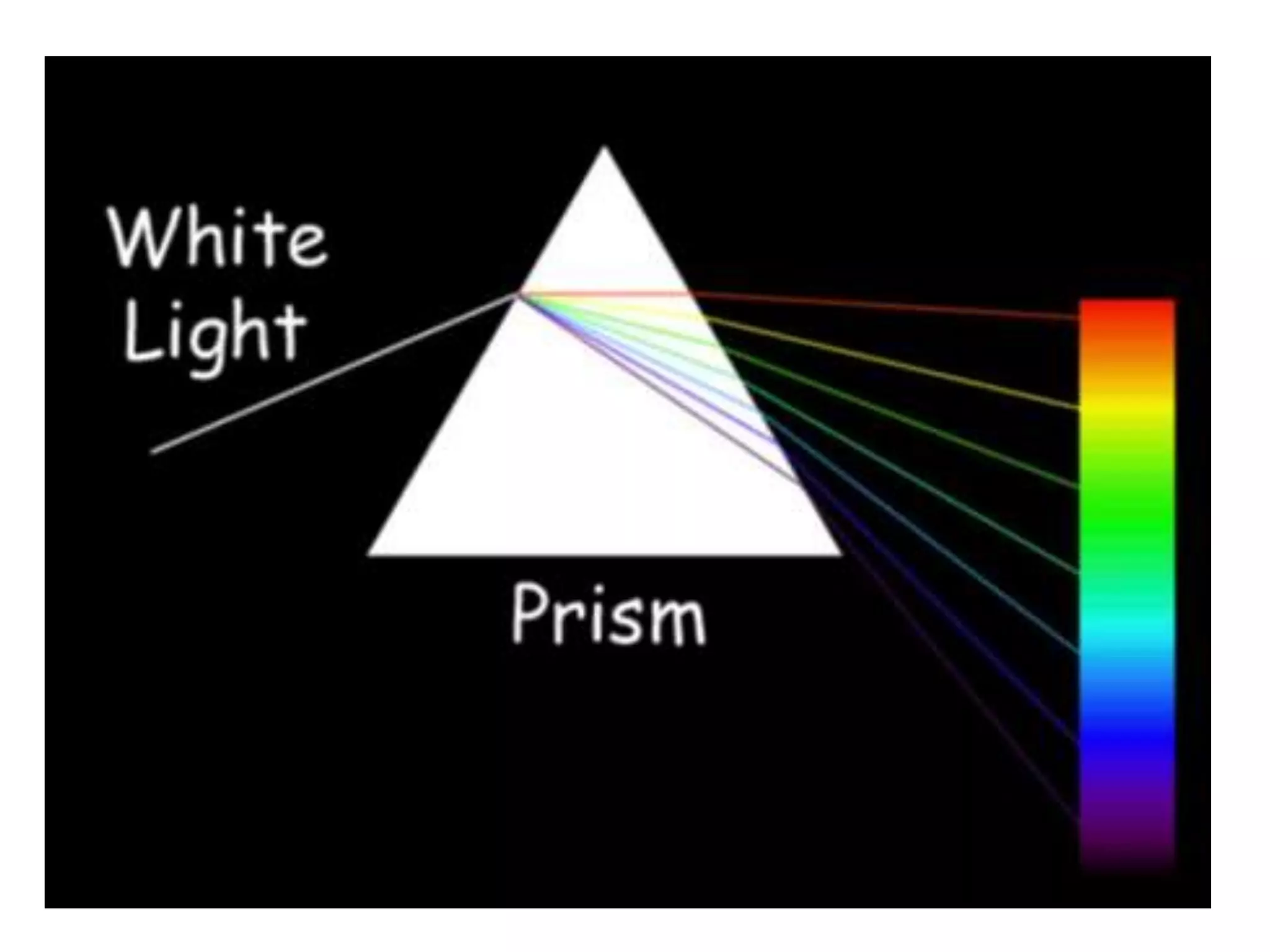
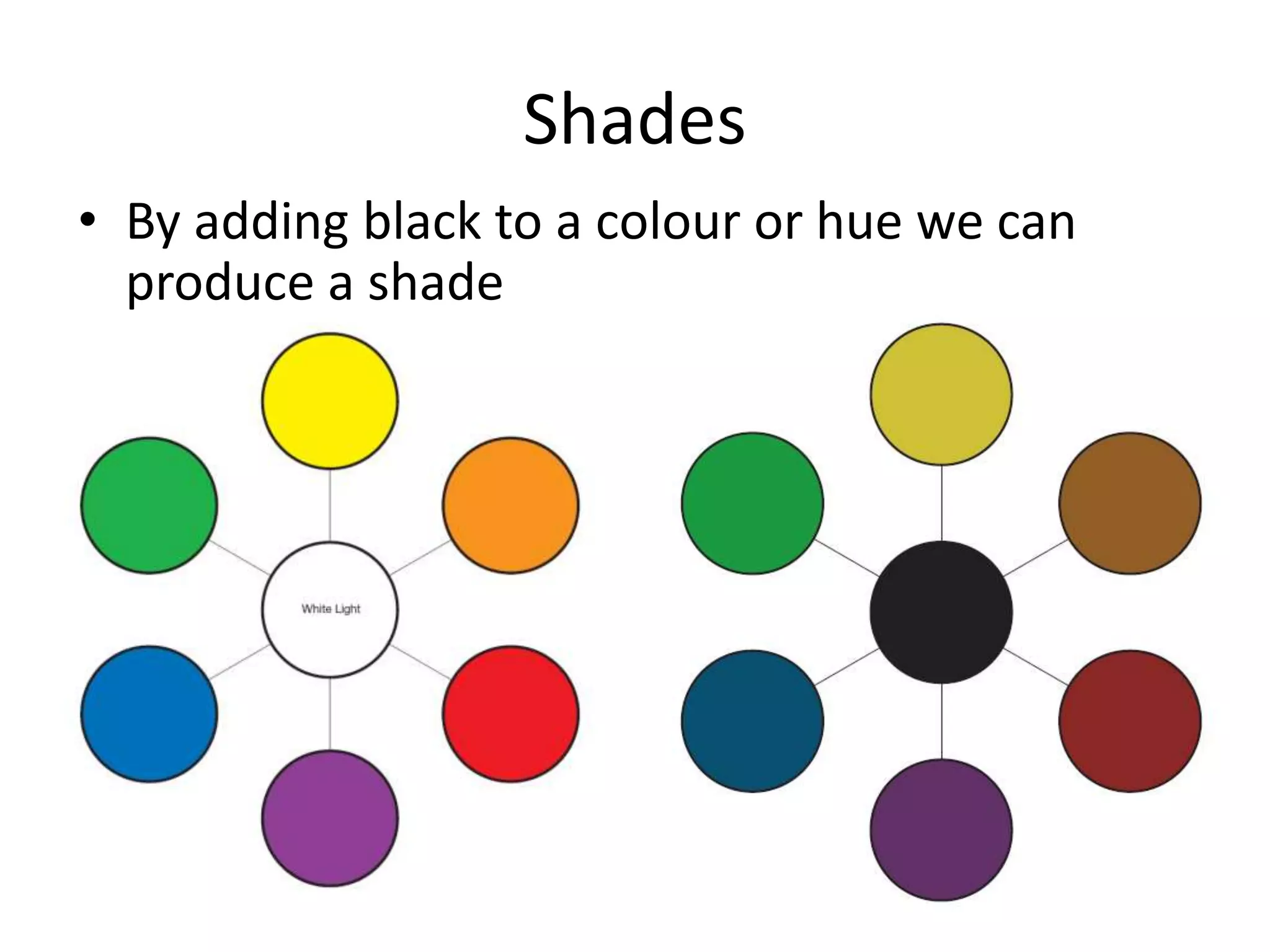
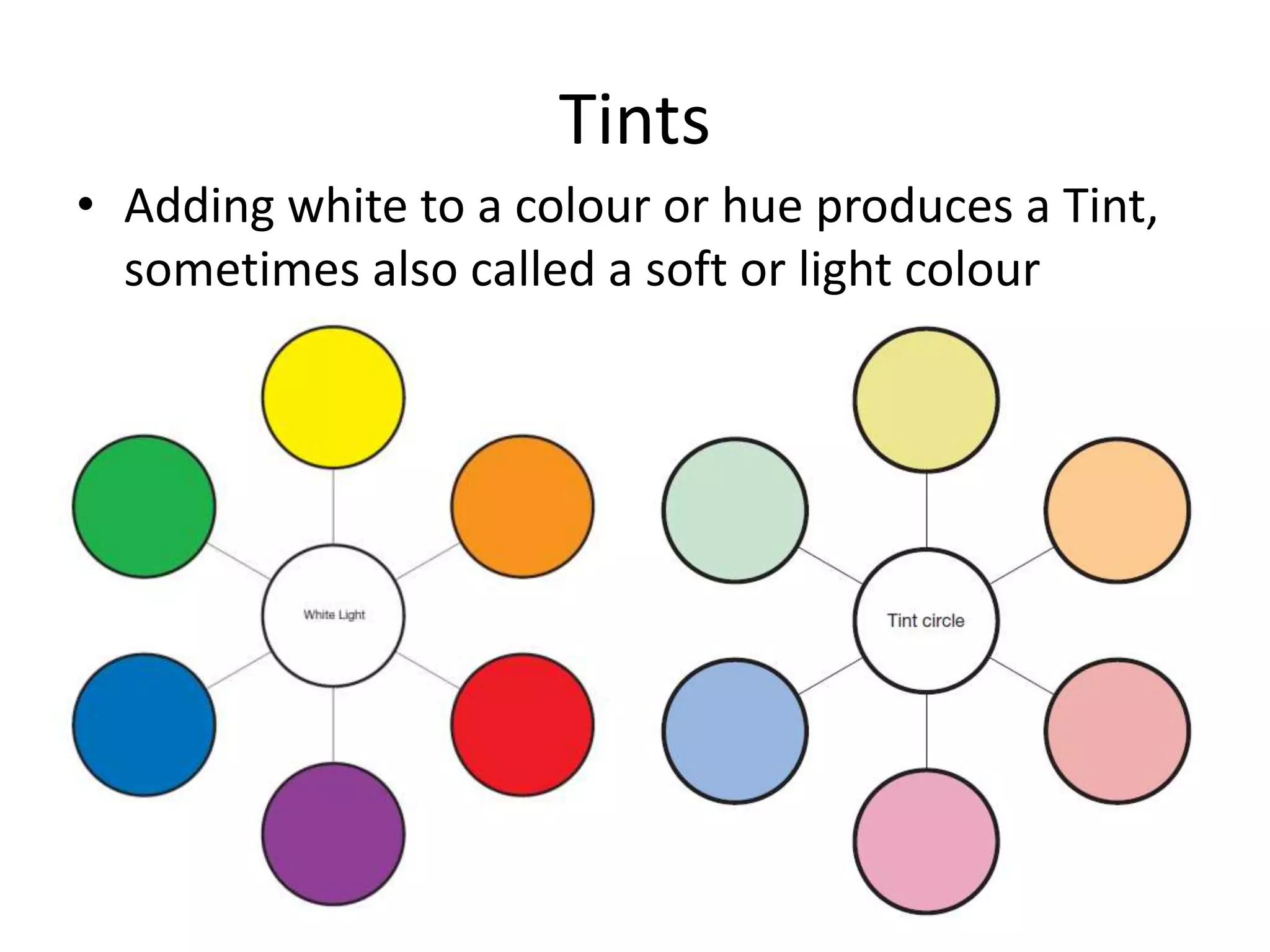
