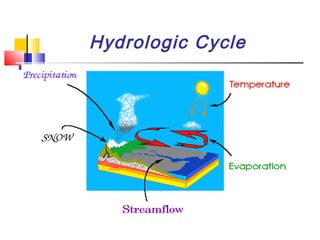
The document explains the hydrologic cycle, also known as the water cycle, highlighting various processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage of water. It emphasizes the movement of water across different phases and environments as well as the potential consequences of uneven distribution, which can lead to floods and droughts. Additionally, it presents the primary storage locations for water in the atmosphere, on the Earth's surface, and underground.