Embed presentation

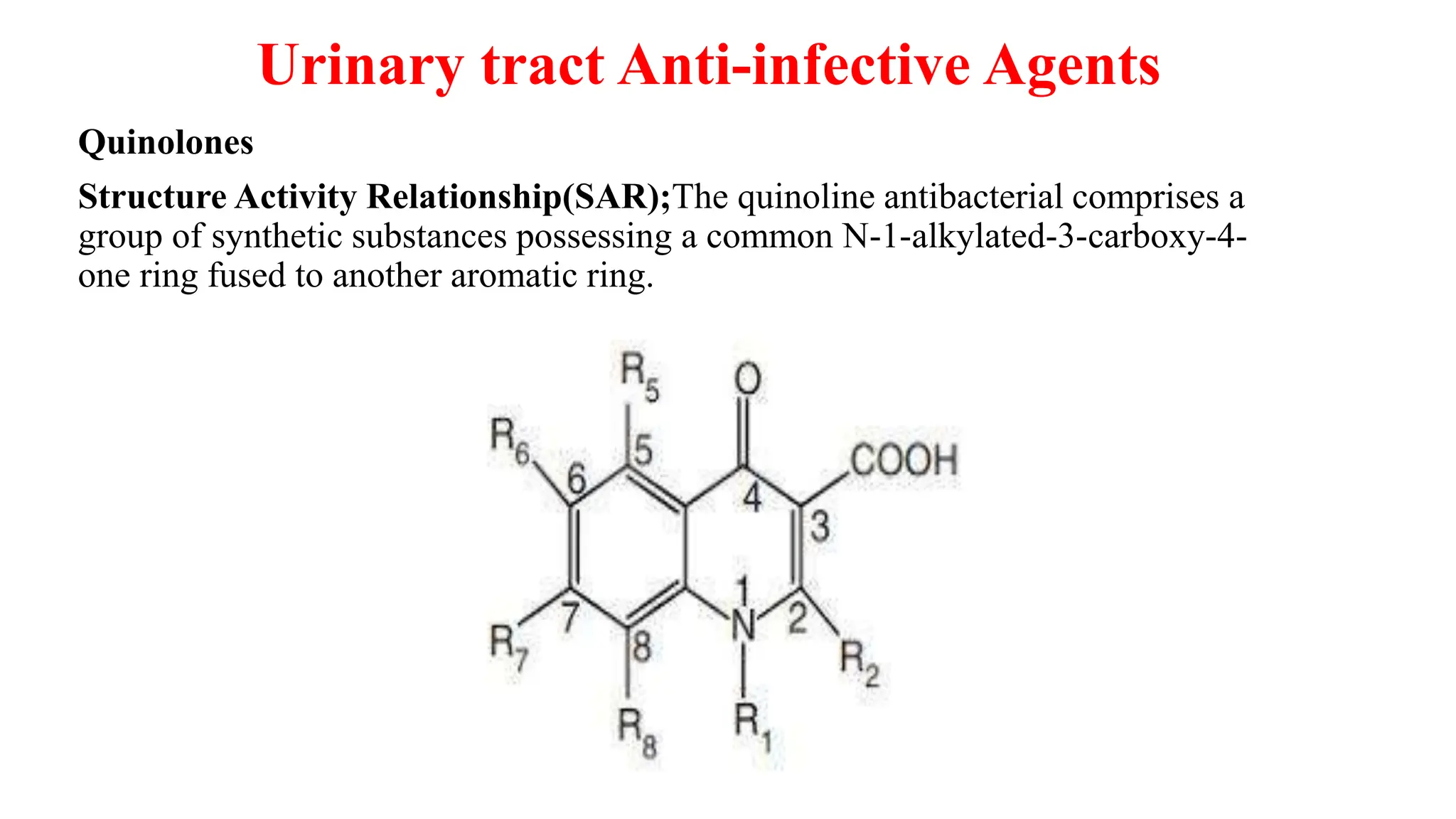

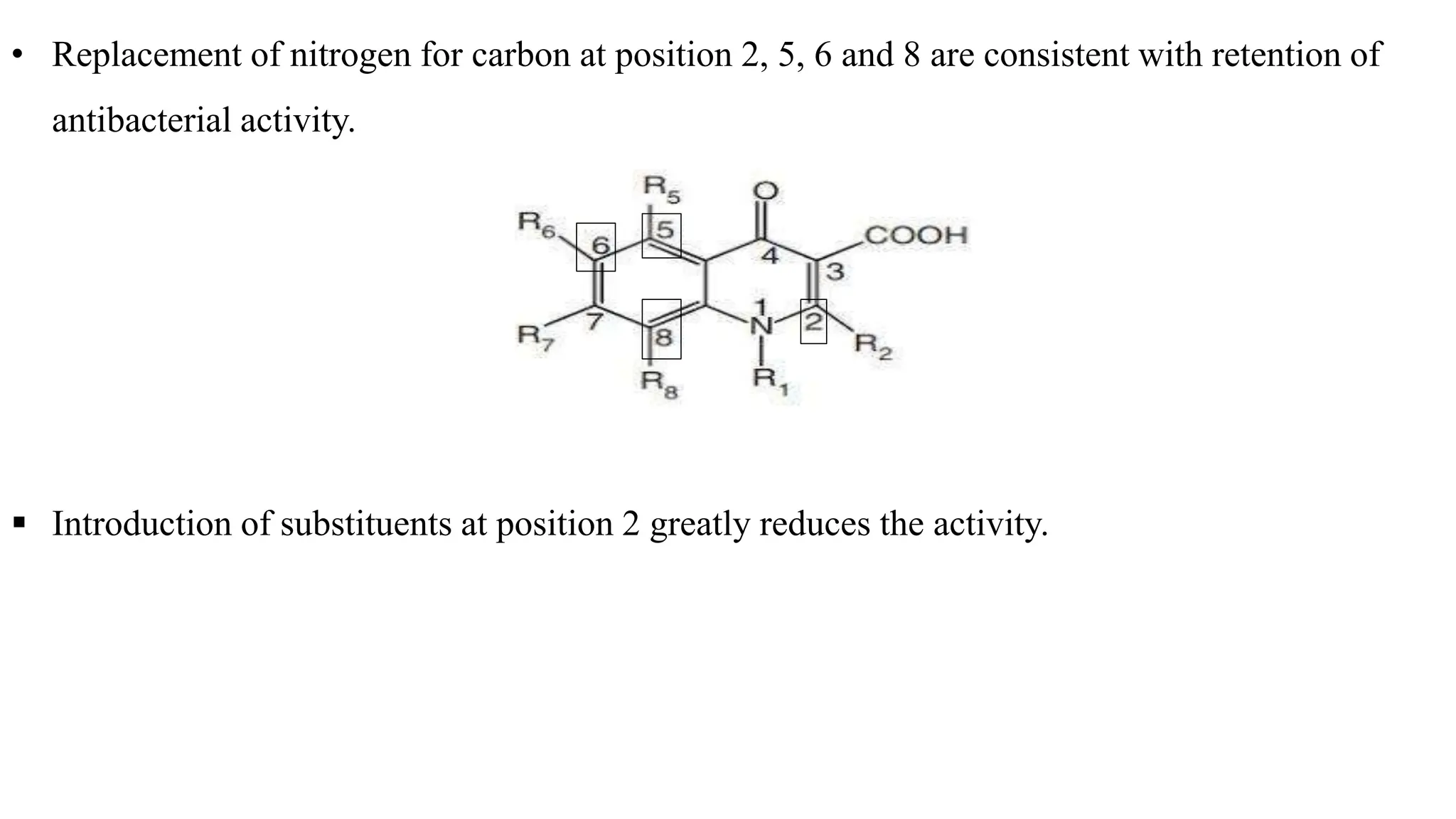
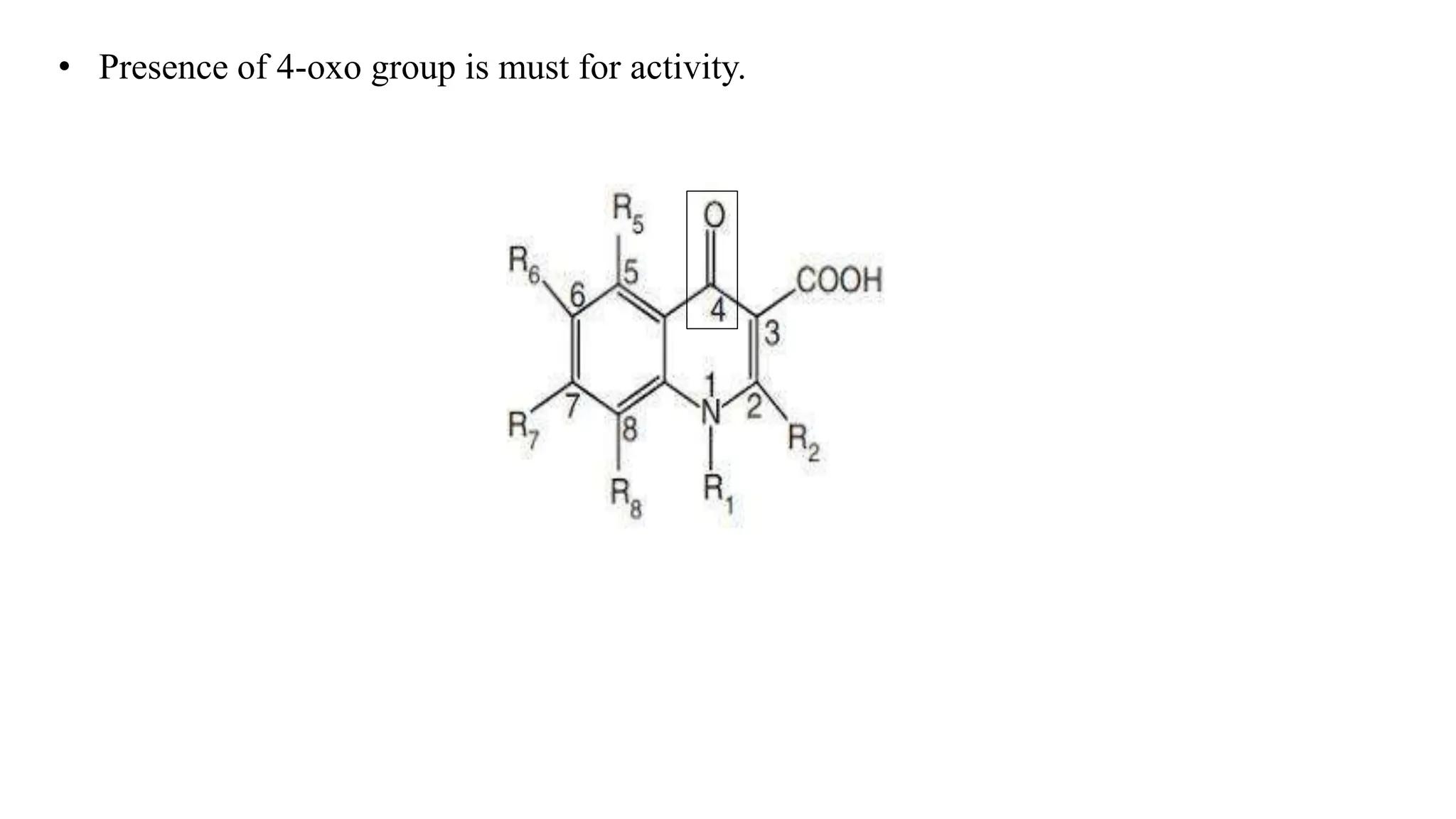
