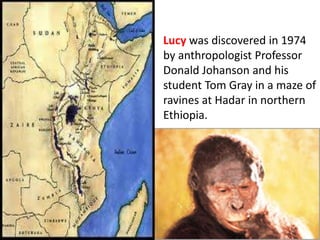
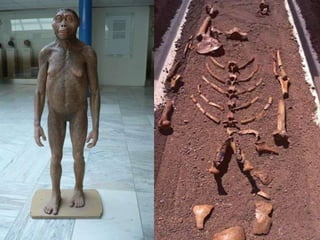
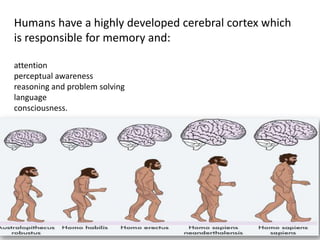
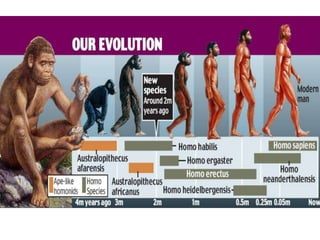
1) Lucy, discovered in 1974 in Ethiopia, was an early human species known as Australopithecus afarensis that lived 3.2 million years ago.
2) Though Lucy had characteristics similar to chimpanzees like a small brain and long arms, analysis of her knee and pelvis showed she routinely walked upright, placing her firmly in the human family.
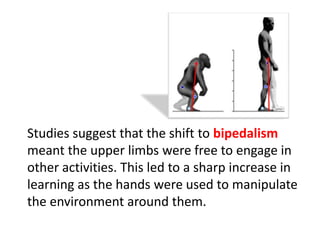
3) Darwin's theory of evolution proposed that humans evolved from earlier species and are simply another form of animal, descended possibly from apes. The development of bipedalism in early humans allowed the hands to be used for other activities like using tools.