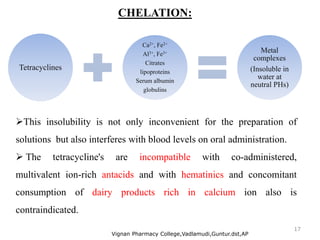
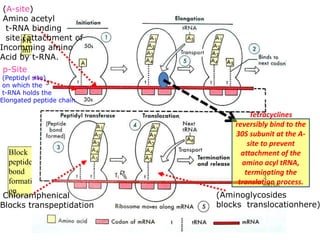
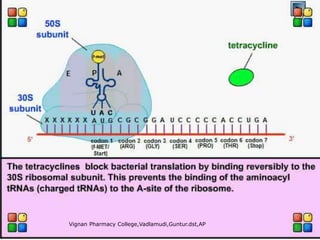
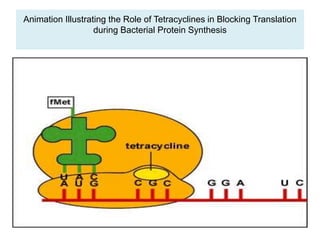
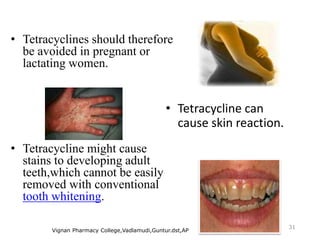
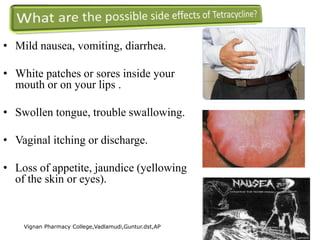
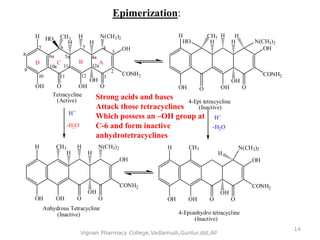
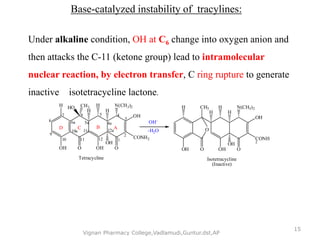
Tetracyclines are broad-spectrum antibiotics effective against a variety of bacteria, including both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms, and have been used for over 50 years. They inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA. Common uses include treating infections such as acne, respiratory infections, and bacterial conjunctivitis, along with their low-cost advantage over other antibiotics.










![O O
OH
NH2
CH3HO
C
O
OH
OHOH
CH3H3C
N
H3C
CH3
H3C
H
N
O
N
H
CH3H3C
N
O O
OH
NH2
C
OH
OHOH
CH3H3C
N
O
CH3H3C
N
O O
OH
NH2
C
OH
OHOH
CH3H3C
N
O
O O
OH
NH2
C
OHCH2
O
OH
OHOH
CH3H3C
N
N
H3C CH3
OH OH
OH
O
OH
C
HO CH3
NH2
OH
OO
N
H3C CH3
Cl
OH OH
OH
O
CH2 OH
C
NH2
OH
OO
O O
OH
NH2
CH3HO
C
Cl
OOH
OH
OH
CH3H3C
N
O O
OH
NH2
H
C
Cl HO
OOH OH
OH
CH3H3C
N
121110
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
METHACYCLINE
[Rondomycin]
OXYTETRACYCLINE
Terramycin, (Urobiotic)
CHLORTETRACYCLINE
Aureomycin
TETRACYCLINE
Achrommycin, Sumycin,
Panmycin, Teracap, Tetracyn, Tetralan
TIGECYCLINE
Tygacil™
MECLOCYCLINE
Meclan
MINOCYCLINE
Arestin, Dynacin,
Vectrin, Minocin
DEMECLOTETRACYCLINE
Declomycin
O O
OH
NH2
C
H3C OHH
OOH OH
OH
CH3H3C
N
DOXYCYCLINE
Vibramycin, Vibra–Tabs
Doryx, Doxy
STRUCTURES OF IMPORTANT TETRACYCLINES
Vignan Pharmacy College,Vadlamudi,Guntur.dst,AP 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tetracyclines-2020-200426173551/85/Tetracyclines-16-320.jpg)