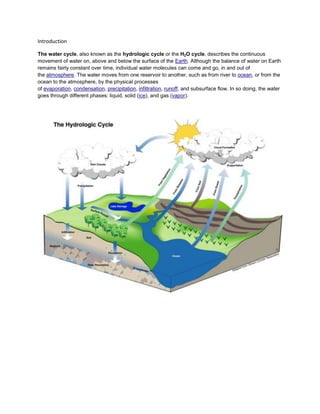
The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the Earth's surface through various physical processes. Water evaporates from oceans, lakes, and vegetation into the atmosphere. It condenses to form clouds and precipitates as rain or snow. Precipitation may fall directly into water bodies, be intercepted by plants, infiltrate soils, or become surface runoff into streams, contributing to the total streamflow or base flow. Water is stored temporarily in the atmosphere, oceans, lakes, soils, aquifers and glaciers before repeating the cycle.