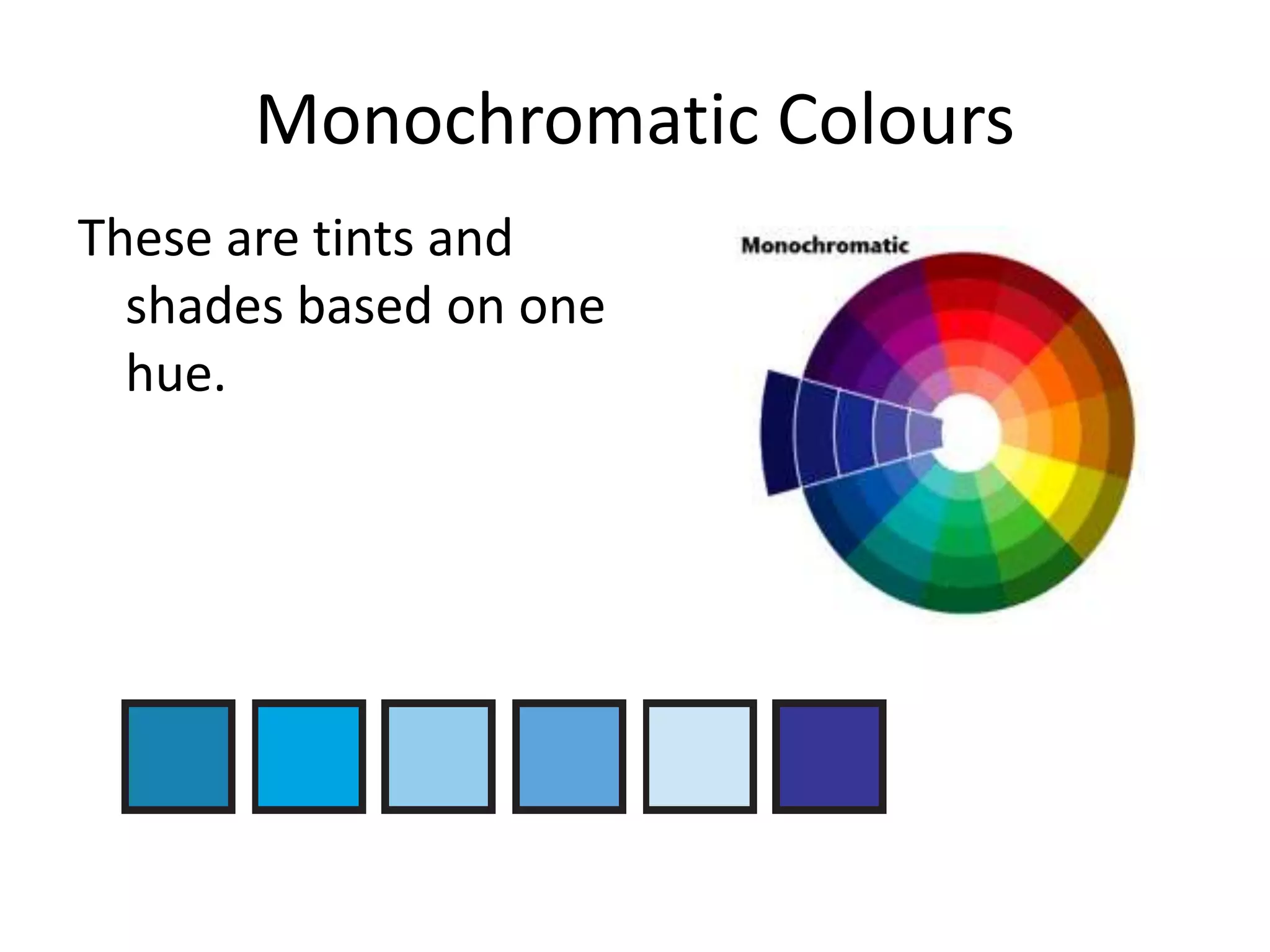
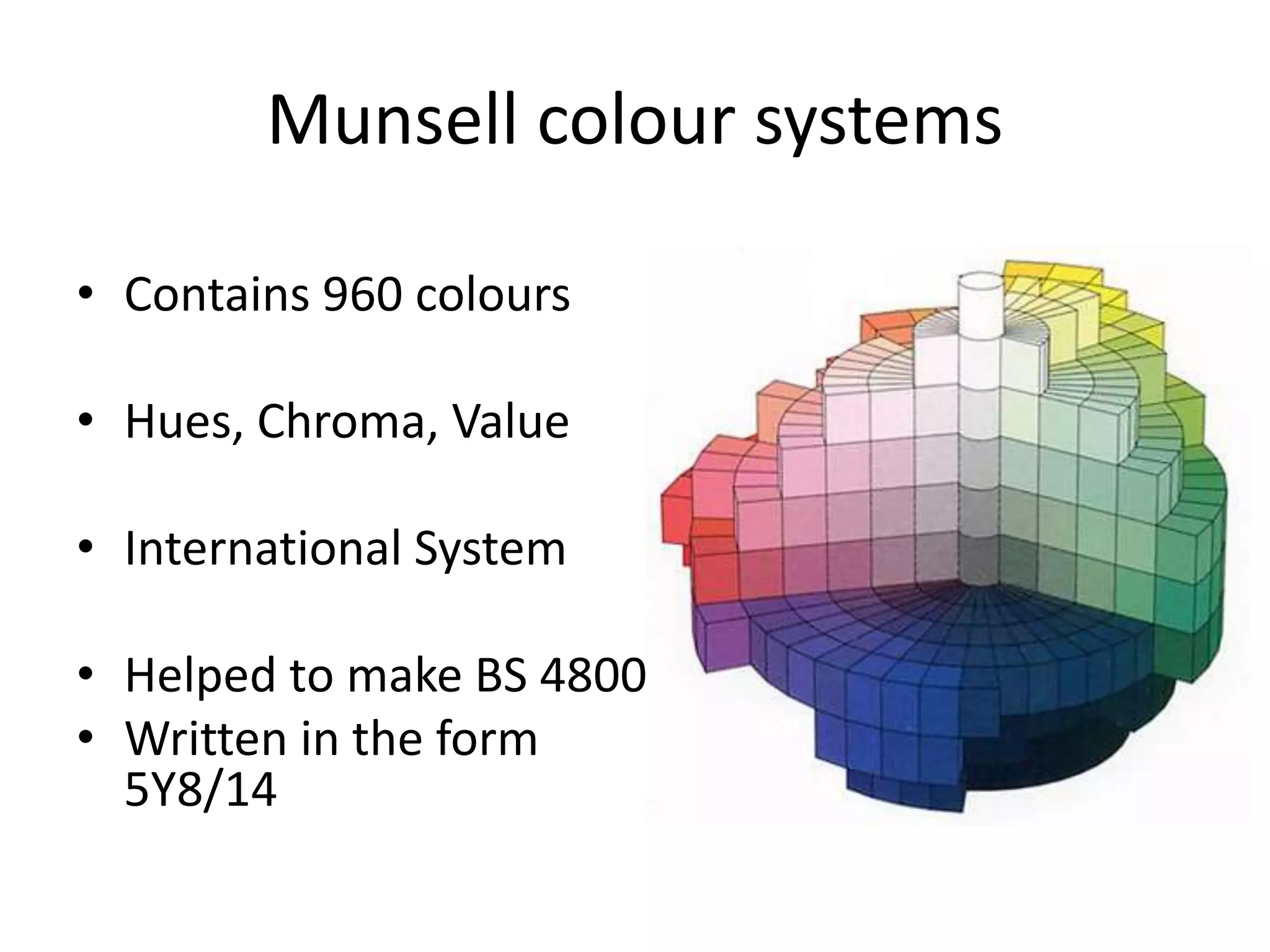
The document discusses colour and how it affects our perception of the world. It explains that colour is caused by light splitting into different wavelengths and frequencies. It also describes key colour concepts like primary colours, secondary colours, the colour wheel, complementary colours, and how factors like lighting can influence our experience of colour.