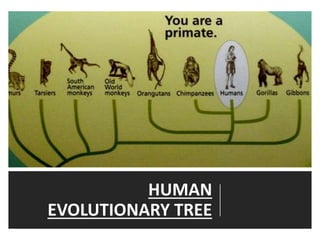
1. Several hominin species evolved in Africa over millions of years, including Australopithecus afarensis, Homo habilis, and Homo erectus.
2. Homo erectus was the first hominin to migrate out of Africa, spreading across Asia and Europe between 1.8 million to 100,000 years ago.
3. Neanderthals evolved in Europe and western Asia between 250,000-30,000 years ago before going extinct, while modern humans emerged in Africa around 200,000 years ago.