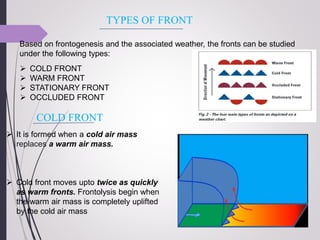
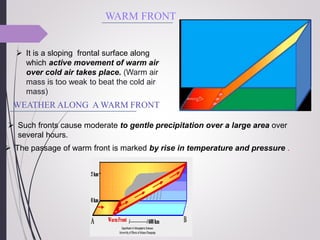
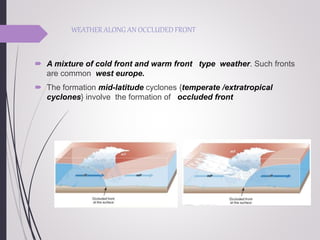
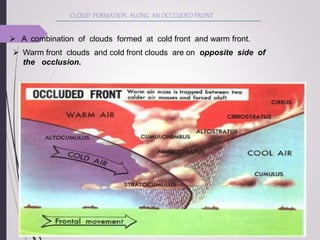
This document discusses different types of air fronts that form due to the interaction between converging air masses with different properties. It describes four main types of fronts: cold fronts, where cold air replaces warm air; warm fronts, where warm air overrides cold air; stationary fronts, where neither air mass advances; and occluded fronts, where cold air overtakes warm air. For each front, it outlines the associated weather patterns and cloud formations.


![“AIR FRONT”
Front means Facing something / interaction between two things.
So air front is basically interaction between two opposite air masses .
Front is a three dimensional boundary zone between two converging air
masses with different physical properties [Temperature, humidity , density
etc]
when the 2 air masses meet ,due to the effect of the converging
atmospheric circulation, they do not merge readily.
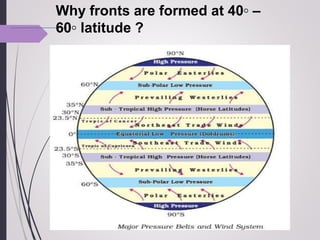
Fronts are features of mid- latitude region [ temperate region i.e. 400 – 650 N
and S ].
They are unusual in tropical and polar regions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frontspptbymadhusmitasahooutkaluniversity-230427183811-fe325a44/85/Fronts-pptx-3-320.jpg)