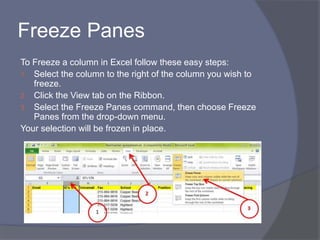
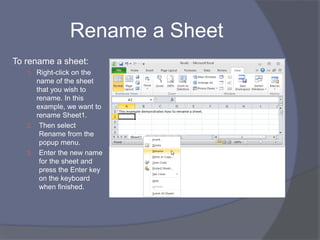
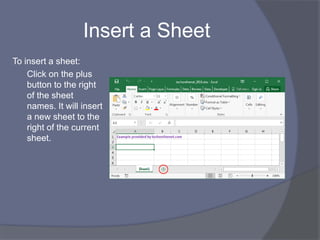
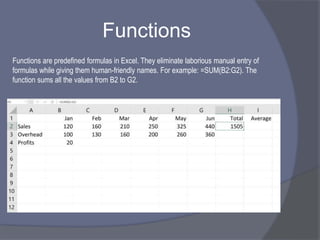
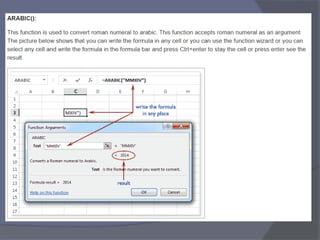
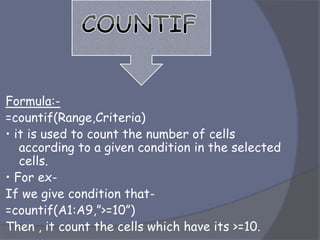
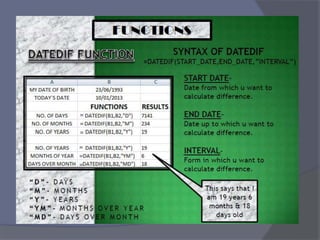
This document provides an overview of Microsoft Excel. It discusses that Excel is a spreadsheet application used to organize data into tables and perform calculations. Key points covered include:
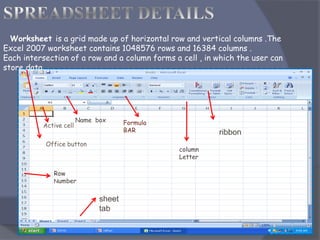
- Excel uses a grid of rows and columns to display data in worksheets.
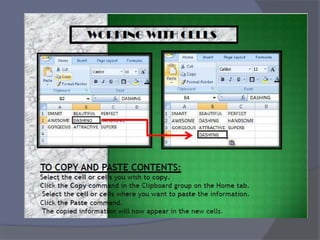
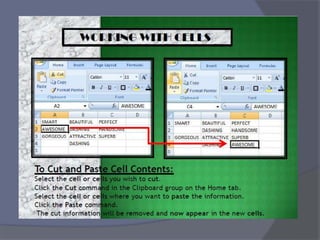
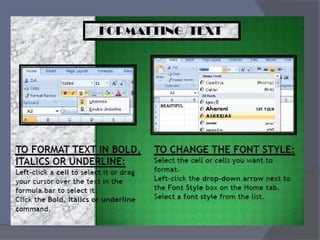
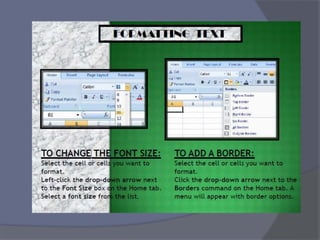
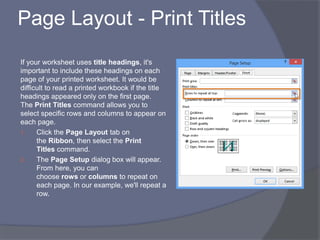
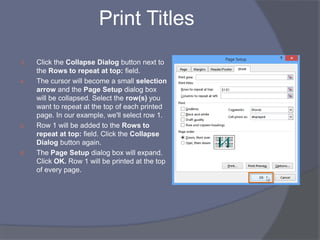
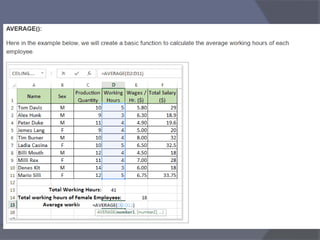
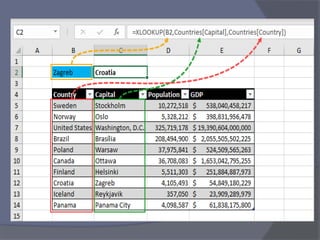
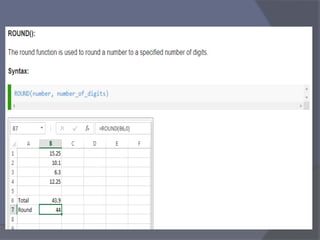
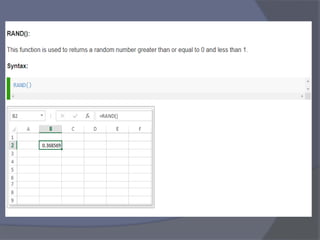
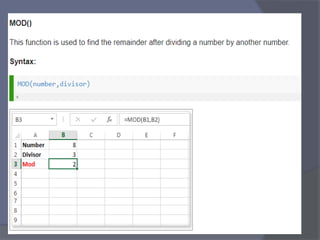
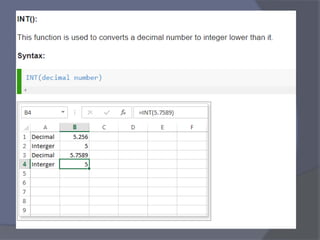
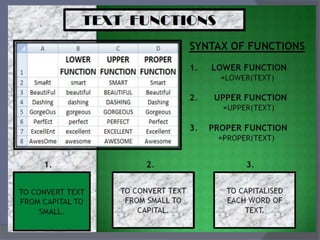
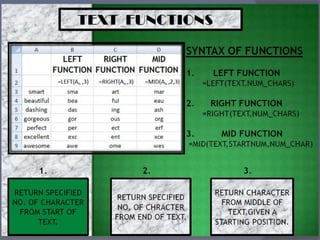
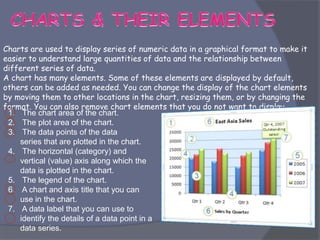
- Common tasks in Excel include entering data, formatting cells, adjusting worksheet layout, printing, using formulas and functions, and creating charts and pivot tables.
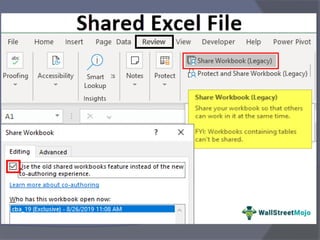
- Advanced features include conditional formatting, comments, grouping worksheets, and sharing workbooks with other users.