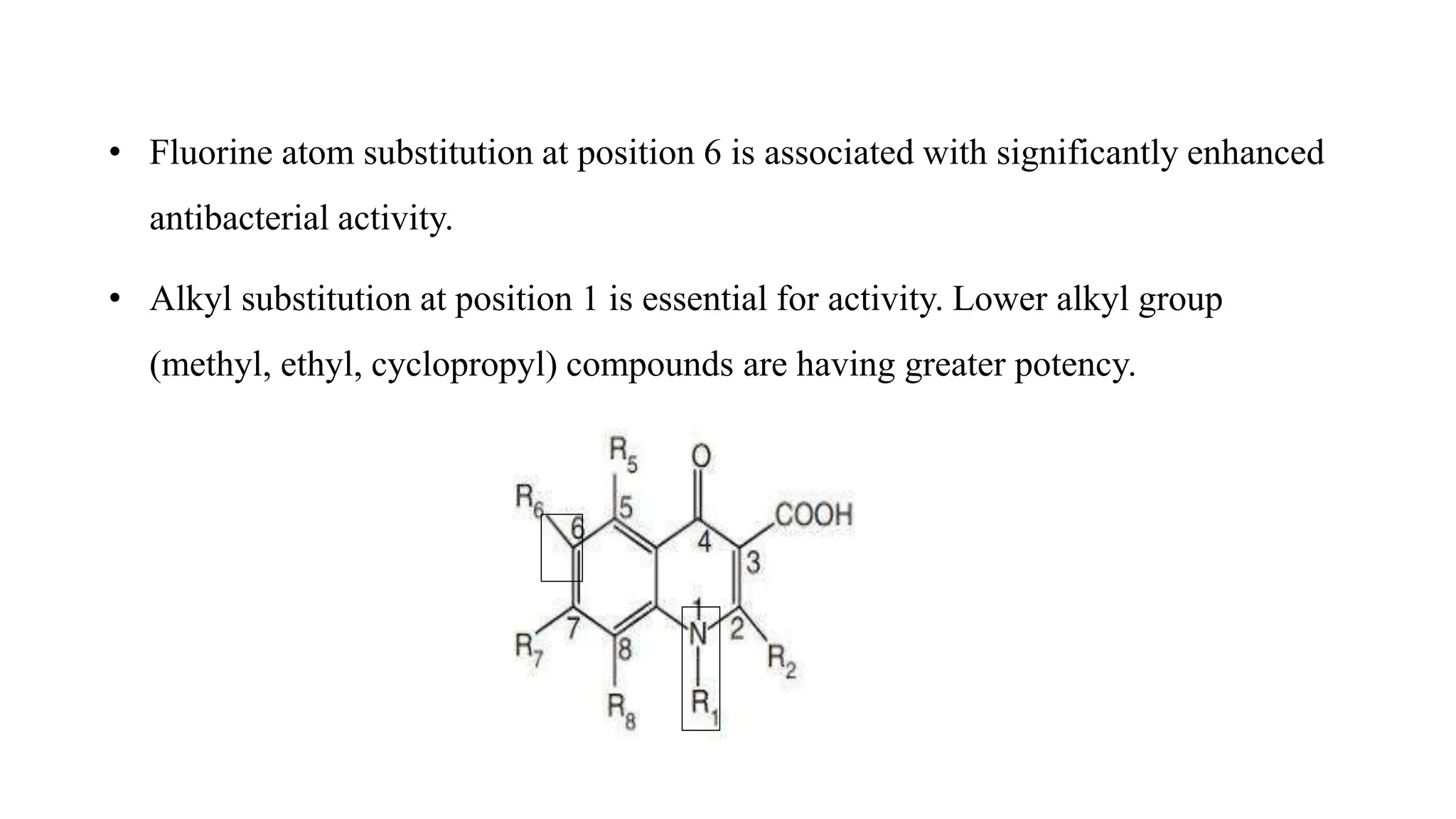
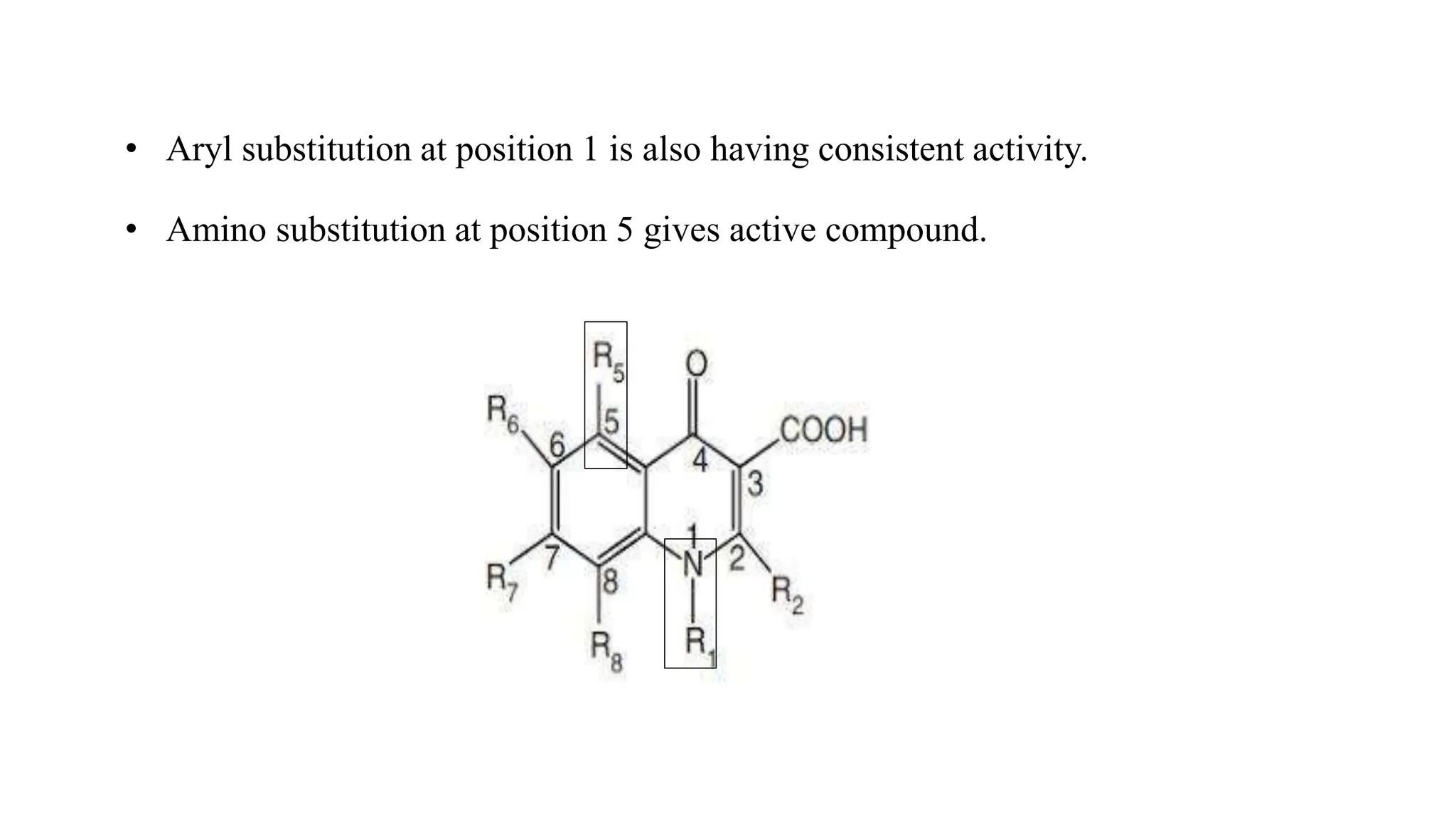
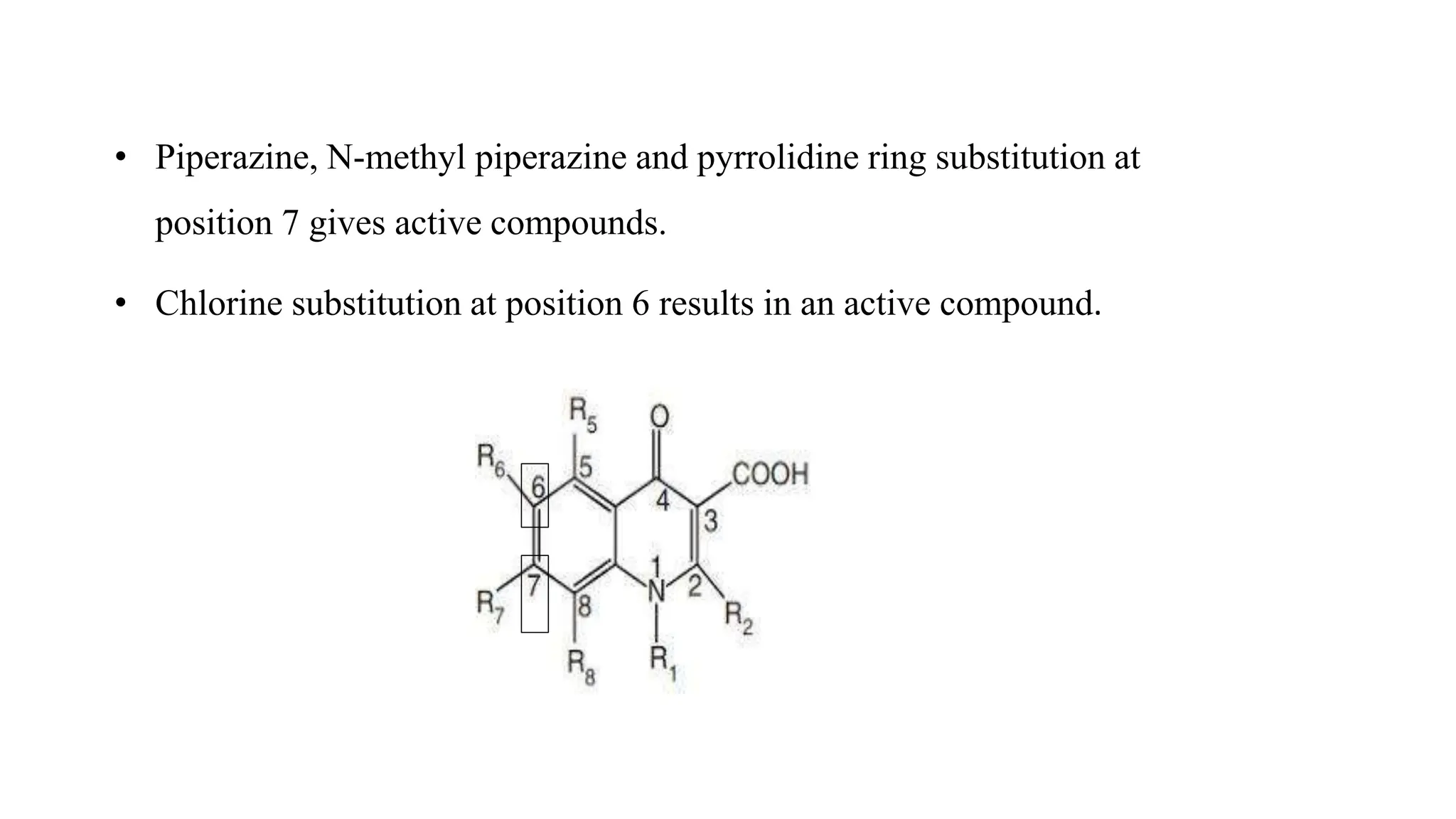

The document discusses the structure-activity relationship of quinolines as urinary tract anti-infective agents. It outlines that the 1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-pyridin-3-carboxylic acid moiety is essential for antibacterial activity, and it must be annulated with an aromatic ring. Substitutions at certain positions, like fluorine at position 6, lower alkyl groups at position 1, and amino at position 5 result in compounds with antibacterial activity. Piperazine, N-methyl piperazine and pyrrolidine ring substitutions at position 7 also lead to active compounds.








