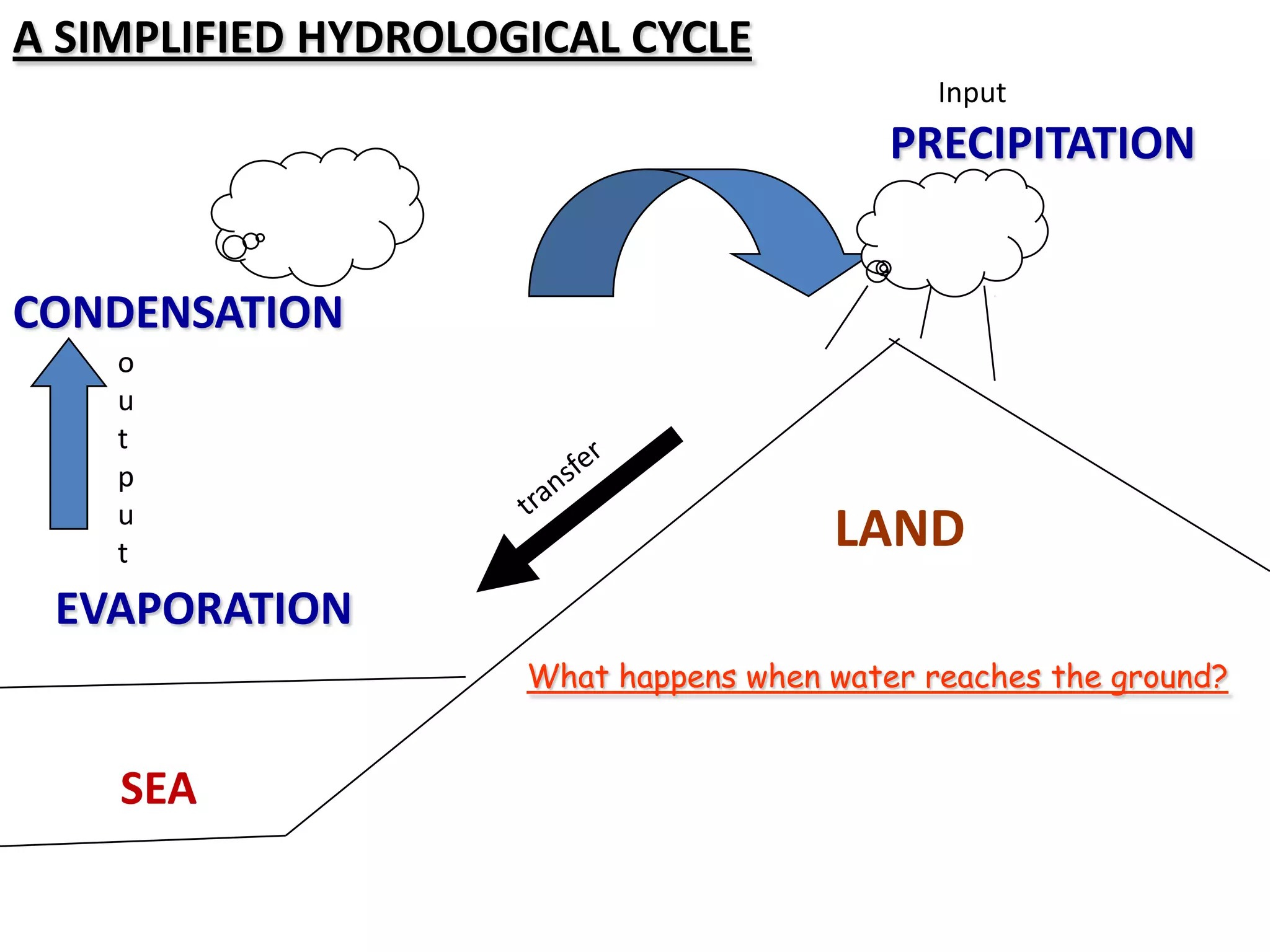
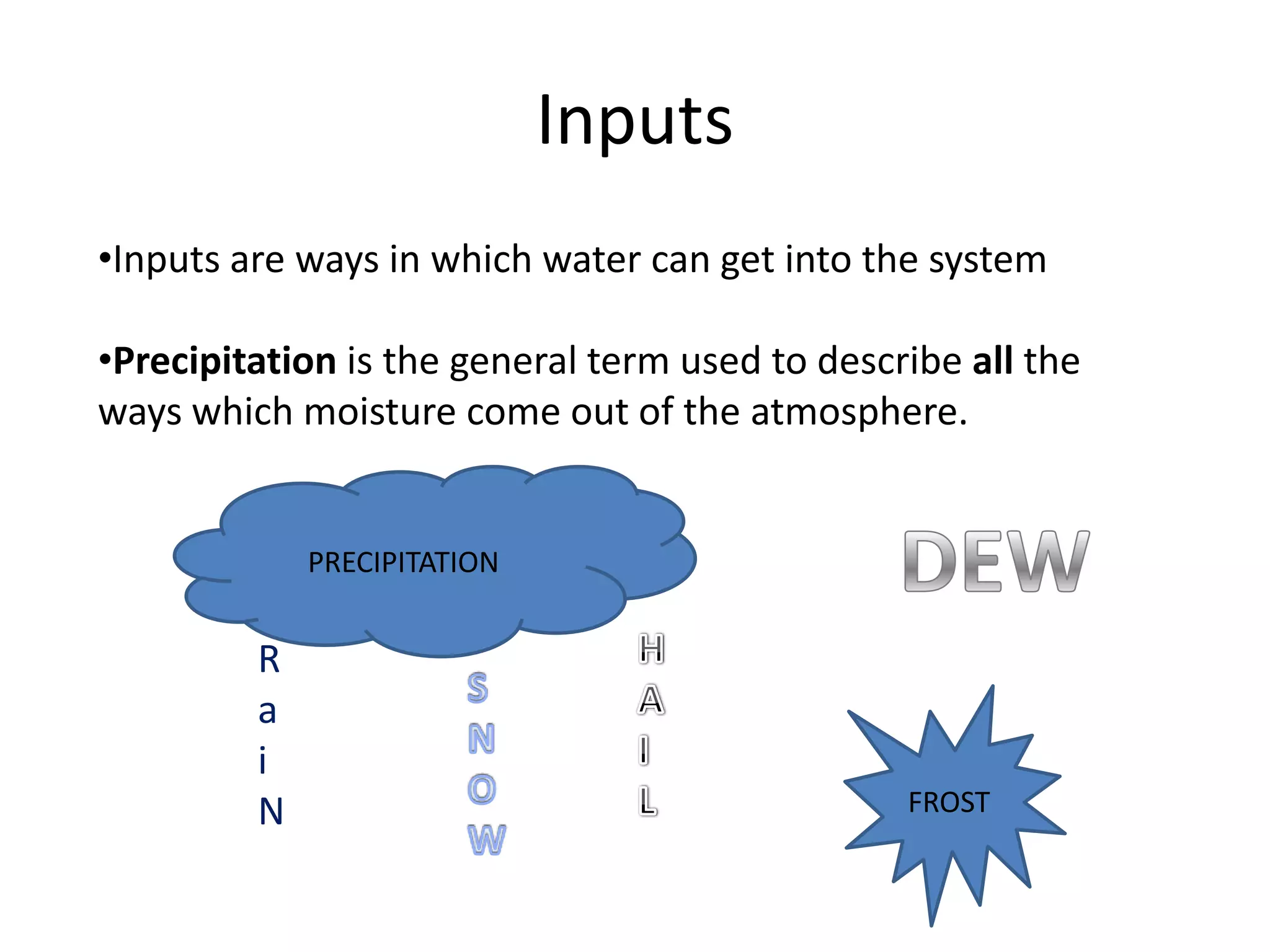
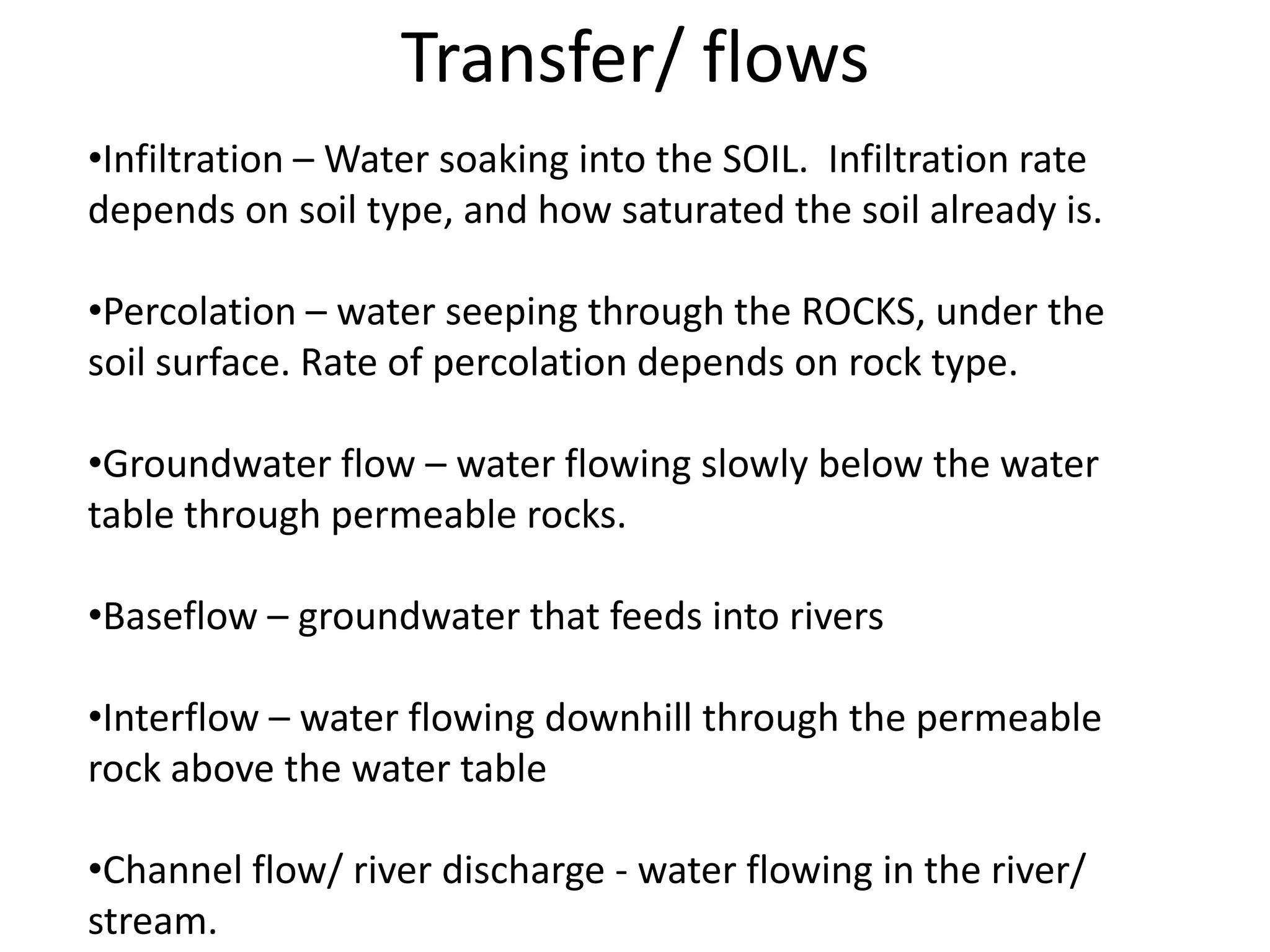
