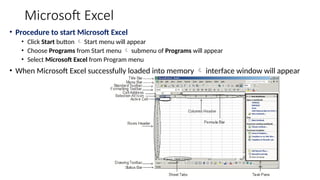
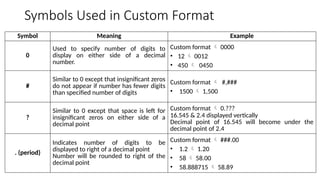
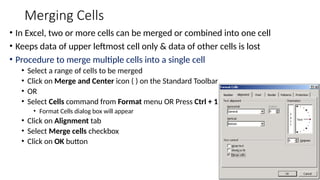
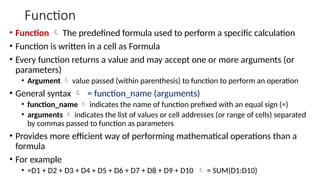
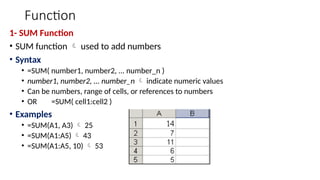
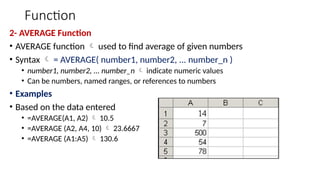
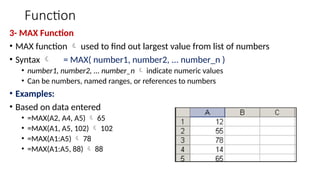
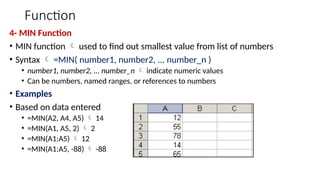
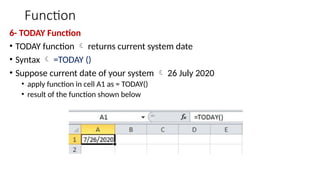
The document provides a comprehensive overview of spreadsheet software, particularly focusing on Microsoft Excel. It covers essential features like basic functions, data entry, cell formatting, and the structure of worksheets and workbooks. Additionally, it explains advanced functionalities such as formulas, cell referencing, and data manipulation techniques.