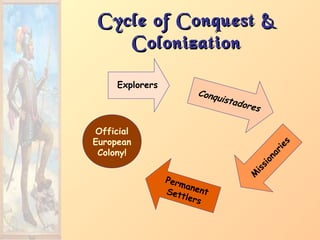
1. The document discusses early European exploration including Prince Henry of Portugal establishing a navigation school in 1419. This led to Portuguese exploration of Africa's coastline by the 15th century and their establishing the first global maritime empire.
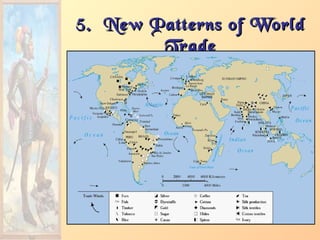
2. Motives for more exploration included seeking new trade routes to Asia following the Crusades, Renaissance curiosity, escaping religious conflicts, and finding new sources of revenue for monarchs. Technological advances like improved ships, navigation instruments, and weapons enabled further voyages.
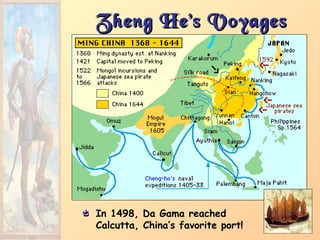
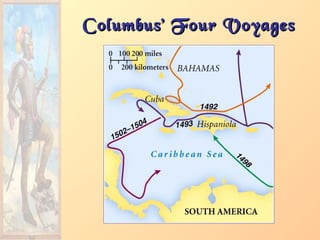
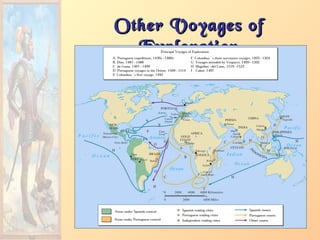
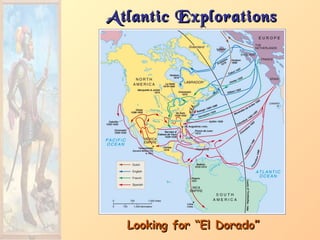
3. Major figures that furthered exploration included Columbus, whose four voyages opened up the Americas to colonization by European powers; Magellan, who completed the first circumnavigation of the world; and conquistadors




![New Maritime TechnologiesNew Maritime Technologies
Hartman Astrolabe
(1532)
Better Maps
[Portulan]
Sextant
Mariner’s Compass](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europeanexplorationandcolonization-161016021010/85/European-explorationandcolonization-6-320.jpg)




![Christofo ColonChristofo Colon [1451-[1451-
1506]1506]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europeanexplorationandcolonization-161016021010/85/European-explorationandcolonization-12-320.jpg)










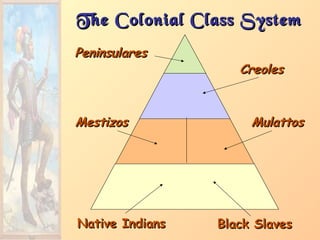





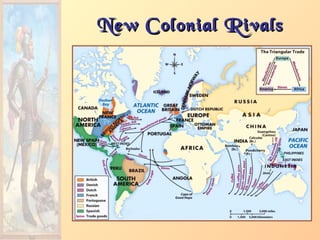
![Impact of EuropeanImpact of European
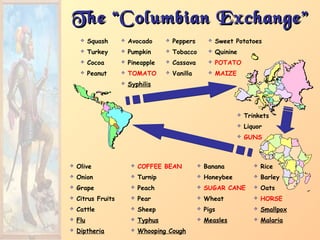
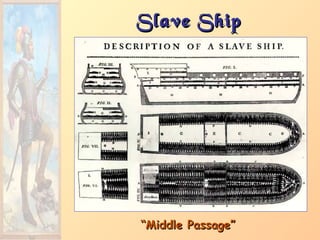
ExpansionExpansion1. Native populations ravaged by
disease.
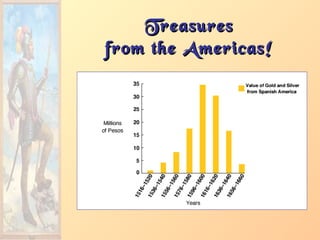
2. Influx of gold, and especially
silver, into Europe created an
inflationary economic climate.
[“Price Revolution”]
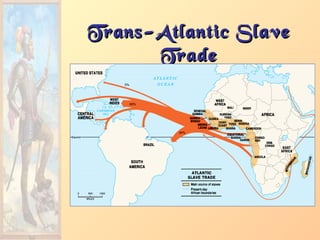
3. New products introduced across
the continents [“Columbian
Exchange”].
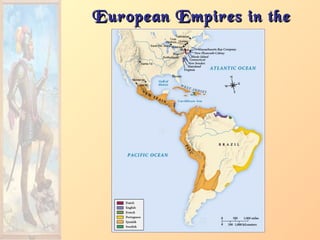
4. Deepened colonial rivalries.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/europeanexplorationandcolonization-161016021010/85/European-explorationandcolonization-39-320.jpg)