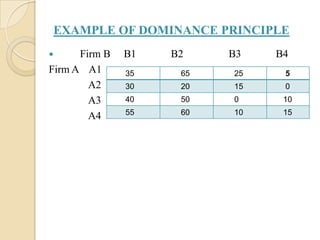
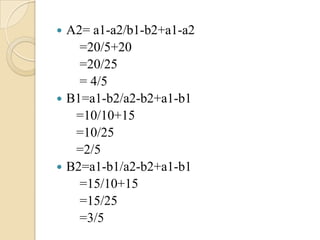The document discusses the dominance method for solving pure and mixed strategy problems in game theory. It explains that the dominance method eliminates inferior strategies by comparing the payoffs between two strategies - if one strategy always has equal or higher payoffs, it dominates and the inferior strategy can be removed. The example shows applying this method by comparing rows and columns to simplify a game down to a 2x2 matrix, then using the odds method formula to find the value of the game and optimal strategies.