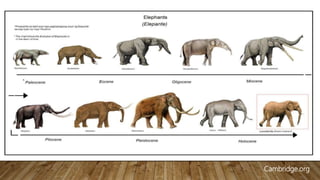
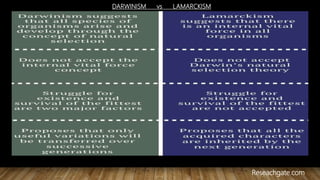
The document summarizes hominid evolution and human origins. It outlines the major theories of human evolution such as Lamarckism, Darwinism, and the modern synthesis. The timeline of human evolution is also presented, beginning around 7 million years ago and progressing through key stages such as Homo erectus and Homo sapiens. Unique characteristics of modern humans like bipedalism and tool use are also discussed.