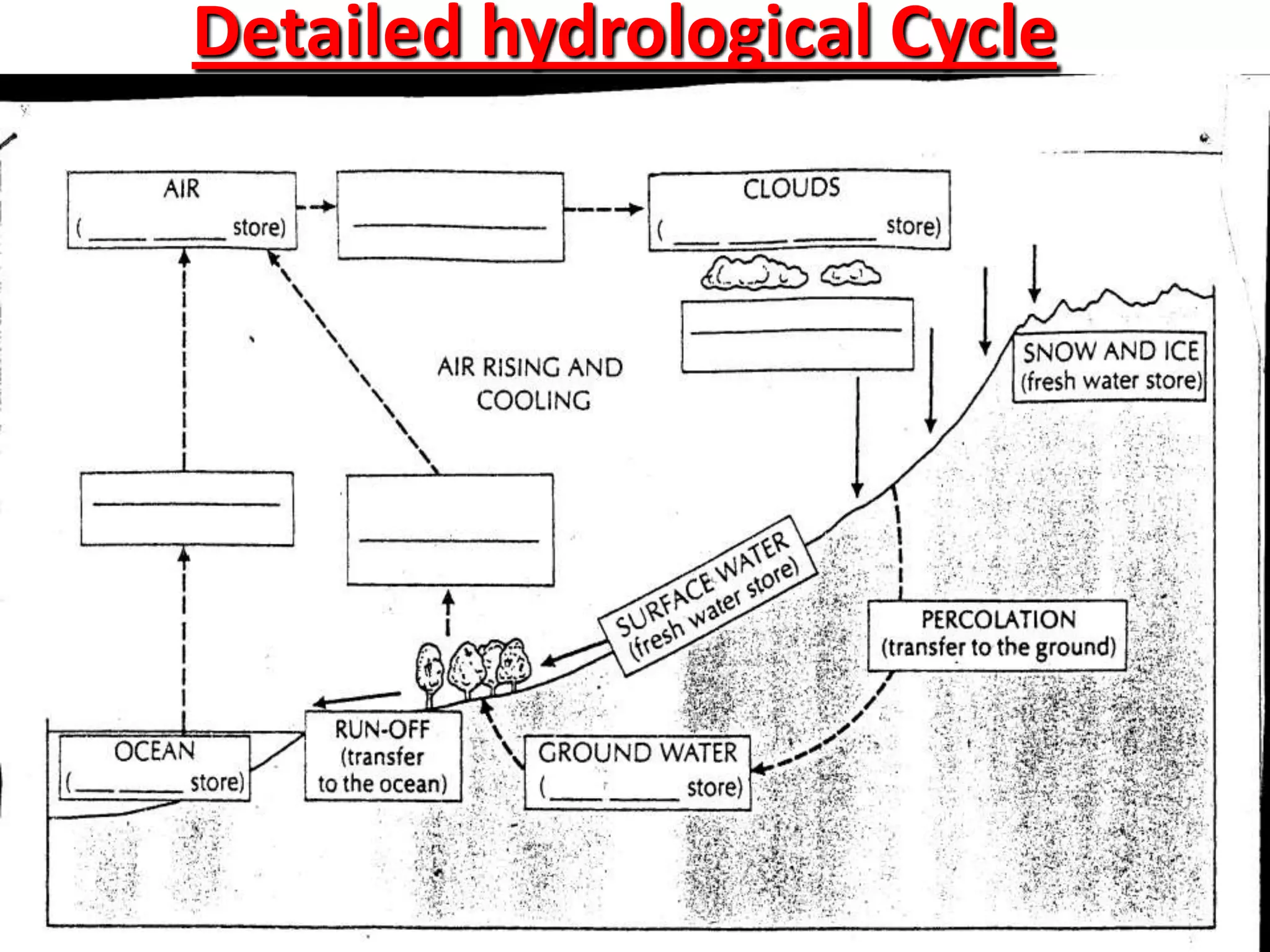
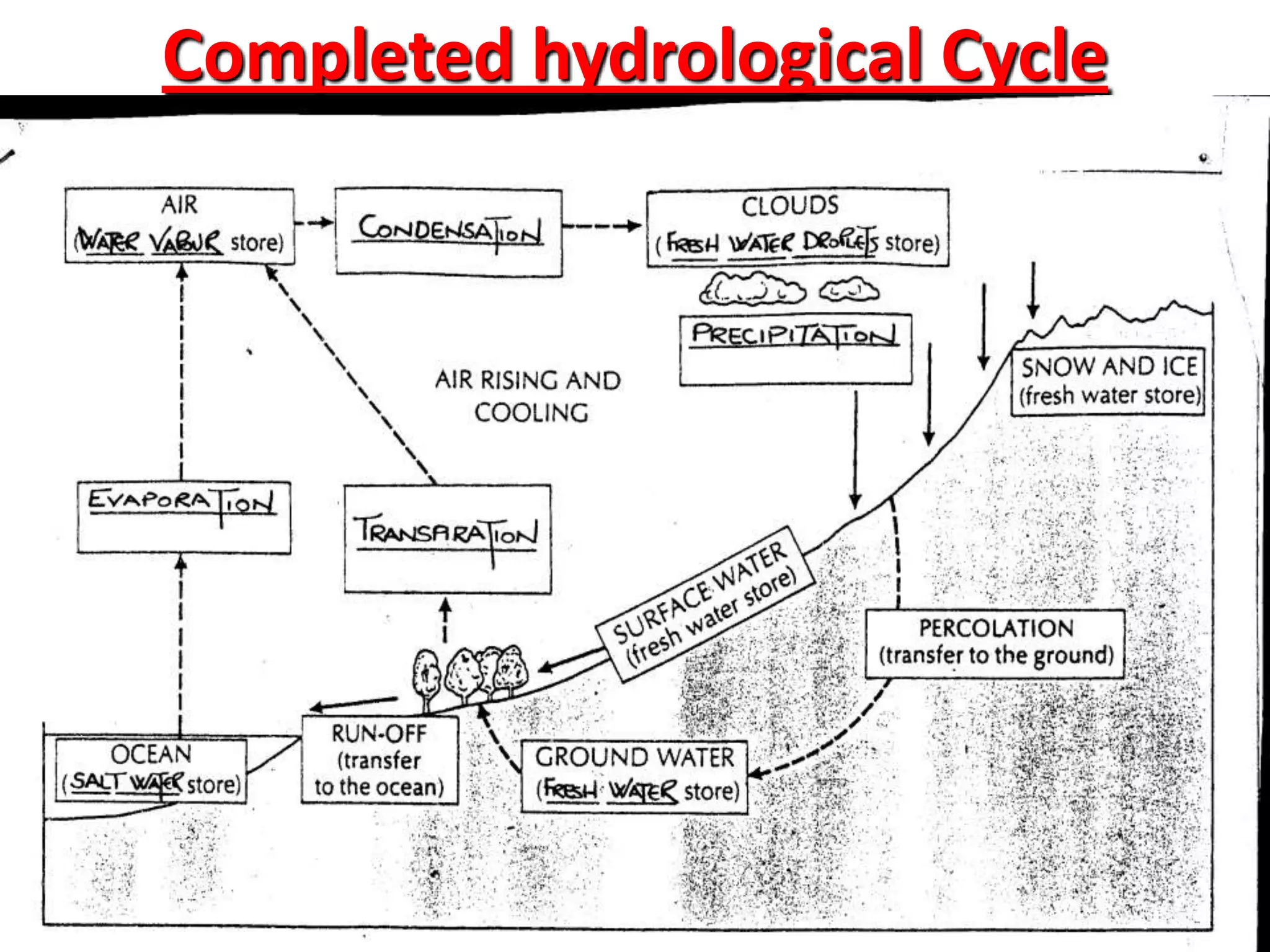
The document provides information about the hydrological cycle including key definitions and processes. It explains that precipitation is an input into the cycle, while evaporation and transpiration are outputs. It also describes several transfer processes by which water moves through the cycle, such as surface runoff, infiltration, percolation, groundwater flow, and river discharge.