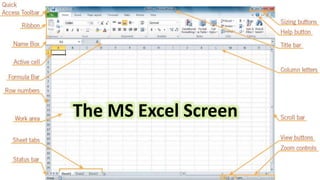
This document provides an overview of the key features and functions of the Microsoft Excel program. It describes the basic components of an Excel workbook including worksheets, cells, columns, rows, and cell references. It explains how to start and quit Excel and gives details on the Excel screen layout and the worksheet. It also outlines the different types of cell entries one can make, including values, labels, formulas using operators, and built-in functions.