1. Early primates evolved adaptations like opposable thumbs and binocular vision to thrive in trees. They divided into prosimians and anthropoids, with the latter including monkeys, apes and humans.
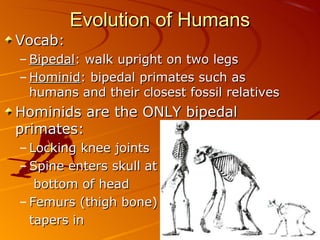
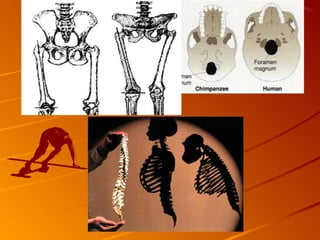
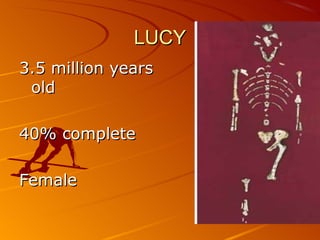
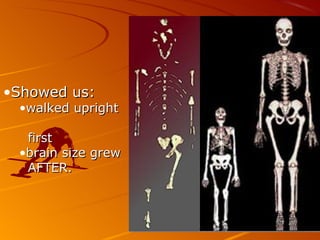
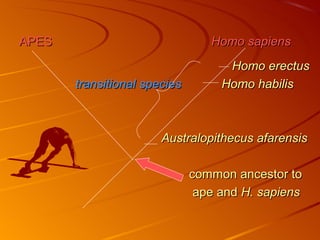
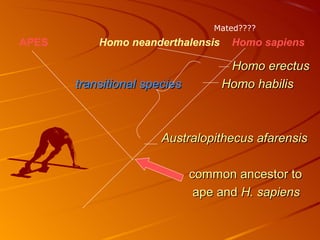
2. The hominid Australopithecus afarensis, including the famous fossil "Lucy", showed evidence of walking upright 3.5 million years ago, even though its brain was chimp-sized.
3. Several hominid species evolved after A. afarensis, with Homo habilis having larger brains and making tools, and Homo erectus spreading across Africa, Asia and Europe around 1.5 million years ago.