This document discusses hydrology and fluvial geomorphology concepts including:
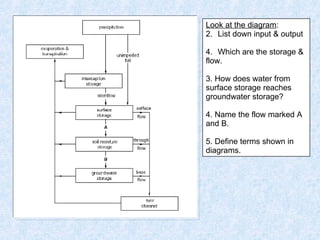
- The water balance and how water moves through drainage basins, including surface storage and groundwater storage.
- How rainfall and basin characteristics influence storm hydrographs and river discharge.
- The different types of water flow through soil and bedrock, including percolation.
- River processes of erosion, transportation, and deposition as well as landforms created by these processes.
- How human activities can impact river flows through changes in land use, water abstraction and storage, and urbanization.





![River erosion 1. Briefly describe the processes by which rivers can erode their channels. [8] 2. Describe the general effects of erosion on the shape of the river channel. [3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrology-fluvial-geomorphology-1227065728305158-9/85/Hydrology-Fluvial-Geomorphology-7-320.jpg)

![Hjustrom curve. 1. Name the type of sediment that requires the lowest velocity to be eroded . [1] 2. Name the type of sediment that is likely to be transported at all velocities. [1] 3. Describe and explain the relationship between water velocity and the erosion of clay and sand particles. [4] 4. Explain the variation in water velocity that is required to transport and to deposit sediments of different particle diameter. [4]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hydrology-fluvial-geomorphology-1227065728305158-9/85/Hydrology-Fluvial-Geomorphology-9-320.jpg)



