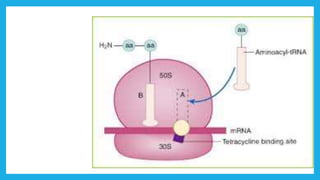
- Tetracyclines are a class of broad spectrum antibiotic drugs derived from bacteria. They work by binding to the bacterial ribosome to inhibit protein synthesis and show bacteriostatic activity.
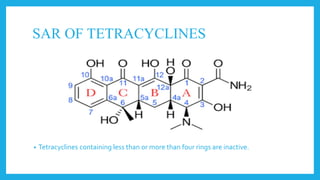
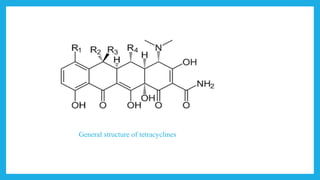
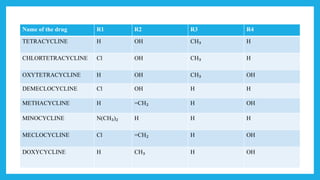
- Structurally, they contain four cyclic rings. Modifications to the structure can impact their activity. They are classified based on their duration of action as long, intermediate, or short acting.
- Common examples include tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline. They are used to treat various bacterial infections but have side effects like nausea, vomiting, and tooth staining when taken.